SEARCH
検索詳細喜多 隆学長・役員等理事
研究者基本情報
■ 学位■ 研究ニュース
- 2021年01月04日, 日常生活を取り戻す ウイルスフリー空調システムを開発
- 2018年04月13日, 神戸大学の教員3名が「科研費NEWS」に掲載されました
- 2017年04月07日, 変換効率50%を超えることができる新型太陽電池構造を提案―発電コストの大幅引き下げに期待―
- 2015年10月16日, 喜多隆教授が公益社団法人応用物理学会フェローの称号を授与されました
- 2015年05月15日, 水銀を使わないフィルム型紫外光源を世界で初めて開発
■ 研究分野
■ 委員歴
- 2022年04月 - 現在, 日本材料学会, 半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会委員長
- 2006年04月 - 現在, 光物性研究会, 組織委員
- 1985年05月 - 現在, 応用物理学会, 正会員
- 2021年02月 - 2022年01月, レーザー学会年次大会, プログラム委員主査
- 1986年10月 - 2021年12月, 日本物理学会, 正会員
- 2021年04月 - 2021年10月, 9th International Symposium on Control of Semiconductor Interfaces (ISCSI IX, 2022), 国際プログラム委員
- 2019年10月 - 2021年10月, 電子材料シンポジウム(EMS), 実行委員長
- 2021年06月 - 2021年08月, SemiconNano 2021 (8th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures), 組織委員長(共同)
- 2018年04月 - 2019年09月, 電子材料シンポジウム(EMS), 実行副委員長
- 2017年09月 - 2019年09月, 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures (SemiconNano2019), 組織委員長
- 2018年02月 - 2019年05月, 2019化合物半導体ウィーク(CSW:ISCS&IPRM), 現地実行委員長
- 2018年09月 - 2019年04月, International Conference on Nanophotonics and Nano-optoelectronics, 組織委員会委員
- 2017年06月 - 2019年03月, 日本材料学会第66期編集委員会, 査読委員
- 2018年02月 - 2018年07月, 9th International Workshop on Bismuth-Containing Semiconductors, プログラム委員
- 2017年04月 - 2018年03月, レーザー学会学術講演会第38回年次大会, プログラム委員
- 2014年12月 - 2017年12月, 光物性研究会, 組織委員長
- 2017年06月 - 2017年10月, 国際シンポジウム (電気通信大学100周年記念)「“Future Earth”エネルギー課題に資する新奇なナノ物質・触媒・表面」, 組織委員
- 2016年04月 - 2017年08月, International Conference on Defects in Semiconductors(ICDS2017), International Program Committeeメンバー
- 2016年08月 - 2017年04月, International Conference on Nanophotonics and Nano-optoelectronics, 組織委員
- 2015年04月 - 2016年09月, 半導体レーザ国際会議(ISLC), 現地実行委員
- 2015年03月 - 2016年06月, 2016化合物半導体ウィーク(CSW:ISCS&IPRM), 展示委員長
- 2015年09月 - 2016年03月, 第17回ナノ構造における光と物質の相互作用に関する国際会議(PLMCN), 実行委員長
- 2015年01月 - 2015年09月, 2015年国際固体素子・材料コンファレンス, 論文副委員長
- 2013年07月 - 2015年07月, 電子材料シンポジウム(EMS), 論文委員長
- 2013年04月 - 2015年03月, 社団法人応用物理学会, 諮問委員
- 2002年04月 - 2013年06月, 電子材料シンポジウム, プログラム委員
- 2012年10月 - 2013年05月, 2013年化合物半導体週間(化合物半導体国際シンポジウム・インジウムリン系材料国際会議合同国際会議), 現地実行委員長
- 2011年04月 - 2013年03月, 社団法人応用物理学会, 理事
- 2009年07月 - 2012年09月, 第17回分子線エピタキシー国際会議, 現地実行委員長
- 2011年04月 - 2012年03月, Journal of Spectroscopy and Dynamics, Editorial Board
- 2009年03月 - 2011年08月, 第24回アモルファス及びナノ結晶半導体国際会議, 実行委員
- 2009年03月 - 2010年06月, 第37回化合物半導体国際会議, 論文委員(サブコミッティチェア)
- 2008年08月 - 2009年07月, EP2DS-18(第18回2次元電子系国際会議)/MSS-14(第14回半導体超構造国際会議), 現地実行委員長
- 2004年04月 - 2009年03月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 編集委員
- 2006年11月 - 2007年10月, 第34回化合物半導体国際会議, 論文委員サブコミッティ幹事
- 2005年07月 - 2005年07月, 第14回分子線エピタキシー国際会議, 論文委員
- 2005年04月 - 2005年04月, 第18回インジウム燐および関連材料に関する国際会議, 組織委員
- 2003年04月 - 2005年03月, 応用物理学会, 関西支部幹事
- 2003年04月 - 2005年03月, 応用物理学会関西支部セミナー「光物性とその応用」, 世話人
- 1998年03月 - 2002年03月, 応用物理学会, 講演分科会世話人
- 1999年09月 - 2001年05月, 第13回インジウム燐および関連材料に関する国際会議, 組織委員
- 1995年04月 - 2000年03月, 日本光学会, 文献抄録委員
- 1993年05月 - 1998年03月, Spring-8利用者懇談会, 正会員
- 1993年07月 - 1996年12月, 日本真空協会, 個人会員
- 1992年07月 - 1996年12月, 日本金属学会, 正会員
- 1992年04月 - 1994年03月, 日本真空協会, 関西支部幹事
- 1992年03月 - 1993年08月, 第5回半導体不純物の物理と制御に関する国際会議, 組織委員
研究活動情報
■ 受賞- 2025年06月 53rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, PVSC 53 Best Poster Award, Excitation Power Dependence and Loss of Photonic Energy Conversion
- 2022年09月 9th International Symposium on Control of Semiconductor Interfaces (ISCSI-XI), ISCSI-XI Young Researcher Award, Photoluminescence Characteristics of InAs Quantum Dots in the Doubled-heterointerface of AlGaAs/GaAs-based Two-step Photon Up-conversion Solar Cells
- 2020年06月 47TH IEEE PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALISTS CONFERENCE (PVSC 47), PVSC 47 Best Student Paper Award, Up-converted photocurrent enhancement in modulation-doped two-step photon up-conversion
- 2020年03月 日本材料学会, 令和元年度日本材料学会論文賞, デュアルヘテロダイン干渉計により光源起因のノイズを低減したサブナノメートル精度ウエハフラットネス計測システム
- 2019年10月 電子材料シンポジウム, EMS賞, Efficient Laser Cooling in Rare-Earth Doped Oxides at High Temperature
- 2019年09月 SemiconNano, SemiconNano2019 Best Poster Award, Laser Cooling Utilizing Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence in Yb-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet
- 2018年07月 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成30年度第1回研究会 学生優秀講演賞, Yb添加Yttrium-Aluminum化合物による固体レーザー冷却
- 2017年07月 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会 平成29年度第1回研究会 学生優秀講演賞, 低温キャップInAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子中間バンド型太陽電池における2段階光吸収の増強
- 2015年09月 応用物理学会, 応用物理学会フェロー表彰 第9回(2015年度), 半導体ナノ電子材料の構造制御と電子状態・光物性に関する研究
- 2014年12月 第25回光物性研究会, 光物性研究会奨励賞, InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子太陽電池における高効率2段階光吸収過程
- 2014年11月 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会 平成24年度第3回研究会 学生優秀講演賞, 低次元量子構造を利用したホットキャリア型太陽電池の提案
- 2014年09月 応用物理学会, APEX/JJAP編集貢献賞, 2014年度(第13回)
- 2014年07月 平成26年度第2回半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会第1回研究会, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成26年度第1回研究会学生優秀講演賞, Dot-in-Well構造を用いた量子ドット太陽電池の室温二段階光吸収
- 2014年06月 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Special Conference, PVSC40 Best Student Paper Award, Carrier Time-of-Flight Measurement Using a Probe Structure for DirectEvaluation of Carrier Transport in Quantum Structure Solar Cells
- 2014年03月 第36回(2014年春季)応用物理学会, 応用物理学会講演奨励賞, プローブ構造を用いた量子構造太陽電池におけるキャリア走行時間の測定” トープラサートポン カシディット
- 2011年12月 The 18th International Display Workshops, IDW'11 Outstanding Poster Paper Award, Effects of Argon Plasma Irradiation on Amorphous In-Ga-Zu-Ofilm Evaluated by Microwave Photoconductivity Decay Method
- 2010年12月 第21回光物性研究会, 第21回光物性研究会奨励賞, 希土類化合物半導体GdNにおけるバンド端光吸収の磁気光学特性
- 2010年10月 6th International Workshop on Nano-Scale Spectroscopy \Nanotechnology, NSS6 Student Award, Band-Edge Structure Induced by Ferromagnetic Spin Ordering in GdN Thin Films
- 2009年12月 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門学生優秀講演賞, 希土類窒化物半導体GdNヘテロ構造の基礎物性
- 2009年03月 財団法人エレクトロニクス実装学会, 第22回エレクトロニクス実装学会学術講演会優秀講演賞, 周期加熱サーモリフレクタンス法による銅めっき膜の熱伝導率評価
- 2008年12月 8th International Conference on Nano-Molecular Electronics 2008, ICNME2008 Outstanding Poster Presentation Award, Side Electron Emission Device Using A Composite of Carbon Nanofibers and Aluminum
- 2008年07月 ICOOPMA組織委員会, Best Poster Award, Lengthening of photoluminescence decay time owing to expansion of electron envelope functions in stacked quantum dots
- 2008年04月 電気関係学会関西支部連合大会実行委員会, 平成19年電気関係学会関西支部連合大会奨励賞, コラムナ量子ドットによる広帯域発光特性制御
- 2007年09月 応用物理学会, 応用物理学会講演奨励賞, InAs/GaAs量子ドット自己形成過程のRHEEDシェブロン構造のその場解析とIn拡散効果
- 2007年03月 日本金属学会, 金属学会写真奨励賞, 単一量子ドットの三次元微細構造解析
- 2006年11月 第67回応用物理学会学術講演会, 応用物理学会講演奨励賞, 高分解能断面TEMによる埋め込み量子ドット形状のマルチアングル直接観測
- 2005年05月 神戸大学, 神戸大学工学部優秀教育賞
- 2004年11月 はりま産学交流会主催, シーズコンペ入賞, 超省電力次世代ディスプレイ材料の開発
- 2000年09月 第46回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 応用物理学会講演奨励賞, Ga0.5In0.5P/GaAsヘテロ界面における自然超格子の影響 - 偏光ラマンスペクトル -
- 1999年09月 第60回応用物理学会学術講演会, 応用物理学会講演奨励賞, 反射率差分光法によるInAs自己形成量子ドット成長表面の観察
- 1998年07月 電子材料シンポジウム運営委員会, EMS賞, Time-Resolved Up-Converted Photoluminescence at Semicoductor Heterointerface
- 1995年07月 The Material Research Society of Japan, 日本MRS若手研究者アワード, AlGaInP混晶半導体自然超格子の電子状態制御
- American Chemical Society (ACS), 2025年11月, The Journal of Physical Chemistry C[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract We theoretically investigated the impact of the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of an InAs/GaAs quantum dot (QD) on the intraband absorption of the surrounding GaAs in the case that both GaAs and InAs are strongly photodoped (around 1 × 10 20 cm –3 ). We found that the intraband absorption for infrared light in the GaAs layer around the QDs can be significantly larger than that of equally strong photodoped bulk GaAs: The LSPR of the QDs significantly enhances intraband absorption in a spectral region of ∼10 meV in the near- to mid-infrared range depending on the carrier and QD density.IOP Publishing, 2025年10月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 64(10) (10), 100909 - 100909, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- We theoretically studied the control of the extraction of anti-Stokes photoluminescence using photonic crystal (PhC) nanocavities. Our fabricated (erbium,oxygen)-codoped GaAs PhC nanocavity showed a positive feedback gain of heating through the excitation of the GaAs host, which suggests the possibility of higher laser-cooling efficiencies at lower temperatures in such systems. Based on this result, we constructed a theoretical framework of laser cooling in PhC nanocavities. The predicted laser cooling efficiency of a PhC nanocavity is six to eight times higher than that of the corresponding bulk system, and we predict that more than 24% can be achieved at 100 K using holmium-doped materials.MDPI AG, 2025年09月, Solids, 6(3) (3), 51 - 51研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract We studied the photovoltaic properties of an InGaAs photodiode from the viewpoint of application as a laser power converter. The short-circuit current increased linearly with the excitation power density, but the open-circuit voltage was significantly influenced by carrier scattering when the excitation power density exceeded a critical excitation power density of 200 mW cm−2. We found that the external luminescence efficiency, which is directly related to the open-circuit voltage, starts to decrease above 200 mW cm−2 due to an increase in the non-radiative recombination rate. This mechanism including its effect on the fill factor determines the value of the optimum excitation power density for this device.IOP Publishing, 2025年06月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 64(7) (7), 074001 - 074001研究論文(学術雑誌)
