SEARCH
検索詳細
西田 勇大学院工学研究科 機械工学専攻准教授
研究活動情報
■ 受賞- 2022年11月 The 19th International Machine Tool Engineers’ Conference IMEC2022 Excellent Poster Award
- 2020年12月 一般財団法人FA財団論文賞
- 2020年07月 ASME International Symposium on Flexible Automation 2020, ASME International Symposium on Flexible Automation 2020 Young Investigator Award in Flexible Automation
- 2020年03月 一般社団法人日本機械学会, 一般社団法人日本機械学会生産システム部門学術業績賞
- 2020年03月 公益社団法人精密工学会, 公益社団法人精密工学会研究奨励賞
- 2019年06月 一般社団法人型技術協会, 一般社団法人型技術協会奨励賞, NCプログラムの自動生成と加工時間予測で実現する製品形状に応じた工作機械の割当て日本国国内学会・会議・シンポジウム等の賞
- 2019年05月 公益財団法人マザック財団, 公益財団法人マザック財団優秀論文賞, Automatic Determination of Cutting Conditions for NC Program Generation by Reusing Machining Case Data based on Geometric Properties of Removal Volume日本国その他の賞
- 2019年04月 日本機械学会, 日本機械学会賞(論文), 切削加工のボクセルシミュレータを用いた工作機械の動的挙動と切削力の時間領域連成シミュレーション日本国学会誌・学術雑誌による顕彰
- 2018年05月 公益財団法人マザック財団, 公益財団法人マザック財団優秀論文賞, ボクセルモデルを用いた切削シミュレーションにおける微小時間および微小空間解析の高速処理手法日本国その他の賞
- 2016年09月 日本機械学会 RC272, 日本機械学会RC272産学連携による若手育成プログラムCIA4YI2016 最優秀賞, 産学連携による若手育成プログラムCIA4YI2016その他の賞
- 2012年06月 日本人間工学会, 2011年度日本人間工学会研究奨励賞, 拮抗筋および二関節筋を考慮した下肢筋力の推定手法 -垂直跳びにおける下肢筋力の推定-日本国学会誌・学術雑誌による顕彰
- 2010年03月 日本機械学会, 2009年度日本機械学会三浦賞, 二関節筋を考慮した筋骨格モデルを用いた人体の運動解析に関する研究日本国その他の賞
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2024年02月, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 18(4) (4), JAMDSM0039 - JAMDSM0039研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2024年, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 18(4) (4), JAMDSM0037 - JAMDSM0037研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2024年, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 18(4) (4), JAMDSM0038 - JAMDSM0038研究論文(学術雑誌)
- In this study, we developed a method for automatically generating computer-aided design (CAD) models of injection molding dies. The method only required 3D CAD models of products in the Standard Triangulated Language (STL) format as the input information. We also developed a system for automatically generating numerical control (NC) programs by automating the system process planning necessary for machining the injection molding dies. The method generated CAD models of the injection molding dies by dividing the STL files of the products into triangular meshes on a specified split plane. For injection molding dies with several free curved surfaces, we acquired the tool positions of a ball end mill (as approximated by a spherical shape) and flat drill (as approximated by a cylindrical shape) from the geometrical relationships of the triangles constituting the CAD model. We generated a CAD model of an injection molding die using the proposed method with respect to the CAD model of a product shape to verify the validity of the developed system. Then, we machined the product based on the NC programs and tool position. In addition, we injection molded a product with a machined die to mold it into its original product shape.Fuji Technology Press Ltd., 2023年11月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 17(6) (6), 619 - 626, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2023年05月, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 17(3) (3), JAMDSM0035 - JAMDSM0035, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- This study proposes a method for automating the determination of assembly order by automating the derivation of the necessary connection relationships between the parts. The proposed method minimizes the information required for the initial conditions and automatically determines the feasible assembly orders. As a general rule, based on the assumption that the assembly order for a product is the reverse of the disassembly order, once the disassembly order is derived based on the 3D CAD model and the connection relationships between the parts, the assembly order can be determined. Until now, however, the relationships between the parts are decided manually by the attendant engineers, thus, hindering the full automation of the determination of the assembly order. To achieve full automation realistically, the connection relationships between the parts should be derived automatically from the 3D CAD model, for which this study proposes an efficient method. The components were extracted from the 3D CAD model, and the bolts were identified. The connection relationships between the parts were derived from the interference conditions determined while moving each part minutely. An association chart diagram was created from the obtained connection relationships, from which multiple assembly order candidates could be derived.Fuji Technology Press Ltd., 2023年03月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 17(2) (2), 167 - 175[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2023年, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 17(2) (2), JAMDSM0025 - JAMDSM0025研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2022年, 日本機械学会論文集, 88(914) (914), 22 - 00208[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- A method for extracting the machining region from a 3D CAD model in Standard Triangulated Language (STL) format and automatically generating a tool path is proposed. First, a method is proposed for extracting the machining region and obtaining the geometrical features such as a convex or concave shape from only the 3D CAD model in STL format. The STL format uses only triangular mesh data and drops all information, which is necessary for extracting the removal volume for the machining and geometrical characteristics. Furthermore, the triangular mesh size is non-uniform. A contour line model is proposed in which the product model is minutely divided on the plane along any one axial direction and is represented by points at intervals below the indicated resolution obtained from the contour line of the cross section of the product. Subsequently, a method is proposed to determine the machining conditions for each extracted machining region and automatically generate a tool path according to the geometrical features of the machining region obtained. A machining experiment was conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. As a result of the machining experiment, it was confirmed that the tool path automatically generated from the 3D CAD model in STL format can be machined without any problems and with a practical level of accuracy.Fuji Technology Press Ltd., 2021年03月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 15(2) (2), 149 - 157[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2021年, Proceedings of the ASME 2021 16th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, MSEC 2021, 1, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2021年, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 15(6) (6), JAMDSM0077 - JAMDSM0077[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- A method to calculate tool path uniquely for roughing using a flat drill is proposed. A flat drill is a drill with a flat tip. Unlike a square end mill, it cannot feed a tool laterally, but it is suitable for machining to feed a tool longitudinally. The advantage offered by the flat drill is expected to reduce machining troubles, such as tool breakages and chatter vibration, owing to the axial sturdiness of the tool. Furthermore, it can be used to machine lapped holes that cannot be machined with a normal drill owing to its flat tip. Hence, roughing using a flat drill by drilling multiple holes at constant intervals is proposed herein. Furthermore, in this method, a tool path for semi-finishing is generated only on the remaining region. A cutting experiment is conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The result of the cutting experiment confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed method based on the machining time and the productivity of machining multiple products simultaneously.Fuji Technology Press Ltd., 2020年11月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 14(6) (6), 1036 - 1044[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society for Precision Engineering, 2020年09月, Journal of the Japan Society for Precision Engineering, 86(9) (9), 708 - 713[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020年07月, Transactions