- The basic photoconductive properties of an InAs/GaAs quantum dot (QD) superlattice have been characterized to develop photoconductive antennas (PCAs) operating with a telecom wavelength excitation for practical terahertz (THz) systems. The multiple-stacked InAs/GaAs QD structure was grown by molecular beam epitaxy and photo-Hall effect measurements were performed under infrared illumination conditions using light-emitting diodes with different emission wavelengths. The results have shown that sign reversal occurs in the Hall coefficient (RH) as the illumination wavelength changes: RH is negative at 940 nm and positive at 1550 nm. The photocurrent at 940 nm illumination is ascribed to the electron hole pair generation in QDs, whereas the photocurrent at 1550 nm is dominated by the hole current generated through the midgap states in the structure. The hole dominant photocurrent has been interpreted by a model in which photogenerated electrons are trapped in QDs and the number of mobile electrons are reduced. High dark resistance of the present QD superlattice material provides an advantage for the application to PCA devices. THz wave generation has been demonstrated by the ultrafast 1550 nm pulse excitation of a PCA device fabricated from the QD superlattice.AIP Publishing, 2025年06月, Journal of Applied Physics, 137(21) (21)研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract The application of the thermoradiative effect of photodiodes, in which photons are emitted to a cold reservoir in the far-field, is a promising approach for renewable electricity generation. Here we derive the radiative limit of the output power density of an ideal thermoradiative diode (TRD) with an intermediate band (IB) using detailed balance calculations. The output power density of an ideal IB-TRD with a given bandgap energy and an optimal IB position increases with the device temperature, and simultaneously the optimal position of the IB shifts away from the mid-gap position due to the current matching constraint. Since the intrinsic carrier density needs to be significantly lower than the doping concentration to form a p–n junction at the operating temperature, IB-TRDs can be advantageous compared to single-junction TRDs consisting of narrow-bandgap semiconductors.Springer Science and Business Media LLC, 2025年03月, Scientific Reports, 15(1) (1)研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract While a significant part of the solar energy lies in the infrared range, common semiconductors cannot absorb this part of the solar irradiance by direct band-to-band transitions, because the corresponding photon energies are below the bandgap energy. Two-step photon up-conversion (TPU) is one of the processes that allows us to harvest energy in the region below the bandgap, and one possible approach to realize a TPU-based solar cell is to use an AlGaAs/GaAs heterointerface with quantum dots in order to induce additional intraband transitions. On the other hand, here we report on the TPU phenomenon at a methylammonium lead bromide/gallium arsenide (MAPbBr3/GaAs) heterointerface without quantum dots. For this heterojunction, we observed high-energy photoemission by low-energy photoinjection, demonstrating the TPU. By using photoluminescence (PL) and time-resolved PL measurement techniques, we elucidate the mechanism of the PL emission from MAPbBr3 observed from MAPbBr3/GaAs samples. Through the comparisons of the experimental PL and TRPL results between the MAPbBr3/GaAs and MAPbBr3/Glass-substrate samples, we successfully distinguish the TPU phenomenon from the ordinal two-photon absorption of MAPbBr3. Our findings in the TPU at the MAPbBr3/GaAs heterointerface may help to realize quantum-dot-free photon up-conversion solar cells.Springer Science and Business Media LLC, 2025年01月, Journal of Optics, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract We studied the photovoltaic properties of a conventional silicon photodiode under monochromatic illumination conditions to clarify the loss mechanisms that are important for application as a laser power converter. While the short-circuit current increases linearly with the excitation power, the power dependence of the open-circuit voltage consists of two regions with different slopes as a result of the Joule heating. At higher excitation power densities, thermal effects play a key role in the current–voltage characteristics, and therefore the maximum conversion efficiency is achieved at a certain excitation-power density. Furthermore, the optimum excitation wavelength shifts towards longer wavelengths as the excitation power density increases, because the optimum value is determined by a trade-off between the optical absorption strength and the excitation power density.IOP Publishing, 2025年01月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 64(1) (1), 014001 - 014001, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Chemical Society (ACS), 2024年12月, ACS Photonics, 12(1) (1), 447 - 456研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract Two-step photon upconversion solar cells (TPU-SCs) based on III–V semiconductors can achieve enhanced sub-bandgap photon absorption because of intraband transitions at the heterointerface. From a technological aspect, the question arose whether similar intraband transitions can be realized by using perovskite/III–V semiconductor heterointerfaces. In this article, we demonstrate a TPU-SC based on a CsPbBr3/GaAs heterointerface. Such a solar cell can ideally achieve an energy conversion efficiency of 48.5% under 1-sun illumination. This is 2.1% higher than the theoretical efficiency of an Al0.3Ga0.7As/GaAs-based TPU-SC. Experimental results of the CsPbBr3/GaAs-based TPU-SC show that both the short-circuit current JSC and the open-circuit voltage VOC increase with additional illumination of sub-bandgap photons. We analyze the excitation power dependence of JSC for different excitation conditions to discuss the mechanisms behind the enhancement. In addition, the observed voltage-boost clarifies that the JSC enhancement is caused by an adiabatic optical process at the CsPbBr3/GaAs heterointerface, where sub-bandgap photons efficiently pump the electrons accumulated at the heterointerface to the conduction band of CsPbBr3. Besides the exceptional optoelectronic properties of CsPbBr3 and GaAs, the availability of a CsPbBr3/GaAs heterointerface for two-step photon upconversion paves the way for the development of high-efficiency perovskite/III–V semiconductor-based single-junction solar cells.Springer Science and Business Media LLC, 2024年11月, Scientific Reports, 14(1) (1)[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract We report lateral photoconductive properties of multilayer-stacked undoped InAs/GaAs quantum dots (QDs) for the application of photoconductive terahertz (THz) antenna devices that operate in a 1.5 μm-telecom-wavelength band. The excitation power-dependent photocurrent showed a high value without saturation under high excitation power for the excitation wavelength of 1460 nm. From the reflection pump-probe signal, a fast photocarrier lifetime was derived. These results, together with the low dark current characteristic, support the applicability of the multilayer-stacked undoped InAs/GaAs QDs to photoconductive THz antennas operating in a 1.5 μm-wavelength band.IOP Publishing, 2024年08月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(8) (8), 082002 - 082002研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science, Japan, 2024年02月, Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 73(2) (2), 178 - 182, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 公益社団法人応用物理学会, 2023年09月, 応用物理, 92(9) (9), 550 - 554, 日本語[査読有り]
- Abstract Ultrafast responses caused by ultrashort pulse excitation can be applied to ultrafast optical switches with high-speed information processing. In this paper, via the impulsive interference of excitons, we achieve an ultrafast optical response suited for ultrafast switches in all-optical networks. Due to the simultaneous excitation of two exciton states in the multiple quantum well on a strained buffer layer without the occurrence of adverse effects like stacking faults, impulsive interference is induced. The small compressive strain from the buffer layer modifies the orientation of the excitons inside the quantum well, and causes the ultrafast response.IOP Publishing, 2023年06月, Applied Physics Express, 16(6) (6), 062009 - 062009, 英語研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Photon upconversion (PU) is a process where an electron is excited from the valence band to the conduction band of a wide-gap semiconductor by the sequential absorption of two or more photons via real states. For example, two-step PU can generate additional photocurrent in the so-called intermediate-band solar cells. In this work, we consider two- and three-step processes; we study multi-step PU in a quantum dot (QD)-based single-junction solar cell with a double-heterointerface structure. The solar cell consists of three different absorber layers: Al0.7Ga0.3As, Al0.3Ga0.7As, and GaAs, which form two heterointerfaces. Just beneath each heterointerface, an InAs/GaAs QD layer was inserted. After band-to-band excitation, electrons accumulate at each heterointerface, and then, below-bandgap photons excite a certain fraction of these electrons above the barrier energy. The photoluminescence spectra of the InAs QDs reveal slightly different QD size distributions at the two heterointerfaces. We show that the external quantum efficiency is improved by additional irradiation with below-bandgap infrared photons, which suggests a multi-step PU process that involves the two heterointerfaces. The dependence of the photocurrent on the infrared excitation power density only shows a superlinear behavior when the GaAs layer is excited but the Al0.3Ga0.7As layer is not. These data demonstrate a multi-step PU process that consists of one intraband transition at each of the two heterointerfaces and one interband transition in GaAs.AIP Publishing, 2023年03月, Journal of Applied Physics, 133(12) (12), 124503 - 124503, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Abstract We elucidate a photocarrier collection mechanism in intermediate band solar cells (IBSCs) with InAs-quantum dots (QDs)-in-an-Al0.3Ga0.7As/GaAs-quantum well structures. When the Al0.3Ga0.7As barrier is excited, the device electrical output can be varied by additional infrared light for the electron intraband optical transition in QDs. The photocurrent in IBSC with a single QDs-in-a-well structure shows a monotonic increase with the intraband-excitation density. Conversely, IBSC with a multilayered QDs-in-a-well structure exhibits a photocurrent reduction when electrons in QDs are optically pumped out. The simultaneously measured photoluminescence spectra proved that the polarity of QD states changes depending on the intraband-excitation density. We discuss the drift and diffusion current components and point out that the hole diffusion current is significantly influenced by carriers inside the confinement structure. Under strong intraband excitations, we consider an increased hole diffusion current occurs by blocking hole-capture in the quantum structures. This causes unexpected photocurrent reduction in the multilayered device.IOP Publishing, 2022年07月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 61(7) (7), 074002 - 074002[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Optica Publishing Group, 2022年03月, Optics Express, 30(7) (7), 11789 - 11789, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- AIP Publishing, 2022年02月, AIP Advances, 12(2) (2), 025110 - 025110[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2022年01月, Chemistry&Chemical Industry(化学と工業), 75(1) (1), 26 - 28, 日本語紫外光によるウイルスの不活化と実証実験[招待有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Institute of Physics Inc., 2021年11月, Journal of Applied Physics, 130(17) (17), 英語研究論文(学術雑誌)