of the JSME (in Japanese), 86(887) (887), 20 - 00153[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2020年06月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 14(3) (3), 459 - 466, 英語Machining time reduction by tool path modification to eliminate air cutting motion for end milling operation[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020年, JSME 2020 Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing/Materials and Processing, LEMP 2020, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020年, JSME 2020 Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing/Materials and Processing, LEMP 2020, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), 2020年, 2020 International Symposium on Flexible Automation, ISFA 2020, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020年, Transactions of the JSME (in Japanese), 86(892) (892), 20 - 00185研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020年, Mechanical Engineering Journal, 7(3) (3), 20 - 00023, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2020年01月, Precision Engineering, 61, 103 - 109[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2020年01月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 14(1) (1), 英語Proposal of contour line model for high-speed end milling simulation[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年09月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 13(5) (5), 700 - 707, 英語Machine tool assignment realized by automated NC program generation and machining time prediction[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年08月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 13(6) (6), 825 - 833, 英語Automated process planning system for end-milling operation considering geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T)[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年06月, Mechanical Engineering Journal, 6(4) (4), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年02月, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 13(1) (1), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 780, 472 - 482, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2019年, ASME 2019 14th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, MSEC 2019, 2[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 一般社団法人 システム制御情報学会, 2019年, システム制御情報学会論文誌, 32(5) (5), 212 - 217, 日本語
According to the change of manufacturing style from mass production to customized production, it is important to manage the process plan and to control the machining quality of products. On machine measurement (OMM) has an advantage that it eliminates the operations of remove and reattachment of the workpiece and eliminates the positioning error at the reattachment. The contact measurement using a touch probe is one of the OMM. However, this measurement requires decision of measuring points and paths in order to conduct the measurement using touch probe. Currently, measuring paths of the touch probe is generated by an operator who can recognize the shape of the workpiece, determine the measuring regions and the measuring points. The objective of this study is automatically generation of the NC program to instruct OMM using a touch probe. This study realizes automatically generation of the NC program to instruct OMM by focusing on recognition of the geometrical property of the product shape based on the removal volume and determination of the measuring points and paths.
[査読有り] - 公益社団法人 精密工学会, 2019年, 精密工学会学術講演会講演論文集, 2019(0) (0), 191 - 192, 日本語
スクエアエンドミル加工の実験から,工具刃先に作用する切削エネルギの累積値と工具逃げ面の摩耗量との間に線形関係があることが明らかとなった。この関係を利用して,切削シミュレーションを行って切削エネルギの累積値を計算することで,加工中の切削状態の変化に依らず工具摩耗量の予測が可能であることを示す。また,実加工において測定した摩耗量の変化と予測した摩耗量の変化とを比較することで本手法の有効性を確認した。
[査読有り] - 公益社団法人 精密工学会, 2019年, 精密工学会学術講演会講演論文集, 2019(0) (0), 719 - 720, 日本語
グラインダ作業は熟練作業者の経験や勘に頼る加工工程で,加工条件と加工形状の関係が不明で自動化が難しい作業である.本研究では産業用ロボットによるグラインダ作業の自動化を目的として,グラインダの送り速度,押し付け力といった作業動作から加工形状を予測するシミュレータを開発した.シミュレータはPrestonの法則を用いて局所的な除去体積を計算しており,加工形状の予測結果が測定結果と一致することを確認した.
[査読有り] - 2019年, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems and Manufacturing, 13(3) (3), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年, International Journal of Automation Technology, 13(5) (5), 583 - 592[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年01月, 精密工学会誌, 85(1) (1), 91 - 97, 日本語工具系の弾性変形に起因する加工誤差の予測結果に基づく加工誤差補正[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年01月, Mechanical Engineering Journal, 6(1) (1), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年12月, International Journal of Automation Technology, 12(6) (6), 英語Customized End Milling Operation of Dental Artificial Crown without CAM Operation[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年07月, Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 12(4) (4), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年02月, 精密工学会誌, 84(6) (6), 572 - 577, 日本語工具系の弾性変形を考慮したボクセルモデルによるエンドミル加工シミュレーション[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年02月, 精密工学会誌, 84(2) (2), 日本語ボクセルモデルを用いた切削シミュレーションにおける微小時間および微小空間解析の高速処理手法[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年, Seimitsu Kogaku Kaishi/Journal of the Japan Society for Precision Engineering, 84(6) (6), 572 - 577[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年, ASME 2018 13th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, MSEC 2018, 4[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年, ASME 2018 13th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, MSEC 2018, 4[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年, Procedia CIRP, 77, 22 - 25[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年, Procedia CIRP, 77, 574 - 577[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年, Proceedings of 2018 ISFA - 2018 International Symposium on Flexible AutomationAutomatic process planning system for end-milling operation reflecting cam operator’s intention[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年, Proceedings of 2018 ISFA - 2018 International Symposium on Flexible AutomationAutomation of on-machine measurement based on 3D CAD model of product[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年, Seimitsu Kogaku Kaishi/Journal of the Japan Society for Precision Engineering, 84(2) (2), 175 - 181[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2018年, 生産システム部門講演会講演論文集, 2018(0) (0), 511 - 511, 日本語
In this study, an automatic process planning system for milling operation is proposed, in which user's intention for process planning is considered. First, our new process planning system stores the geometrical properties of the selected machining region when a user decides the machining sequence. After storing the geometrical properties, the appropriate machining sequence can be automatically selected by referring geometrical properties of the machining region. User's intention, which is involved implicitly in the stored geometrical properties of the machining region, can be applied to decide machining sequence. A case study was conducted to show the effectiveness of our new proposed process planning system. In the case study, user-specific machining sequences were automatically determined based on the implicit relation among the geometrical properties of the machining region and the individual user's intention.
[査読有り] - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2018年, 関西支部講演会講演論文集, 2018(0) (0), 517 - 517, 日本語
In this study, autonomous end milling system for manufacturing custom-made dental prostheses was developed. This system can decide suitable machining orientation of dental prostheses to minimize unmachined volume automatically, and can prevent tool breakage by tool feed rate control based on the predicted cutting forces in end milling operation.
[査読有り] - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2018年, 関西支部講演会講演論文集, 2018(0) (0), 509 - 509, 日本語
This paper describes an automation system to realize autonomous sheet metal bending operation by industrial robot. This system can derive bending sequences using topological information in a CAD model of a sheet metal product, and can generate operation paths to control an industrial robot in consideration of its positions and configurations.