- AIP Publishing, 2021年09月, Journal of Applied Physics, 130(12) (12), 124505 - 124505[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- AIP Publishing, 2021年08月, Journal of Applied Physics, 130(8) (8), 085701 - 085701, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- IOP Publishing, 2021年08月, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 54(33) (33), 335106 - 335106[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- The Optical Society, 2021年07月, Optics Express, 29(15) (15), 24387 - 24387[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2021年06月, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 1786 - 1788, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2021年05月, KOGAKU Japanese Journal of Optics, 50(10) (10), 432 - 437解説:希土類イオンを利用した水銀フリ-ナロ-バンド紫外光源[査読有り]
- SPIE, 2021年04月, Photonic Heat Engines: Science and Applications III[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- AIP Publishing, 2021年02月, Journal of Applied Physics, 129(7) (7), 074503 - 074503, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science, Japan, 2020年10月, 材料, 69(10) (10), 727 - 732, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- {AIP} Publishing, 2020年09月, AIP Advances, 10(9) (9), 095016 - 095016, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- IOP Publishing, 2020年08月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(8) (8), 082005 - 082005, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Physical Society (APS), 2020年07月, Physical Review Applied, 14(1) (1), 014010-1 - -7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2020年07月, Applied Physics Letters, 117(041104) (041104), 1 - 5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Springer Science and Business Media LLC, 2020年07月, Scientific Reports, 10(1) (1)[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2020年06月, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2020-, 0146 - 0148, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2020年06月, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2020-, 0902 - 0904, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- AIP Publishing, 2020年06月, Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(6) (6), 065114 - 065114, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- SPIE, 2020年02月, Photonic Heat Engines: Science and Applications II, 11298, 112980B-1 - 10, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2020年02月, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 59, 032002-1 - 5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- IOP Publishing, 2019年12月, Applied Physics Express, 12(12) (12), 125008 - 125008, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- The Optical Society, 2019年11月, Optics Express, 27(24) (24), 34961 - 34961, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science, Japan, 2019年10月, Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 68(10) (10), 762 - 766[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年10月, 材料 別冊, 68(10) (10), 762 - 766, 日本語Yb添加イットリウムアルミニウムガーネット結晶粉末におけるアンチストークス発光を利用した理想レーザー冷却効率[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年10月, 材料 別冊, 68(10) (10), 757 - 761, 日本語金属上に形成した2次元フォトニック結晶の光学応答[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年10月, 材料 別冊, 68(10) (10), 767 - 771, 日本語加速度計により振動の影響を低減したサブナノメートル精度ウエハフラットネス計測システム[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Chemical Society (ACS), 2019年08月, J. Phys. Chem, 123(32) (32), 19447 - 19452[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- IOP Publishing, 2019年08月, Semiconductor Science and Technology, 34(9) (9), 094003 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- AIP Publishing, 2019年07月, Journal of Applied Physics, 126, 033103 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Institute of Physics Inc., 2019年06月, Journal of Applied Physics, 125(23) (23), 英語研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2019年06月, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2623 - 2626, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2019年06月, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2597 - 2599, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2019年06月, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 3004 - 3006, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Physics, 2019年05月, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1220, 012013 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- We studied the dynamics of electrons generated by two-step photoexcitation in an intermediate-band solar cell (IBSC) comprising InAs/GaAs/Al0.3Ga0.7As dot-in-well (DWELL) structure using time-resolved photocurrent (TRPC) measurement. The examined IBSC exhibited considerably slower photocurrent decay than a conventional InAs/GaAs quantum dot IBSC, which is due to the extraordinaNature Publishing Group, 2019年05月, Scientific Reports, 9, 7859 - 1-8, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- OSA Publishing, 2019年04月, OSA Continuum, 2, 1621 - 1628, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2019年03月, Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 111, 179 - 184, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Nature Publishing Group, 2019年02月, Nature Communications, 10, 956 - 1-3, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2019年, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 68(10) (10), 767 - 771, 日本語研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 55 - 79, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 81 - 137, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 15 - 24, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 157 - 202, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 139 - 156, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 25 - 42, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 43 - 54, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Verlag, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology, 1 - 13, 英語論文集(書籍)内論文
- Springer Singapore, 2019年, Green Energy and Technology[査読有り]
- Nature Publishing Group, 2018年12月, Scientific Reports, 8(1) (1), pp. 872 - 1-8, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2018年11月, 2018 IEEE 7th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, WCPEC 2018 - A Joint Conference of 45th IEEE PVSC, 28th PVSEC and 34th EU PVSEC, 3447 - 3450, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年11月, Proceedings of the 35th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 126 - 128, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年10月, Physical Review Applied, A 10(044035) (044035), pp. 044035 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2018年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 67(9) (9), 829 - 833, 日本語研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年09月, 材料 別冊, Vol. 67(No. 9) (No. 9), pp. 829 - 833, 日本語デュアルヘテロダイン干渉計により光源起因のノイズを低減したサブナノメートル精度ウエハフラットネス計測システム[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年07月, Applied Physics Express, Vol. 11(No. 1) (No. 1), pp.082303 - 1-4, 英語Hot-Carrier Generation in a Solar Cell Containing InAs/GaAs Quantum-Dot Superlattices as a Light Absorber[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Institute of Physics, 2018年07月, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 51, 305102 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2018年06月, 電気評論, (6月号) (6月号), 13 - 17, 日本語高変換効率太陽光発電の研究開発~50%を超える変換効率実現に向けた取り組み[査読有り]
- OSA - The Optical Society, 2018年, Optics InfoBase Conference Papers, 2018, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- SPIE, 2018年, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 10527, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2018年01月, APPLIED PHYSICS EXPRESS, 11(1) (1), pp. 012301 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年10月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 96(15) (15), pp. 155210 - 1-8, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2017年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 66(9) (9), 629 - 633, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年09月, JOURNAL OF THE PHYSICAL SOCIETY OF JAPAN, 86(9) (9), pp. 094710 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年09月, 材料 別冊, 66(9) (9), pp. 629 - 633, 日本語InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子を用いたホットキャリア型太陽電池の基礎特性[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年07月, SCIENTIFIC REPORTS, 7, pp. 5865 - 1-10, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年06月, PHYSICS LETTERS A, 381(22) (22), 1905 - 1909, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年05月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 110(19) (19), pp. 193104 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2017年04月, NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, 8, pp. 14962 - 1-9, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2017年03月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 66(3) (3), 244 - 249, 日本語[査読有り]