[査読有り] - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2018年, 年次大会, 2018(0) (0), S1310002, 日本語
Since motion accuracy of 5-axis machining centers directly influences the geometrical accuracy of the machined workpieces, accuracy enhancement of the 5-axis machining centers is strongly demanded. In order to improve the geometrical accuracy during the machining by a 5-axis machining centers, a method that modifies the CL-data based on the tracking errors normal to the machined surface at each command point has been proposed. In this study, the proposed method is applied to simultaneous 5-axis controlled machining to improve the motion accuracy. A normal vector calculation method for the simultaneous 5-axis controlled motion is newly proposed, and the compensation method is applied to the turbine blade machining by 5-axis controlled motions. Measurement tests of the cutting motion for the blade shape machining by a ball-end mill are carried out with the different control mode of the controller. The CL-data for machining tool path is also modified based on the calculated trajectory of the tool center point. Experimental results show that the feed speed and machining accuracy significantly depend on the control mode, and that the shape accuracy can be improved by applying the proposed compensation method without any decreasing of the motion speed.
[査読有り] - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2018年, 日本機械学会論文集, 84(857) (857), 17 - 00433-17-00433, 日本語
This study aims to develop a monitoring system, which can automatically detect tool wear in end-milling operation. A feature of this system is the utilization of the predicted cutting torque for detecting the difference between normal and cutting trouble. The cutting torque predicted by a cutting force simulator is compared with the cutting torque measured and evaluated from the driving torque of a spindle motor. Because the dynamic change of the cutting torque can be predicted by the cutting force simulator as the reference cutting torque, it is possible to detect cutting trouble correctly without disturbance arise from the changes of the cutting conditions and the machining form at every moment. In the cutting simulator, this study uses the workpiece voxel model in order to calculate the uncut chip thickness for the estimation of the cutting force. For the tool wear detection, 200 % increase of the average cutting torque is set as the threshold to detect 300 μm flank wear. In an experimental milling of a workpiece with holes using a worn square end mill, it is confirmed that the increase of the average cutting torque can be identified clearly in both of stationary and transient milling situations. It was verified that the tool flank wear could be detected correctly even in the dynamic change of milling operation.
[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - ラジアスエンドミル加工の切削力予測のために,工具切れ刃形状および被削材形状のボクセルモデルで実切込み厚さを計算する切削力シミュレータを開発した.複雑な被削材形状を特殊な切れ刃形状のラジアスエンドミルで加工する場合でも実切込み厚さを検出することができる.予測した切削力は実測した切削力とよく一致した.公益社団法人 自動車技術会, 2018年, 自動車技術会論文集, 49(1) (1), 107 - 111, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年12月, Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ASME), 140(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年11月, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century, LEM 2017[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2017年11月, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century, LEM 2017[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2017年11月, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century, LEM 2017[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2017年05月, Journal of Ergonomics, 7(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- エンドミル加工を対象に,シミュレーションで予測できる切削トルクと主軸モータから検出できる切削トルクを比較し,加工異常を検出する方法を提案する.加工中に加工状態が変化しても切削トルクの増大割合から工具摩耗を検出できることを確認し,また切削トルク波形のモニタリング結果とシミュレーション結果の類似度の変化から工具欠損を検出できることを確認した.一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2017年, 生産システム部門講演会講演論文集, 2017(0) (0), 309 - 309, 日本語[査読有り]
- 切削力は送り駆動系や主軸駆動系に外乱として作用し,断続切削では送り速度や主軸回転数の変動や機械の構造振動を励起するとともに,その振動で一刃当たりの送り量や切削速度が変動して切削力も変化する.本研究では主軸駆動系と送り駆動系の運動および機械の構造振動と切削力との連成シミュレーション技術を開発し,切削力により駆動系が振動し,それにより切削力が変動する現象を開発した方法で表現できることを確認した.公益社団法人 精密工学会, 2017年, 精密工学会学術講演会講演論文集, 2017(0) (0), 65 - 66, 日本語[査読有り]
- 加工中の切削力を推定し,切削力による工具の静変形を予測可能なシミュレータを開発した.このシミュレータは被削材のボクセルモデルを用いて,工具微小回転角ごとに実切込み厚さを計算して切削力を推定する.推定した切削力から工具変形および工具把持部の並進変形量を予測した.実加工による加工面とシミュレーションで予測した加工面を比較して,工具の静変形を考慮した切削加工シミュレーションの有効性を確認した.公益社団法人 精密工学会, 2017年, 精密工学会学術講演会講演論文集, 2017(0) (0), 999 - 1000, 日本語[査読有り]
- 2017年, PROCEEDINGS OF THE ASME 12TH INTERNATIONAL MANUFACTURING SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CONFERENCE - 2017, VOL 3, 英語CUTTING FORCE PREDICTION OF BALL END MILLING BASED ON FULLY VOXEL REPRESENTATION OF CUTTING EDGE AND INSTANTANEOUS WORKPIECE SHAPE[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2017年, PROCEEDINGS OF THE ASME 12TH INTERNATIONAL MANUFACTURING SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CONFERENCE - 2017, VOL 3, 英語MACHINING OPERATION PROCESS PLANNING SYSTEM CONSIDERING USER STRATEGIES AND INTENTIONS[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 一般社団法人 システム制御情報学会, 2017年, システム制御情報学会論文誌, 30(3) (3), 81 - 86, 日本語
A new method of the process planning for end-milling operation considering product design constraints in this study. In our previous study, the process planning system, in which the Total Removal Volume is divided by the planes parallel with the XY, YZ or ZX planes to analyze machining sequence from top to bottom of the target product, is proposed. In this study, the process planning system, in which the Total Removal Volume is divided by all planes (including slope planes) existing on the target product, is proposed. Furthermore, the product design constraints or the designer's intention such as separate through holes which have the same central axis to be slide bearing is considered. A case study was conducted and the result showed that the proposed method can generate efficient multiple process plans for the machining operation. These multiple process plans or machining sequences are available to select adaptively the most suitable process plan or machining sequence under the several conditions such as the machine tool to be used and the product design constructions.
[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2017年, 日本機械学会論文集, 83(856) (856), 17 - 00254-17-00254, 日本語
It is known that the cutting force excites the structural vibration of machine tool. In addition, cutting force acts on feed and spindle drive system as a force disturbance, and feed speed and spindle speed are changed. As the results, cutting force is also changed because the depth of cut and cutting speed are changed due to the machine vibration, feed and spindle speed changes. The purpose of this study is to analyze the coupled vibration between the machine tool behavior and the cutting force. In order to achieve the purpose, in this study, a coupled simulation method of the vibration of machine tool, the dynamic behaviors of feed and spindle drive systems and the cutting force is developed. Cutting force and machined surface geometry is simulated using the voxel simulator in which the workpieces is represented by voxels. Undeformed chip thickness can be calculated based on the relative position between the tool and workpieces, and the tool rotational angle at the each time step based on the voxel model. The cutting force is estimated based on the calculated undeformed chip thickness. The relative position between tool and workpiece at each time step is simulated by the feed drive system and machine tool structural models. The tool rotational angle is simulated by the spindle drive system model. The coupled simulation between the cutting force, structural vibration of machine tool and feed and spindle drive systems is carried out by applying the simulated cutting force and cutting torque as a disturbance to the feed and spindle drive systems and machine tool structure. Cutting tests and simulations are carried out with two kinds of radial depth of cut, 5 mm and 20 mm. It is confirmed that the machine tool dynamic behaviors due to the cutting force and torque which is also influenced by the machine tool behaviors can be simulated by the proposed method. It is also confirmed that the chatter vibration which is observed in case of the 20 mm depth of cut can be simulated by the proposed method.
[査読有り][招待有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2017年, 日本機械学会論文集, 83(856) (856), 17 - 00247-17-00247, 日本語
In end milling, in order to improve machining efficiency and accuracy, instantaneous rigid force model is widely used to predict cutting force and improve cutting conditions. The instantaneous rigid force model is well known as the practically simple model to predict cutting force. However this model requires the six parameters called cutting coefficients which have to be determined by the experimental milling operation. So several experimental milling operations are needed before cutting force prediction. In this study, a new instantaneous rigid force model based on oblique cutting is proposed. In this force model, the end milling process is modeled using the oblique cutting model. Therefore, cutting force prediction can be realized using only the one parameter such as shear angle instead of the six parameters such as cutting coefficients required for a conventional instantaneous rigid force model. The shear angle can be determined from tangential milling force or milling torque. And this force model is easier to apply for practical cutting force prediction, because time and effort to determine the parameter(s) before cutting force prediction. The validation of this force model compared with the conventional force model is performed. As the result, cutting forces predicted by the proposed force model has good agreement with the measured cutting forces. Also, the proposed force model has good performance in a wide range of cutting conditions compared with the conventional force model.
[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - 2016年11月, 型技術ワークショップ2016 in なにわ講演論文, 46 - 47, 日本語被削材のボクセルモデルによるボールエンドミルの工具姿勢変化を考慮した5軸加工の切削力シミュレーション研究論文(その他学術会議資料等)
- 2016年11月, 第17回国際工作機械技術者会議論文集, 116 - 117, 日本語CAM-CNC統合による革新的な知能化工作機械の開発研究論文(その他学術会議資料等)
- 砥粒加工学会, 2016年08月, 2016年度砥粒加工学会学術講演会(ABTEC2016)講演論文集, A03 - A03, 日本語切削トルクの予測結果と実測結果の比較に基づく加工異常検出システムの提案[査読有り]研究論文(その他学術会議資料等)
- 2016年07月, 精密工学会2016年度関西地方定期学術講演会講演論文集, 32 - 33, 日本語被削材のボクセルモデル表現によるボールエンドミル加工の切削力推定[査読有り]研究論文(その他学術会議資料等)
- 2016年07月, 精密工学会2016年度関西地方定期学術講演会講演論文集, 34 - 35, 日本語歯科補綴物の一貫加工システムの開発[査読有り]研究論文(その他学術会議資料等)
- 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2016年07月, 日本機械学会, 82(840) (840), 1600006 - 1600006, 日本語
For several decades, factory automation or unmanned factory productivity has been progressed to realize much higher productivity in manufacturing. However, human centered manufacturing system is getting attention to realize much more flexibility for manufacturing of wide product variety and volume. So it is necessary to provide the safe and efficient environment to workers considering their own physical properties. This study investigated a mechanism of muscle fatigue and proposed a muscular fatigue model to evaluate muscle fatigue progress under several muscular force patterns. Previous studies have already proposed a muscular fatigue model. However, these previous studies discussed about the condition of maximum voluntary contraction. The new point of this study is considering several muscular force patterns including muscle recovery progress. This study proposed the method to estimate the endurance times for keeping constant forces considering the physical characteristics. This study also proposed the method to estimate the iteration numbers for keeping constant forces with interval. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, experimental verifications were conducted. The experimental results had a good agreement with the evaluation of muscle fatigue progress using the proposed method although it is necessary to consider the method to raise the precision of determining the physical parameters and the method to decrease the dispersion of experiments derived from the subjective judgement of participants. Success of resolving these issues will provide ergonomically safe and efficient working environments considering the physical properties of each worker.
[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - 2016年03月, Journal of Ergonomics, 6(2) (2), 100158 - 1000158, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年, 2016 INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON FLEXIBLE AUTOMATION (ISFA), 2016(ISFA) (ISFA), 352 - 355, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2016年, 年次大会, 2016(0) (0), S1320203 - S1320203, 日本語
A new methodology to revise cutting conditions for machining operation planning has been developed in this study. In order to automate machining operation planning, reuse of cutting conditions in the past machining operations was proposed in our previous study. However, assessment and revision of cutting conditions are required to apply for the objective machining operation from the reference machining operation. For the assessment of cutting conditions, an acceptable area to select cutting conditions (AACC) is calculated. The AACC can be calculated under several limitations such as spindle power and maximum feed speed of machine tools, torsional and bending strength of cutting tools and so on. In the case that the reference cutting condition stays in the AACC, the reference cutting condition can be applied for the objective machining operation without any revision. In the case that the reference cutting condition stays out the AACC, the reference cutting condition should be revised to adapt for the objective machining operation. In our study, a methodology, which revises cutting conditions under keeping productivity, surface roughness (cusp height) and tool life, was proposed. In this report, an expanded methodology to revise cutting conditions by qualified relaxation of machining requirements is proposed to achieve wide range adaptation of the reference cutting conditions to the objective machining operation.
[査読有り]研究論文(その他学術会議資料等) - 一般社団法人 日本機械学会, 2016年, 生産加工・工作機械部門講演会 : 生産と加工に関する学術講演会, 2016(0) (0), D18 - 206, 日本語
Instantaneous cutting force model is widely used for the cutting force prediction for end milling operation. However this model is required to prepare 6 parameters called cutting coefficients which can be determined from experimentally measured cutting forces. In this study, a new end-milling force prediction method based on oblique cutting model is proposed. This method can predict cutting force using only the experimentally predetermined shear angle instead of 6 cutting coefficients required for a conventional instantaneous cutting force model. This method is easier to apply for practical cutting force prediction, because it is easier to predetermine shear angle than 6 cutting coefficients.