- 2017年03月, 材料 別冊, 66(3) (3), pp. 244~249, 日本語半導体材料・デバイスの最新の進展 3. 太陽電池の変換効率限界を引き上げる半導体材料設計[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- OSA - The Optical Society, 2017年, Optics InfoBase Conference Papers, 2017, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- OSA - The Optical Society, 2017年, Optics InfoBase Conference Papers, 2017, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2017年01月, Scientific Reports, 7, pp. 41496 - 1-7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2016年12月, Conference Digest - IEEE International Semiconductor Laser Conference, 英語Transverse-magnetic laser oscillation from highly stacked InAs/GaAs quantum dots研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2016年11月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 94(19) (19), pp. 195313 - 1 -9, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年10月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 120(13) (13), pp. 134313 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2016年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 65(9) (9), 647 - 651, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 65(9) (9), 642 - 646[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 日本材料学会, 2016年09月, 日本材料学会会誌「材料」, 65(9) (9), pp. 647 - 651, 日本語量子ドット超格子太陽電池における2段階光励起電流生成ダイナミクスの電界依存特性[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 日本材料学会, 2016年09月, 日本材料学会会誌「材料」, 65(9) (9), pp. 642 - 646, 日本語ペロブスカイト太陽電池へのITO透明電極スパッタリング直接堆積の影響[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年07月, AIP ADVANCES, 6(7) (7), pp. 075209 - 1-7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年05月, Applied Physics Express, 9(6) (6), 062801 - 1-3, 英語Effects of exciton line widths on the amplitude of quantum beat oscillations[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年05月, J. Appl. Phys., 119(19) (19), pp. 194306 - 1-8, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年03月, IEEE JOURNAL OF PHOTOVOLTAICS, 6(2) (2), 465 - 472, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年03月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 93(11) (11), pp. 115303 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2016年03月, Appl. Phys. Lett., 108(11) (11), pp. 111905 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2016年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 71, 1502 - 1502, 日本語[査読有り]
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2016年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 71, 1351 - 1351, 日本語[査読有り]
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2016年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 71, 1458 - 1458, 日本語[査読有り]
- 2016年, 2016 COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTOR WEEK (CSW) INCLUDES 28TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE & RELATED MATERIALS (IPRM) & 43RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS (ISCS), 英語Polarization anisotropy of electroluminescence and net-modal gain in highly stacked InAs/GaAs quantum-dot laser devices[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2016年, 2016 INTERNATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR LASER CONFERENCE (ISLC), 英語Transverse-magnetic laser oscillation from highly stacked InAs/GaAs quantum dots[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2016年, 2016 COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTOR WEEK (CSW) INCLUDES 28TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE & RELATED MATERIALS (IPRM) & 43RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS (ISCS), 英語Two-Dimensional Energy Dispersion in Thermally Annealed Epitaxial Nitrogen Atomic Sheet in GaAs[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2016年, 2016 COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTOR WEEK (CSW) INCLUDES 28TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE & RELATED MATERIALS (IPRM) & 43RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS (ISCS), 英語GaAs first-spacer-layer thickness dependence of polarized photoluminescence properties of closely-stacked InAs/GaAs quantum dots with long-wavelength emission[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2016年, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 9743(974315) (974315), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ({IEEE}), 2015年11月, IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 5(6) (6), 1613 - 1620, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年10月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 118(15) (15), pp. 154301 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- The Society of Materials Science, Japan, 2015年09月, 材料, 64(9) (9), 690 - 695, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2015年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 64(9) (9), 685 - 689, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年09月, Journal of the Society of Materials Science, 64(9) (9), pp. 685 - 689, 日本語近接積層InAs/GaAs量子ドット半導体光アンプの光導波モード解析[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年09月, Journal of the Society of Materials Science, 64(9) (9), pp. 690~695, 日本語InAs/GaAs/Al0.3Ga0.7As中間バンド型太陽電池における室温2段階光励起の飽和現象の解析[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2015年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 64(9) (9), 690 - 695, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- {AIP} Publishing, 2015年07月, Applied Physics Letters, 107(4) (4), 043901 - 043901, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- In this study, we propose a carrier time-of-flight technique to evaluate the carrier transport time across a quantum structure in an active region of solar cells. By observing the time-resolved photoluminescence signal with a quantum-well probe inserted under the quantum structure at forward bias, the carrier transport time can be efficiently determined at room temperature. The{AIP} Publishing, 2015年07月, Applied Physics Letters, 107(4) (4), 043901 - 043901, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年07月, MATERIALS RESEARCH EXPRESS, 2(7) (7), pp. 076402 - 1-7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年06月, APPLIED PHYSICS REVIEWS, 2(2) (2), pp. 021302 - 1-48, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年05月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 91(20) (20), pp. 201303 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年04月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 117(16) (16), pp. 193105 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年03月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 91(12) (12), pp. 125307 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2015年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 70, 1271 - 1271, 日本語[査読有り]
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2015年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 70, 1115 - 1115, 日本語[査読有り]
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2015年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 70, 1158 - 1158, 日本語[査読有り]
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2015年, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 70, 1413 - 1413, 日本語[査読有り]
- 2015年, 2015 IEEE 42ND PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALIST CONFERENCE (PVSC), 英語Ultrafast Photocarrier Transport Dynamics in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Solar Cell[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2015年, 2015 IEEE 42ND PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALIST CONFERENCE (PVSC), 英語Saturable Two-step Photo current Generation in Intermediate-band Solar Cells Including InAs Quantum Dots Embedded in Al0.3Ga0.7As/GaAs Quantum Wells[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2015年, 2015 IEEE 42ND PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALIST CONFERENCE (PVSC), 英語Comparison of Electron and Hole Mobilities in Multiple Quantum Well Solar Cells Using a Time-of-Flight Technique[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2015年, 2015 IEEE 42ND PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALIST CONFERENCE (PVSC), 英語Time-Resolved Photoluminescence of MBE-Grown 1 eV GaAsSbN for Multi-Junction Solar Cells[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2015年, 2015 IEEE 42ND PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALIST CONFERENCE (PVSC), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2015年01月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 117(4) (4), 043909 - 1~6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2015年, PHYSICS SIMULATION AND PHOTONIC ENGINEERING OF PHOTOVOLTAIC DEVICES IV, 9358, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ({IEEE}), 2014年11月, IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 4(6) (6), 1518 - 1525, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年11月, 14th International Symposium on Advanced Fluid Information, 148 - 149, 英語Photoluminescence Properties of InAs Quantum Dots on Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAs研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2014年11月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 105(18) (18), pp. 1 - 3, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年10月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 105(17) (17), pp. 1 - 5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年08月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 116(6) (6), pp. 063510 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年06月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 115(23) (23), 233512 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年05月, J. Appl. Phys., 115(17) (17), 173508 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年05月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 115(20) (20), 203717 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 応用物理学会, 2014年05月, 応用物理, 83(5) (5), 348 - 355, 日本語中間バンド型高効率太陽電池―量子ナノ構造中における光キャリアダイナミックス―[査読有り]