研究論文(その他学術会議資料等) - 2016年, ADVANCES IN PHYSICAL ERGONOMICS AND HUMAN FACTORS, 489, 515 - 525, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2012年01月, 日本人間工学会, 48(2) (2), 62 - 69, 日本語拮抗筋および二関節筋を考慮した下肢筋力の推定手法 -ジョギング動作における下肢筋力の推定-[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年09月, 日本人間工学会, 47(6) (6), 244 - 251, 日本語拮抗筋および二関節筋を考慮した下肢筋力の推定手法 -垂直跳びにおける下肢筋力の推定-[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年06月, Biomechanics in Sports, 11(2) (2), 547 - 550, 英語Estimation of Ground Reaction Forces during Walking[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年, 5TH ASIA-PACIFIC CONGRESS ON SPORTS TECHNOLOGY (APCST), 13, 338 - 343, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- The analysis and clarification of man's physical properties are very important in the field of sport and welfare engineering. The results of these analysis and clarification contribute to the improvement of physical ability, the prevention of injury in sports, the effective rehabilitation and the evaluation of dynamic load in daily life. The solid body link model, which has been used for the analysis on human body performance, can estimate the force and torque which acts on each joint from the recorded human motion. However, the muscle functionality is not considered in the solid body link model. In order to evaluate the muscular power during human motion, the human musculo-skeletal model considering bi-articular muscle function is required. In this study, the basic two dimensional musculo-skeletal model of man's lower limb was constructed and the muscular power of each effective muscle was estimated from the recorded human motion. The lower limbs muscular power in vertical jump is estimated to verify the musculo-skeltal model constructed.一般社団法人日本機械学会, 2008年, ジョイント・シンポジウム講演論文集:スポーツ工学シンポジウム:シンポジウム:ヒューマン・ダイナミックス, 2008, 335 - 340, 日本語
- B9 筋肉の疲労進展を評価する筋疲労モデルの提案(筋特性)For several decades, factory automation or unmanned factory productivity has been progressed to realize much higher productivity in manufacturing. However, human centered manufacturing system is getting attention to realize much more flexibility for manufacturing of wide product variety and volume. In this study, a mechanism of muscle fatigue is investigated, and a muscular fatigue model to evaluate muscle fatigue progress under several muscular force patterns is proposed. Furthermore, the endurance time for keeping constant force by the participant is estimated considering physical characteristics of the participant. In order to show the effectiveness of the proposed method, experimental verifications were conducted. The experimental results had a good agreement with the evaluation of muscle fatigue progress using the proposed method. The proposed model contributes to evaluate the ergonomic working environments and the comfortable working motions.一般社団法人日本機械学会, 2011年10月30日, シンポジウム: スポーツ・アンド・ヒューマン・ダイナミクス講演論文集 : symposium on sports and human dynamics, 2011, 298 - 302, 日本語
- B33 短距離走クラウチングスタートにおけるブロッククリアランス技術(走動作,ほか)In the sprint, the sprinters are required to use starting blocks at the crouch start. Therefore, it is important to clarify the technique of block clearance in order to improve sprint performance. The purpose of this study is to examine the technique of block clearance from joint torque and joint power in lower extremity applied to the starting blocks by sprinters. From starting blocks, six sprinters did the "starting dash" as is done in a sprint running race, and the forces applied to the right and left starting block were measured by with the force plates (1kHz). And, the block clearance movement was recorded by Hi-speed camera (250Hz). The results can be summarized as follows. There were two different patterns about the joint torque and power applied to the rear block. The type of pushing the rear block was presumed to have exhibited the extension torque and power at the hip and ankle of the rear leg. On the other hand, the type of pulling the rear leg from the rear block was presumed to have exhibited the flexion torque at the hip and the extension torque and power at the knee and ankle of the rear leg.一般社団法人日本機械学会, 2011年10月30日, シンポジウム: スポーツ・アンド・ヒューマン・ダイナミクス講演論文集 : symposium on sports and human dynamics, 2011, 412 - 417, 日本語