- 2014年03月, JOURNAL OF PHYSICS D-APPLIED PHYSICS, 47(10) (10), 105101 - 1~5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年02月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 115(8) (8), 083510 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年02月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 115(8) (8), 083503 - 1~4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2014年01月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 104(4) (4), 041907 - 1~4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年11月, 13th International Symposium on Advanced Fluid Information, 102 - 103, 英語Fabrication of InAs Qantum Dots on Nitrided GaAs (001) Surface[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2013年09月, スマートプロセス学会誌(別刷), Vol.2(No.5) (No.5), 206 - 212, 日本語自己形成過程を原子レベルで制御した量子ドットの作製と高機能光応答の実現[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年07月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 114(3) (3), 033517 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年06月, Journal of Applied Physics, 113(22) (22), 223511 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年06月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 87(23) (23), 2353323 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年06月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 102(22) (22), 222408 1 - 4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年03月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(3) (3), 03BA01 - 5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年, PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, 1566, 325 - +, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2013年, 2012 IEEE 38TH PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALISTS CONFERENCE (PVSC), VOL 2, 英語Carrier Dynamics in Intermediate States of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots Embedded in Photonic Cavity Structure[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2013年, 2012 IEEE 38TH PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALISTS CONFERENCE (PVSC), VOL 2, 英語Carrier Dynamics in Intermediate States of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots Embedded in Photonic Cavity Structure[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2013年01月, J. Appl. Phys., 113(1) (1), 074305 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年, European Physical Journal B, 86(2) (2), 52 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2013年, 15TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THIN FILMS (ICTF-15), 417, 012053 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2013年, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 8620, 862008 - 1-7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Institute of Physics Publishing, 2013年, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 417(1) (1), 012049 - 1-6, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2013年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 10, NO 11, 10(11) (11), 1492 - 1495, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 応用物理学会, 2012年12月, Jpn J Appl Phys, 52, 012001 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年11月, IEICE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRONICS, E95C(11) (11), 1724 - 1729, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年09月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 112(5) (5), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年08月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 101(7) (7), 072403 - 1-5, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年07月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 86(3) (3), 035301 - 1-7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年06月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 100(23) (23), 232410 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年04月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 111(8) (8), 083526 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年04月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 111(7) (7), 074305 - 1-4, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年, 2012 19TH INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON ACTIVE-MATRIX FLATPANEL DISPLAYS AND DEVICES (AM-FPD): TFT TECHNOLOGIES AND FPD MATERIALS, 147 - 150, 英語Physical properties of amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O films deposited under various sputtering pressure[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- Springer New York, 2012年01月, Quantum Dot Devices, 197 - 222, 英語[査読有り]論文集(書籍)内論文
- 2012年, Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, 1342, 87 - 92, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2012年01月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 111(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2012年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 9, NO 2, 9(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2012年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 9, NO 12, 9(12) (12), 2473 - 2476, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年11月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 60(11) (11), 1004 - 1008, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年11月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 110(10) (10), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年11月, Progress in Photovoltaics:Research and Applications, Vol. 19, Issue8, pp. 1~9, 英語Intermediate Band Photovoltaics Based on Interband-intraband Transitions Using In0.53Ga0.47As/InP Superlattice[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年11月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 110(9) (9), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年11月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 110(9) (9), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年10月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 110(8) (8), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年10月, J. Appl. Phys, 110(8) (8), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年09月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 84(11) (11), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年08月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 110(4) (4), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年06月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 98(23) (23), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年06月, APPLIED PHYSICS EXPRESS, 4(6) (6), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年04月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 83(15) (15), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年04月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 109(7) (7), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年03月, JOURNAL OF CERAMIC PROCESSING RESEARCH, 12, S73 - S77, 英語Narrowband ultraviolet light emission from AlGdN polycrystalline thin films[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年02月, Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol 80. No. 3, pp. 034704-1-5, 英語Dephasing of excitonic polaritons confined in GaAs thin films[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年02月, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI B-BASIC SOLID STATE PHYSICS, 248(2) (2), 464 - 467, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年, IDW'11: PROCEEDINGS OF THE 18TH INTERNATIONAL DISPLAY WORKSHOPS, VOLS 1-3, 103 - 106, 英語Effects of argon plasma irradiation on amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O film evaluated by microwave photoconductivity decay method[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 002625 - 002628, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, 材料, vol.60,No11,pp.1004-1008, 日本語希土類窒化物半導体GdN薄膜の強磁性相転移とスピン秩序誘起のバンドギャップ減少[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年01月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 109(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2011年, PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS: 30TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, 1399, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 8, NO 2, 8(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 8, NO 2, 8(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 8, NO 1, 8(1) (1), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 8, NO 1, 8(1) (1), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 8, NO 2, 8(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 8, NO 2, 8(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, Physica Status Solidi C, 8(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2011年, PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS: 30TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, 1399, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年11月, JOURNAL OF THE JAPAN INSTITUTE OF METALS, 74(11) (11), 740 - 745, 日本語Spatially Resolved Thermal Conductivity of Intermetallic Compounds Measured by Micro-Thermoreflectance Method[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年11月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 97(19) (19), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年11月, IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, 46(11) (11), 1582 - 1589, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年09月, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 59(9) (9), 666 - 670, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年09月, J. Appl. Phys, 108(6) (6), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年05月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 96(21) (21), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年04月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 96(15) (15), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年04月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 107(7) (7), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年02月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 107(4) (4), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年, 2010 22ND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS (IPRM), 英語All-optical switch using InAs quantum dots in a vertical cavity[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, 35TH IEEE PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALISTS CONFERENCE, 1808 - 1813, 英語ENERGY BAND STRUCTURE AND ABSORPTION COEFFICIENTS IN THE QUANTUM-DOT INTERMEDIATE BAND SOLAR CELLS[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, QUANTUM DOTS AND NANOSTRUCTURES: SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION, AND MODELING VII, 7610, 英語Self-assembled InAs quantum dots within a vertical cavity structure for all-optical switching devices[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, PHYSICS AND SIMULATION OF OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICES XVIII, 7597, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, 35TH IEEE PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALISTS CONFERENCE, 英語INTRABAND RELAXATION OF PHOTOEXCITED CARRIERS IN MULTIPLE STACKED QUANTUM DOTS AND QUANTUM DOT CHAINS[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, 35TH IEEE PHOTOVOLTAIC SPECIALISTS CONFERENCE, 1834 - 1837, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, 材料, Vol. 59, No.9, pp. 666-670, 日本語低温成長したAlGdN蛍光体薄膜における深紫外発光効率の向上[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2010年, QUANTUM DOTS 2010, 245, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2010年, QUANTUM DOTS AND NANOSTRUCTURES: SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION, AND MODELING VII, 7610, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2009年12月, JOURNAL OF LUMINESCENCE, 129(12) (12), 1448 - 1453, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2009年12月, REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS, 80(12) (12), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2009年11月, THIN SOLID FILMS, 518(2) (2), 530 - 533, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2009年07月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 95(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2009年06月, Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi/Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals, 73(6) (6), 434 - 438, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2009年, 2009 IEEE 21ST INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE & RELATED MATERIALS (IPRM), 406 - +, 英語Quantum dots in a vertical cavity for all-optical switching devices[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 応用物理学会, 2009年, 応用物理, Vol. 78, No.4, pp. 355-359(4) (4), 355 - 359, 日本語原子層窒素ドープGaAsを用いた励起子微細構造の制御と光子源に向けた展開[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 神戸大学大学院工学研究科, 2009年, Memoirs of the Graduate School of Engineering Kobe University, 1(1) (1), 1 - 8, 英語Controlling Polarization in Quantum-dot Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers[査読有り]研究論文(大学,研究機関等紀要)