- B11 立幅跳びにおける桔抗筋および二関節筋を考慮した下肢筋力の推定手法の検証(筋特性)Estimation of muscle forces during human motions is important in the fields of sport, ergonomics and bioengineering in order to improve sport techniques, rehabilitation procedures, product designs and work environments, and so on. In general, in the musculoskeletal models that have been developed, the functions of antagonistic muscles and biarticular muscles are not considered to estimate muscle forces. In this study, a musculoskeletal model that considered the functions of the antagonistic muscles and biarticular muscles was investigated. In this model, muscles acting across the hip, knee and ankle joints were treated simultaneously. Furthermore, in this study, standing long jump as dynamic motion was conducted to validate the proposed model to estimate muscle forces. Surface electromyograms (EMGs) of tibialis anterior, gastrocnemius, soleus, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, semimembranosus, biceps femoris and short head and gluteus maximus were measured to compare with the estimated muscle forces. The experimental results showed that the muscle forces estimated by the proposed method had a good agreement with the EMGs of muscles.一般社団法人日本機械学会, 2011年10月30日, シンポジウム: スポーツ・アンド・ヒューマン・ダイナミクス講演論文集 : symposium on sports and human dynamics, 2011, 309 - 314, 日本語
- 2010年, ENGINEERING OF SPORT 8: ENGINEERING EMOTION - 8TH CONFERENCE OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPORTS ENGINEERING ASSOCIATION (ISEA), 2(2) (2), 3463 - 3463, 英語研究発表ペーパー・要旨(国際会議)
- 8th International Conference on Virtual Machining Process Technology, 2019年04月, 英語, CIRP, Vancouver, 国際会議Influence of Non-linear Friction Characteristics of Linear Guide and Ball Screw in Milling Operation口頭発表(一般)
- 型技術者会議2019, 2019年, 日本語, 国内会議切削シミュレータを統合したエンドミル加工用CAMの開発口頭発表(一般)
- 14th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 2019年, 英語, 国際会議Automated measuring planning for on-machinine measurement and re-machining process口頭発表(一般)
- the ASME 2018 Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 2018年06月, 英語, ASME, Colleage Station, 国際会議Enhancement of Motion Accuracy for Cone-frustum Cutting Motion by Modified NC Program口頭発表(一般)
- 第18回国際工作機械技術者会議, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議熟練者のノウハウを反映した工具経路自動生成ポスター発表
- 日本機械学会2018年度年次大会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議作業設計を考慮したエンドミル加工用自動工程設計システム(工具交換回数を最小化する工程設計)口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会生産システム部門研究発表講演会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議機械加工用自動工程設計におけるユーザの意図を反映した工程案の導出口頭発表(一般)
- 精密工学会第25回学生会員卒業研究発表講演会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議機械加工部品の設計情報を利用した機上計測の自動化口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会関西支部第93期定時総会講演会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議ロボットによる板金曲げ加工の自律作業を実現する曲げ順序計画および動作経路生成の自動化口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会関西支部2017年度学生員卒業研究発表講演会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議ボールエンドミル先端部の切削抵抗を考慮した切削力シミュレーション口頭発表(一般)
- 精密工学会2018年度秋季大会学術講演会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議エンドミル加工における工具系の弾性変形の予測結果に基づく加工誤差補正法ポスター発表
- 13th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Voxel based cutting force simulation of ball end milling considering cutting edge around ceter web口頭発表(一般)
- 8th CIRP Conference on High Performance Cutting, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Virtual milling force monitoring method based on in-process milling force prediction model to eliminate predetermination of cutting coefficients口頭発表(一般)
- 17th International Conference on Precision Engineering, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Tool chipping detection based on spindle motor torque distortion in end-milling口頭発表(一般)
- 型技術ワークショップ2018 in ふくい, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議NCプログラムの自動生成と加工時間予測で実現する製品形状に応じた工作機械の割当て口頭発表(一般)