- 2009年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 6, SUPPL 1, 6, S139 - S142, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2009年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 6, SUPPL 1, 6, S146 - S149, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2008年11月, Appl. Phys. Lett, 93(21) (21), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年11月, APPLIED PHYSICS EXPRESS, 1(11) (11), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年11月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 104(10) (10), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年10月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 104(7) (7), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年08月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 78(7) (7), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年07月, APPLIED PHYSICS EXPRESS, 1(7) (7), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年06月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 92(24) (24), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年06月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 103(11) (11), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年05月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 77(19) (19), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年04月, REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS, 79(4) (4), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年03月, Journal of Luminescence, Vol 128. No. 5-6, pp. 975-977, 英語Photoluminescence dynamics of coupled quantum dots[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年, 2008 IEEE 20TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS (IPRM), 231 - 233, 英語EXCITON FINE STRUCTURE OF NITROGEN ISOELECTRONIC CENTERS IN GaAs[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2008年01月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 92(3) (3), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2008年, IUMRS-ICA 2008 SYMPOSIUM AA. RARE-EARTH RELATED MATERIAL PROCESSING AND FUNCTIONS, 1, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2007年05月, Guti Dianzixue Yanjiu Yu Jinzhan/Research and Progress of Solid State Electronics, 27(2) (2), 151 - 153, 中国語Investigation of nitrided InAs/GaAs self-assembled quantum dots研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2007年04月, JOURNAL OF CRYSTAL GROWTH, 301, 34 - 37, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2007年04月, JOURNAL OF CRYSTAL GROWTH, 301, 709 - 712, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2007年, 2007 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS, CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS, 579 - 581, 英語Multidirectional transmission electron microscope observation of a single InAs/GaAs self-assembled quantum dot[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2007年, PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, PTS A AND B, 893, 249 - +, 英語Confined electronic structures of nitrogen isoelectronic centers in GaAs grown by atomically controlled doping technique[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2007年, PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, PTS A AND B, 893, 1245 - +, 英語Anisotropic magnetic-field evolution of valence-band states in one-dimensional diluted magnetic semiconductors[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2007年, 2007 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS, CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS, 303 - 306, 英語Real time probing of self-assembling process steps in InAs/GaAs quantum dot growth[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2007年01月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 90(4) (4), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2007年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C - CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 4 NO 7 2007, 4(7) (7), 2490 - +, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2007年, 2007 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS, CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS, pp. 197-200, 197 - 200, 英語Control of optical emission from coupled excitonic states in quantum dot superlattice structures[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2006年12月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 74(24) (24), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2006年11月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 2-LETTERS & EXPRESS LETTERS, 45(42-45) (42-45), L1186 - L1189, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2006年07月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 2-LETTERS & EXPRESS LETTERS, 45(24-28) (24-28), L650 - L653, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2006年07月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 74(3) (3), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2006年05月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 88(21) (21), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2006年, Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics and 2006 Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference, CLEO/QELS 2006, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2006年, Physica Status Solidi C: Conferences, 3(3) (3), 667 - 670, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2006年, 2006 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS, 201 - +, 英語Emission-wavelength extension of InAs/GaAs quantum dots by controlling lattice-mismatch strain[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2006年, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C - CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 3 NO 3, 3(3) (3), 667 - +, 英語Valence-band mixing induced by sp-d exchange interaction in CdMnTe quantum wires[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年10月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 1-REGULAR PAPERS BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS & REVIEW PAPERS, 44(10) (10), 7390 - 7394, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2005年06月, AIP Conference Proceedings, 772, 387 - 388, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年04月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 1-REGULAR PAPERS BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS & REVIEW PAPERS, 44(4B) (4B), 2528 - 2530, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2005年03月, 日本学術振興会科学研究費補助金・基盤研究(B)(2),平成16年度研究実績報告書, 日本語形状制御した量子ドットによる偏光無依存吸収端の実現[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2005年02月, JOURNAL OF CRYSTAL GROWTH, 275(1-2) (1-2), E2221 - E2224, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2005年, IQEC, International Quantum Electronics Conference Proceedings, 2005, 265 - 266, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年, IQEC, International Quantum Electronics Conference Proceedings, 2005, 261 - 262, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年, 2005 International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 52 - 55, 英語Mechanism of emission-wavelength extension in nitrided InAs/GaAs quantum dots[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年, 2005 International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 355 - 358, 英語Wavelength control of nitrided InAs/GaAs quantum dots in fiber-optic communication region[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年, ULTRAFAST PHENOMENA XIV, 79, 263 - 265, 英語Ultrafast anisotropic processes of exciton magnetic polarons in CdTe/CdMnTe quantum wires[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2005年01月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 97(2) (2), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2005年, Physics of Semiconductors, Pts A and B, 772, 1353 - 1354, 英語Hole-spin reorientation in (CdTe)(0.5)(Cd0.75Mn0.25Te)(0.5) tilted superlattices grown on Cd0.74Mg0.26Te(001) vicinal surface[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2004年06月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 69(23) (23), 1 - 233308, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2004年06月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 69(23) (23), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2004年04月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 1-REGULAR PAPERS SHORT NOTES & REVIEW PAPERS, 43(4B) (4B), 1978 - 1980, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2004年03月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 84(11) (11), 1820 - 1822, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2004年03月, PHYSICA E-LOW-DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS & NANOSTRUCTURES, 21(2-4) (2-4), 345 - 348, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Society of Materials Science Japan, 2004年, Zairyo/Journal of the Society of Materials Science, Japan, 53(12) (12), 1346 - 1350, 日本語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2004年, 神戸大学版ベンチャー・ビジネス・ラボラトリー年報, VOL.9,102-107, 日本語半導体量子ナノ構造のスピンエレクトロニクス応用[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2004年, 神戸大学版ベンチャー・ビジネス・ラボラトリー年報, VOL.9,6-13, 日本語フォトニクスマテリアル量子ナノ構造におけるスピン制御[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年11月, APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS, 83(20) (20), 4152 - 4153, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年11月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 94(10) (10), 6487 - 6490, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年07月, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI B-BASIC RESEARCH, 238(2) (2), 229 - 232, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年05月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 67(19) (19), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年04月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 1-REGULAR PAPERS SHORT NOTES & REVIEW PAPERS, 42(4B) (4B), 2329 - 2331, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年03月, 日本学術振興会科学研究費補助金・基盤研究(B)(2),平成14年度研究成果報告書, 未記入, 日本語形状制御量子ドットによる超高速・高非線形光学応答の同時実現[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年02月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 67(8) (8), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年02月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 67(8) (8), 853011 - 853017, 英語Excitonic states in CdTe/Cd0.74Mg0.26Te quantum wires grown on vicinal substrates研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年02月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 67(8) (8), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年02月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 1-REGULAR PAPERS SHORT NOTES & REVIEW PAPERS, 42(2A) (2A), 371 - 374, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Optical Society of American (OSA), 2003年, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics Series, 88, 534 - 535, 英語Wideband polarization insensitivity in quantum dot optical amplifier研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2003年, 2003 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE INDIUM PHOSPHIDE AND RELATED MATERIALS, CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS, 531 - 533, 英語Novel characterization technique for GaAs/GaInP heterojunction bipolar transistor wafers based on Fourier transformed photoreflectance enabling selective determination of interface electric fields[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2003年, 2ND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SEMICONDUCTOR QUANTUM DOTS, 0(4),1137-1140, 1137 - 1140, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2003年, COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS 2002, 174, 173 - 177, 英語One-dimensional free exciton in CdTe/Cd0.74Mg0.26Te quantum wires[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2003年, 神戸大学ベンチャー・ビジネス・ラボラトリー年報2003, Vol.8,pp.5-14, 日本語GaAs/AlGaAsフォトリフラクティブ多重量子井戸のフェムト秒光回析[査読有り]
- 2003年, 神戸大学ベンチャー・ビジネス・ラボラトリー年報2003, Vol.8,pp.126-129, 日本語CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線における磁気光学特性の異方性[査読有り]
- 2002年11月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 66(19) (19), 1953171 - 1953177Magnetophotoluminescence study of the Ga
0.5 In0.5 P/GaAs heterointerface with a ordering-induced two-dimensional electron gas[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - 2002年11月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 66, 1953121 - 1953126[査読有り]
- American Physical Society (APS), 2002年11月, Physical Review B, 66(19) (19), 195312 - 195312, 英語[査読有り]
- 2002年11月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 66(19) (19), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年10月, JAPANESE JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS PART 2-LETTERS, 41(10B) (10B), L1143 - L1145, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年04月, Physica Status Solidi (A) Applied Research, 190(3) (3), 703 - 707, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2002年04月, PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI A-APPLIED RESEARCH, 190(3) (3), 699 - 702, 英語Radiative lifetimes of excitons in CdMgTe/CdTe tilted superlattices grown on vicinal surfaces[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年03月, PHYSICA E-LOW-DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS & NANOSTRUCTURES, 13(2-4) (2-4), 329 - 332, 英語Two-dimensional electron gas at Ga0.5In0.5P/GaAs heterointerface spontaneously induced by atomic ordering[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 515 - 518High-density electron gas induced by atomic ordering in undoped Ga
0.5 In0.5 P/GaAs heterostructure[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス) - 2002年, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 66(19) (19), 1 - 7, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年, COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS 2001, (170) (170), 519 - 524, 英語Biexciton formation in CdTe/Cd0.74Mg0.26Te quantum wires[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年, COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS 2001, (170) (170), 525 - 530, 英語Stranski-Krastanov growth of (In,Ga)As quantum dots by controlling the wetting layer[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2002年01月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 66, 1 - 6[査読有り]
- 2001年04月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 63(16) (16), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2001年03月, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 63(12) (12), 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2001年, New Diamond and Frontier Carbon Technology, 11(5) (5), 339 - 345, 英語Optical Characterization of CVD-Diamond Films研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2001年, PROCEEDINGS OF THE 25TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, PTS I AND II, 87, 453 - 454, 英語Plasmon-phonon coupling at Ga0.5In0.5P/GaAs heterointerfaces induced by CuPt-type ordering[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2001年, PROCEEDINGS OF THE 25TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, PTS I AND II, 87, 365 - 366, 英語Optical anisotropy of Stranski-Krastanov growth surface of InAs on GaAs (001)[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2001年, PROCEEDINGS OF THE 25TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, PTS I AND II, 87, 353 - 354, 英語Reflectance-difference spectroscopy of (001) InAs surfaces in ultrahigh vacuum[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2001年, PROCEEDINGS OF THE 25TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON THE PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS, PTS I AND II, 87, 218 - 219, 英語Energy relaxation by phonon scattering in long-range ordered (Al0.5Ga0.5)(0.5)In0.5P[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 2001年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 330 - 333Internal electric field effects at ordered Ga
0.5 In0.5 P/GaAs heterointerface investigated by photoreflectance spectroscopy[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス) - 2000年06月, Applied Surface Science, 159, 503 - 507[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2000年05月, Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 7(3) (3), 891 - 895[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- SPIE, 2000年, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 4086, 535 - 539, 英語研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- IOP Publishing, 2000年01月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 39(S1) (S1), 328 - 328研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 2000年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 154 - 157Interdiffusion effects at long-range ordered Ga
0.5 In0.5 P and GaAs heterointerfaces[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - 2000年, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 4110, 9 - 16, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Up-converted photoluminescence (UPL) was observed at thelong-range ordered (Al0.5Ga0.5)0.5In0.5P/GaAs(001)heterointerface, during the excitation of GaAs. Excitation-powerdependence of the UPL intensity reflects carrier-localizationproperties caused by potential fluctuations due to a multidomainstructure in the ordered(Al0.5Ga0.5)0.5In0.5P. When we excited the GaAslayer, photoexcited carriers spatially transferred to the(Al0.5Ga0.5)0.5In0.5P layer and relaxed fromhigher lying states to lower lying states in the fluctuatedpotential. Time-resolved measurements were performed for the UPL andnormal photoluminescence (NPL) excited by an above-gap light. Weobserved a slowly rising component in the time-resolved UPL, whereasthe NPL showed an exponential decay profile. These results revealthat the carrier-relaxation processes are different near the surfaceand near the interface of the epitaxial layer.社団法人応用物理学会, 1999年02月, Japanese journal of applied physics. Pt. 1, Regular papers & short notes, 38(2) (2), 1001 - 1003, 英語[査読有り]
- 1999年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 159 - 162Energy relaxation by multiphonon processes in partially ordered (Al
0.5 Ga0.5 )0.5 In0.5 P[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌) - American Institute of Physics Inc., 1999年, Journal of Applied Physics, 86(6) (6), 3140 - 3143, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1999年, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 59(23) (23), 15358 - 15362, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Institute of Physics Inc., 1998年07月, Journal of Applied Physics, 84(1) (1), 359 - 363, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1998年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 521 - 524Efficiency of photoluminescence up-conversion at (Al
0.5 Ga0.5 )0.5 In0.5 P and GaAs heterointerface[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス) - 1998年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 525 - 528Spin-polarized excitons in long-range ordered Ga
0.5 In0.5 P[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス) - 1998年, Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 3175, 465 - 469, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- 1998年, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 57(24) (24), R15044 - R15047, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1998年01月, Superlattices and Microstructures, 23(1) (1), 173 - 176[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Elsevier, 1997年, Applied Surface Science, 113-114, 631 - 637, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1997年, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 55(7) (7), 4411 - 4416, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1996年10月, Journal of Applied Physics, 80(8) (8), 4592 - 4598[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- Japan Society of Applied Physics, 1996年, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1: Regular Papers and Short Notes and Review Papers, 35(10) (10), 5367 - 5373, 英語研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1996年, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 54(23) (23), 16714 - 16718, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1996年, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 53(23) (23), 15713 - 15718, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- American Inst of Physics, 1995年04月, Applied Physics Letters, 66(14) (14), 1794 - 1796, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- IEEE, 1995年, Conference Proceedings - International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 257 - 260, 英語Anisotropic photocurrent in long-range ordered Ga0.5In0.5P研究論文(国際会議プロシーディングス)