- 9th International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Muscle force prediction method considering the role of antagonistic muscle口頭発表(一般)
- 8th CIRP Conference on High Performance Cutting, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Cutting Force and Finish Surface Simulation of End Milling Operation in Consideration of Static Tool Deflection by Using Voxel Model口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会関西支部第93期定時総会講演会, 2018年, 日本語, 国内会議CAM操作を必要としない歯科補綴物の自律加工口頭発表(一般)
- 2018 International Symposium on Flexible Automation, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Automation of on-machine measurement based on 3D CAD model of product口頭発表(一般)
- 2018 International Symposium on Flexible Automation, 2018年, 英語, 国際会議Automatic process planning system for end-milling operation reflecting CAM operator’s intentnion口頭発表(一般)
- 9th International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century (LEM21), 2017年11月, 英語, JSME, 広島市, 国際会議Determination of Cutting Conditions for NC Program Generation by Reusing Machining Case Data based on Removal Volume Feature口頭発表(一般)
- 9th International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century (LEM21), 2017年11月, 英語, JSME, 広島市, 国際会議Coupled Simulation between Machine Tool Behavior and Cutting Force using Voxel Simulator口頭発表(一般)
- 9th International Conference on Leading Edge Manufacturing in 21st Century (LEM21), 2017年11月, 英語, JSME, 広島市, 国際会議A revised instantaneous rigid force model for end-milling operation to eliminate predetermination of cutting coefficients口頭発表(一般)
- 2017年度精密工学会秋季大会学術講演会, 2017年09月, 日本語, 豊中市, 国内会議ボクセルモデルを用いた切削力シミュレータによる工作機械の動的挙動と切削力の時間領域連成シミュレーション口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会シンポジウム:スポーツ工学・ヒューマンダイナミクス2017, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議冗長筋群を考慮した筋骨格モデルによる筋力推定口頭発表(一般)
- 自動車技術会2017年春季大会学術講演会, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議工具切れ刃形状および被削材形状のボクセルモデルによるラジアスエンドミルの切削力シミュレーション口頭発表(一般)
- 精密工学会2017年度秋季大会学術講演会, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議工具の静変形を考慮したエンドミル加工の切削加工シミュレーション口頭発表(一般)
- 密工学会2017年度関西地方定期学術講演会, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議ロボットによる板金曲げ加工のための工程設計および作業設計の自動化ポスター発表
- 密工学会2017年度関西地方定期学術講演会, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議ユーザの戦略や意図を考慮した機械加工用工程設計支援システムの開発ポスター発表
- 密工学会2017年度関西地方定期学術講演会, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議スクエアエンドミル加工における工具摩耗予測手法ポスター発表
- 日本機械学会生産システム部門研究発表講演会2017, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議エンドミル加工における切削トルクの予測結果と実測結果の定量比較による加工異常検出口頭発表(一般)
- ASME 2017 12th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 2017年, 英語, 国際会議Machining operation process planning system considering user strategies and intentions口頭発表(一般)
- ASME 2017 12th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 2017年, 英語, 国際会議Cutting force prediction of ball end milling based on fully voxel representation of cutting edge and instantaneous workpiece shape口頭発表(一般)
- 型技術ワークショップ2017 in 岡山, 2017年, 日本語, 国内会議CAM-CNC統合による革新的な工作機械の知能化 –試作版の実装と評価-口頭発表(一般)
- 精密工学会2016年度関西地方定期学術講演会, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議被削材のボクセルモデル表現によるボールエンドミル加工の切削力推定ポスター発表
- 型技術ワークショップ2016 in なにわ, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議被削材のボクセルモデルによるボールエンドミルの工具姿勢変化を考慮した5軸加工の切削力シミュレーション口頭発表(一般)
- 2016年度砥粒加工学会学術講演会, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議切削トルクの予測結果と実測結果の比較に基づく加工異常検出システムの提案口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会シンポジウム:スポーツアンド・ヒューマンダイナミクス2016, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議疾走時の地面反力の推定に関する研究口頭発表(一般)
- 精密工学会2016年度関西地方定期学術講演会, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議歯科補綴物の一貫加工システムの開発ポスター発表
- 日本機械学会第11回生産加工・工作機械部門講演会, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議傾斜切削理論に基づくエンドミル加工の切削力予測モデルの提案口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会2016年度年次大会, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議加工事例を参照する作業設計における切削条件の適応的修正法(第2報:制約条件緩和による切削条件修正法の拡張)口頭発表(一般)
- 2016 International Symposium on Flexible Automation, 2016年, 英語, 国際会議Process Planning System of 5-Axis Machining Center Considering Constraint Condition口頭発表(一般)
- 第17回国際工作機械技術者会議, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議CAM-CNC統合による革新的な知能化工作機械の開発ポスター発表
- 型技術ワークショップ2016 in なにわ, 2016年, 日本語, 国内会議CAM-CNC統合による革新的な工作機械の知能化 -切削力の予測結果に基づく適応制御-口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会シンポジウム:スポーツアンド・ヒューマンダイナミクス2011, 2011年, 日本語, 国内会議立幅跳びにおける拮抗筋及び二関節筋を考慮した下肢筋力の推定手法の検証口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会シンポジウム:スポーツアンド・ヒューマンダイナミクス2011, 2011年, 日本語, 国内会議短距離走クラウチングスタートにおけるブロッククリアランス技術口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会シンポジウム:スポーツアンド・ヒューマンダイナミクス2011, 2011年, 日本語, 国内会議筋肉の疲労進展を評価する筋疲労モデルの提案口頭発表(一般)
- International Society of Biomechanics 2011, 2011年, 英語, 国際会議Validation of muscle forces during jogging estimated with an ergonomic musculoskeletal model口頭発表(一般)
- 5th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, 2011年, 英語, 国際会議Development of an ergonomic musculoskeletal model to estimate muscle forces during vertical jumping口頭発表(一般)
- 2010 Asian Conference on Design and Digital Engineering, 2010年, 英語, 国際会議Optimization of Lifting Posture Based on Motion Analysis Using Musculoskeletal Human Model Considering Bi-articular Muscle Function口頭発表(一般)
- 8TH CONFERENCE OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPORTS ENGINEERING ASSOCIATION (ISEA), 2010年, 英語, 国際会議A study on improving performance in vertical jump motion considering bi-articular muscle functionポスター発表
- 4th Asia-Pacific Congress on Sports Technology, 2009年09月, 英語, 国際会議Lower Limbs Muscular Power In Vertical Jump Estimated By Human Musculo-Skeletal Model Considering Bi-Articular Muscle Function口頭発表(一般)
- 精密工学会2009年度秋季大会, 2009年, 日本語, 国内会議作業評価に用いる二関節筋を考慮した筋骨格モデルの研究口頭発表(一般)
- 日本機械学会シンポジウム:スポーツアンド・ヒューマンダイナミクス2008, 2008年, 日本語, 国内会議二関節筋を考慮した筋骨格モデルを用いた垂直跳びにおける下肢筋力の推定口頭発表(一般)
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(C), 基盤研究(C), 神戸大学, 2022年04月 - 2025年03月, 研究代表者切削による一品生産の自動化を志向したCAMシステムに関する研究
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2018年04月 - 2021年03月競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2017年04月 - 2020年03月競争的資金
- 学術研究助成基金助成金/若手研究(B), 2017年04月 - 2019年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 形状認識装置,および形状認識方法特願2020-085466, 2020年05月14日特許権
- NCデータ生成装置,およびNCデータ生成プログラム特願2019-226707, 2019年12月16日特許権
- NCデータ変更装置,およびNCデータ変更プログラム特願2019-169667, 2019年09月18日特許権
- 生産計画策定装置,生産計画策定プログラム,および生産計画策定方法特願2019-121418, 2019年06月28日特許権
- 加工シミュレーションシステム,および加工シミュレーションプログラム特願2019-094659, 2019年05月20日特許権
- 工程設計システム,および加工順序決定方法特願2018-084733, 2018年04月26日特許権
- 切削シミュレーション方法および装置特願2017-196099, 2017年10月06日特許権
- 加工支援システム特願2017-043061, 2017年03月07日特許権
- 加工支援システム特願2016-243789, 2016年12月15日特許権
- 工程設計支援システム、および、工程設計支援方法特願2016-114701, 2016年06月08日特許権
研究シーズ
■ 研究シーズ- 機械加工のレベル5自動運転で実現する自律生産システムシーズカテゴリ:情報通信, ものづくり技術(機械・電気電子・化学工業)研究キーワード:CAD/CAM, マスカスタマイゼーション, 切削加工, 工作機械研究の背景と目的:わが国の製造業は少子高齢化による従事者の減少と熟練者の退職という問題に直面しています。一方で、世界が掲げている持続可能な開発目標(SDGs)では、社会の多様なニーズに決め細やかに対応可能なものづくりが求められており、持続可能な産業化を実現するためには、従来のような人に依存したやり方ではなく、コンピュータ技術やIoT技術を駆使した新しいものづくりの仕組みを構築する必要があります。研究内容:私の研究では、製品の3次元のデジタル情報(CADモデル)のみを入力として、工具の経路情報の作成を完全に自動で実現するシステムを構築しています。CADモデルの形状を解析して、除去すべき領域の情報や各領域の加工に使用する工具の選定、加工条件の決定、加工順序の決定など、従来では熟練の技術者が行っていた高度な判断をソフトウェアに組み込むことで自動化を実現しています。本研究によってこれまで高品質な製品を作り出してきたわが国のものづくり基盤をデジタル技術で置き換え、加工現場に人がいなくてもカスタマイズ製品を高品質・高効率で生産することを可能にする自律生産システムを構築します。これにより、自動化できる加工はシステムに任せて、熟練の技術者はより高付加価値の加工に専念することができます。人とシステムのいいとこ取りをして、共存していくことが大事です。
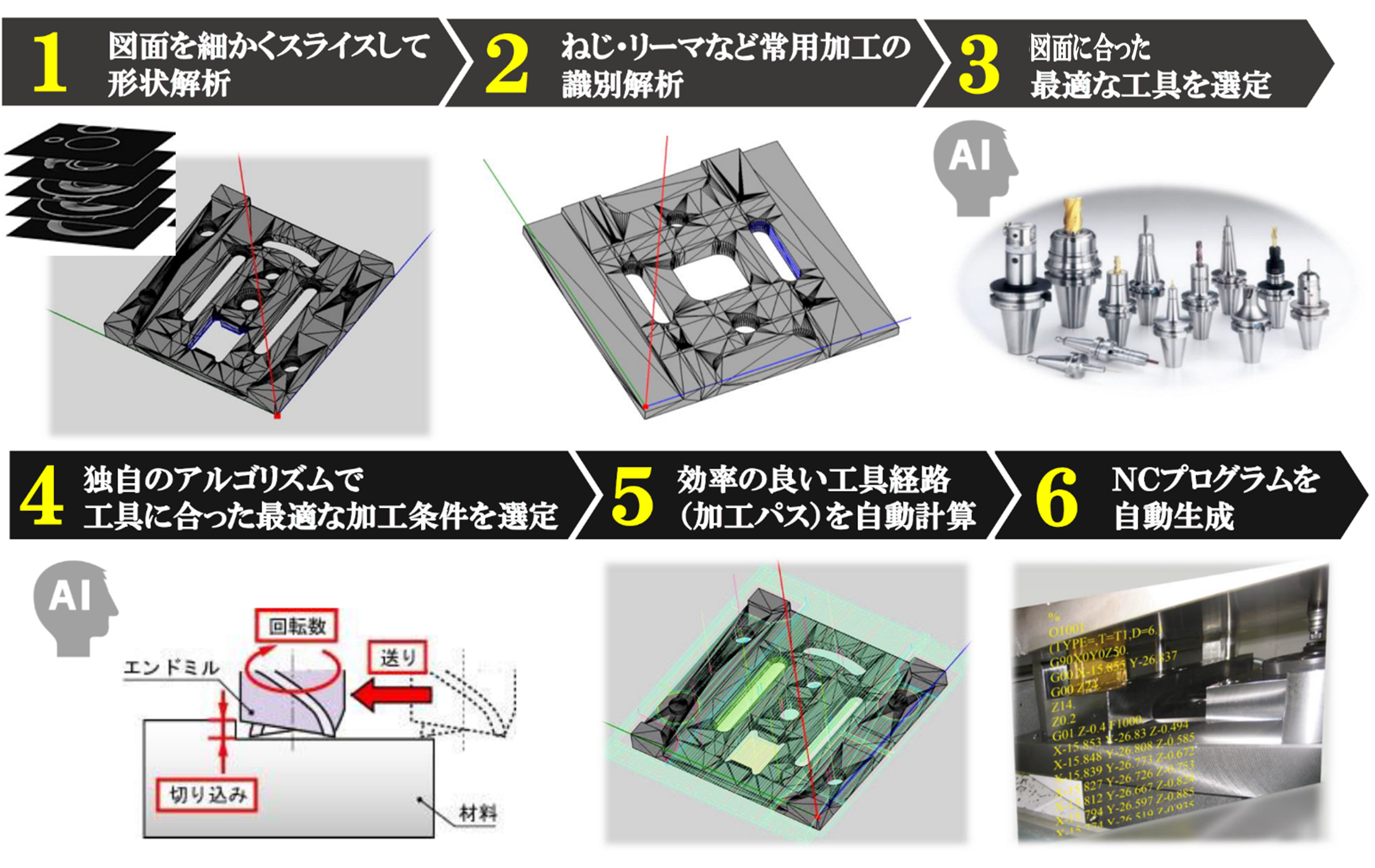
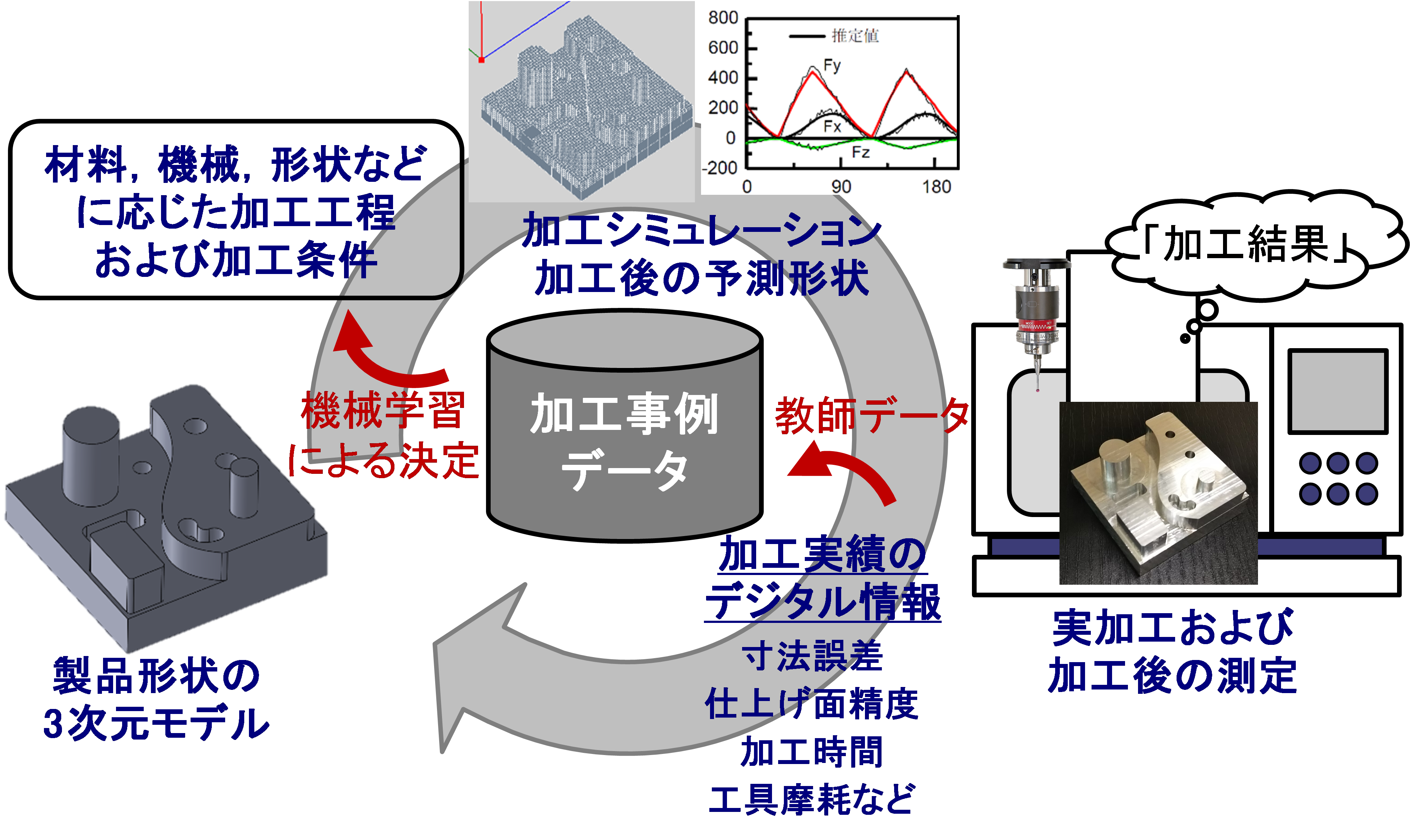 期待される効果や応用分野:機械がすべての動的運転タスクおよび作動継続が困難な場合への応答を持続的かつ無制限に実行する自動化、つまりレベル5の自動運転技術を目指します。ただし、このようなものづくり技術とは産業革新やイノベーションのシーズ創出の手段であり、目的ではないことを最近は感じており、構築してきたものづくり技術を基盤として、医療分野や宇宙開発に展開することを考えています。関係する業績:私は実現したシステムを社会に展開するために大学発ベンチャーであるBESTOWS株式会社を起ち上げ、技術移転をして活動もしています。研究成果を実社会で活用してもらい、そこで得た資金を大学へ還元して研究環境を充実して、新たな研究活動を行うような好循環を生み出せればと思い、日々奮闘しています。
期待される効果や応用分野:機械がすべての動的運転タスクおよび作動継続が困難な場合への応答を持続的かつ無制限に実行する自動化、つまりレベル5の自動運転技術を目指します。ただし、このようなものづくり技術とは産業革新やイノベーションのシーズ創出の手段であり、目的ではないことを最近は感じており、構築してきたものづくり技術を基盤として、医療分野や宇宙開発に展開することを考えています。関係する業績:私は実現したシステムを社会に展開するために大学発ベンチャーであるBESTOWS株式会社を起ち上げ、技術移転をして活動もしています。研究成果を実社会で活用してもらい、そこで得た資金を大学へ還元して研究環境を充実して、新たな研究活動を行うような好循環を生み出せればと思い、日々奮闘しています。

 mech.kobe-u.ac.jp
mech.kobe-u.ac.jp