- JJAP, 1994年10月, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1: Regular Papers and Short Notes and Review Papers, 33(10) (10), 6032 - 6038, 英語Theoretical analysis of photoacoustic displacement for inhomogeneous materials研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1994年, Physical Review B, 50(4) (4), 2420 - 2424, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- 1994年, Journal of Applied Physics, 76(10) (10), 5681 - 5689, 英語[査読有り]研究論文(学術雑誌)
- The electronic structure of n-Al0.28Ga0.72As/In0.23Ga0.77As/GaAs has been investigated by photoluminescence (PL) and photoreflectance (PR) spectroscopies. Transitions associated with the $n{=}1$ and 2 electron subbands in the In0.23Ga0.77As single quantum well were observed. Two-dimensional carrier density was evaluated in terms of the quantum confined Franz-Keldysh (FK) effect of the transition between the lowest states of electrons and heavy holes. Because of penetrations of the confined electron density into the neighboring layers, PR spectra of GaAs show FK oscillation.社団法人応用物理学会, 1992年06月, Jpn J Appl Phys, 31(6) (6), L756 - L758, 英語[査読有り]
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2014年08月22日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 69(2) (2), 514 - 514, 日本語8aAJ-6 GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸におけるアップコンバージョン発光(8aAJ 励起子・ポラリトン(量子井戸・超格子),領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2014年03月05日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 69(1) (1), 689 - 689, 日本語27aAU-9 多重量子井戸における高温での励起子量子ビート制御(27aAU 量子細線・量子井戸・超格子・光応答,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2013年08月26日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 68(2) (2), 600 - 600, 日本語25pDD-2 量子ビートによる超高速応答に対するフォノンの効果(量子井戸・光応答,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2013年08月26日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 68(2) (2), 665 - 665, 日本語26pPSA-41 積層方向を制御したInAs/GaAs量子ドットの発光偏光特性(領域5ポスターセッション(励起子,微粒子・ナノ結晶,その他),領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2013年03月26日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 68(1) (1), 742 - 742, 日本語26aXQ-4 GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における励起子量子ビートによる光パルス強度変調(26aXQ 量子井戸・超格子・光応答,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- Published by the Japan Society of Applied Physics through the Institute of Pure and Applied Physics, 2013年03月, Japanese journal of applied physics : JJAP, 52(3) (3), 03BA01 - 1-5, 英語Physical Properties of Amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O Films Deposited at Different Sputtering Pressures (Special Issue : Active-Matrix Flatpanel Displays and Devices : TFT Technologies and FPD Materials)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2012年08月24日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 67(2) (2), 614 - 614, 日本語18aFB-6 光共振器構造中のInAs/GaAs量子ドットにおけるサブバンド間遷移ダイナミクス(18aFB 量子井戸・超格子・光応答,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2012年03月05日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 67(1) (1), 778 - 778, 日本語24pPSA-24 歪み補償多層積層量子ドットにおける非共鳴励起キャリアダイナミクス(24pPSA 領域5 ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年08月24日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(2) (2), 728 - 728, 日本語21pPSA-37 GaAs中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子分子の磁気光学特性(21pPSA 領域5ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年08月24日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(2) (2), 731 - 731, 日本語21pPSA-48 GaAs nipi超格子におけるコヒーレントプラズモン振動のドーピング濃度依存性(21pPSA 領域5ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年08月24日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(2) (2), 746 - 746, 日本語21pPSB-46 歪み補償多層積層量子ドットにおける非共鳴励起緩和過程(21pPSB 領域5ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年08月24日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(2) (2), 713 - 713, 日本語21aRB-9 GaAs薄膜における励起子状態の光制御に対する入射光エネルギー依存性(21aRB 超高速現象,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年08月24日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(2) (2), 670 - 670, 日本語21pTL-7 強磁性薄膜GdNの強磁性共鳴による研究II(21pTL 若手奨励賞・磁性半導体,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年03月03日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(1) (1), 698 - 698, 日本語25pHD-3 強磁性薄膜GdNの強磁性共鳴による研究II(25pHD 磁性半導体・量子井戸・超格子,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年03月03日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(1) (1), 699 - 699, 日本語25pHD-7 多層積層量子ドット励起子とスペーサー層キャリアとの相関(25pHD 磁性半導体・量子井戸・超格子,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年03月03日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(1) (1), 750 - 750, 日本語25pPSA-20 GaAs薄膜における励起子状態制御に対する空間電場コヒーレンスの効果(25pPSA 領域5ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2011年03月03日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 66(1) (1), 750 - 750, 日本語25pPSA-19 GaAs/AlAs超格子における励起子非線形光学特性に対するミニバンド形成の効果(25pPSA 領域5ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(2) (2), 657 - 657, 日本語25aWQ-1 高密度多層積層量子ドットにおけるキャリア移動(25aWQ 量子井戸・超格子,領域4(半導体メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(2) (2), 658 - 658, 日本語25aWQ-4 GaAs/AlAs超格子における励起子非線形光学特性に対する励起子分子の寄与(25aWQ 量子井戸・超格子,領域4(半導体メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(2) (2), 667 - 667, 日本語26aWQ-2 強磁性薄膜GdNの強磁性共鳴による研究(26aWQ 磁性半導体・半導体スピン物性,領域4(半導体メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(2) (2), 699 - 699, 日本語24pRC-8 変調ドープGaAsにおける長寿命コヒーレントプラズモン(24pRC 超高速現象,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(2) (2), 731 - 731, 日本語25pPSB-31 GaAs薄膜における閉じ込め励起子状態の制御性(25pPSB 領域5ポスターセッション(光誘起相転移・励起子・非線形等),領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年03月01日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(1) (1), 806 - 806, 日本語23aPS-40 GaAs/AlAs超格子における励起子非線形応答の励起光強度依存性(23aPS 領域5ポスターセッション(光電子分光・光誘起相転移等),領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年03月01日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(1) (1), 715 - 715, 日本語21aHW-8 高密度多層積層量子ドットにおける励起子緩和ダイナミクス(21aHW 量子井戸・超格子・光応答,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2010年03月01日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 65(1) (1), 782 - 782, 日本語22pPSB-8 窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける発光スペクトルの反磁性シフト(22pPSB 領域5ポスターセッション(微粒子・ナノ結晶等),領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2009年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 64(2) (2), 651 - 651, 日本語27aPS-28 GaAs薄膜の励起子非線形光学応答制御における第一パルス光強度依存性(領域5ポスターセッション,領域5,光物性)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2009年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 64(2) (2), 657 - 657, 日本語27aPS-54 GaAs中の窒素等電子束縛励起子微細構造におけるポピュレーション(領域5ポスターセッション,領域5,光物性)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2009年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 64(2) (2), 593 - 593, 日本語26aXD-13 GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における励起子非線形光学応答制御(量子井戸・超格子・光応答,領域4,半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2008年08月25日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 63(2) (2), 660 - 660, 日本語22aPS-43 GaAs薄膜における超高速励起子密度制御(22aPS 領域5ポスターセッション,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2008年08月25日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 63(2) (2), 605 - 605, 日本語21aYK-11 CdTe/CdMnTe分数層超格子における異方的な磁気光学特性のMn組成分布依存性(21aYK 磁性半導体,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2008年08月25日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 63(2) (2), 648 - 648, 日本語21pYH-2 GaAs薄膜における励起子ポラリトン伝播効果の膜厚依存性(21pYH 非線型光学,領域5(光物性))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2008年02月29日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 63(1) (1), 738 - 738, 日本語26aPS-27 GaAs薄膜における複数準位励起下での閉じ込め励起子の過渡反射スペクトル(ポスターセッション,領域5,光物性)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2008年02月29日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 63(1) (1), 683 - 683, 日本語25pWJ-6 CdTe/CdMnTe分数層超格子における発光線幅の磁場依存性(量子井戸・超格子ほか,領域4,半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2007年08月21日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 62(2) (2), 688 - 688, 日本語22aTG-7 CdTe/CdMnTe分数層超格子における異方的なZeemanシフト(磁性半導体,領域4,半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2007年02月28日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 62(1) (1), 663 - 663, 日本語18pTA-11 II-VI族分数層超格子の近接場分光(量子井戸・超格子,領域4,半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2007年02月28日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 62(1) (1), 673 - 673, 日本語19pTA-6 CdTe/CdMnTe分数層超格子における磁気光学特性の面内異方性(磁性半導体,領域4,半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2006年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 61(2) (2), 528 - 528, 日本語23pXJ-4 CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線の近接場光学スペクトル(23pXJ 量子細線,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2006年08月18日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 61(2) (2), 544 - 544, 日本語25aXJ-12 CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線における電子状態の磁場依存性(25aXJ 磁性半導体,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2006年03月04日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 61(1) (1), 691 - 691, 日本語28pPSB-1 CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線における交換相互作用と電子状態の制御(28pPSB 領域4ポスターセッション,領域4(半導体,メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 2006年01月31日, 電気学会研究会資料. : The Papers of Technical Meeting on Electromagnetic Theory, IEE Japan. EMT, 電磁界理論研究会, 2006(1) (1), 157 - 160, 日本語InAs/GaAsコラムナ量子ドットの光学利得偏波特性 : 半導体光増幅器の実現に向けて
- InAs/GaAsコラムナ量子ドットの光学利得偏波特性 : 半導体光増幅器の実現に向けて(フォトニックNW・デバイス, フォトニック結晶・ファイバとその応用, 光集積回路, 光導波路素子, 光スイッチング, 導波路解析, 及び一般)コラムナ量子ドットの光学利得をVSL(Variable Stripe Length)法を用いて測定した。コラムナ量子ドットはStranski-Krastanow成長モードInAs島層を密接に積層し成長させた量子ドットである。この積層数を変化させることにより量子ドットのアスペクト比を制御することが出来る。われわれはコラムナ量子ドットの光学利得の積層数依存性について詳細に調べた。その結果、積層数が増加するにつれ、TMモードに高感度な利得特性を示すことが明らかになった。また、量子ドットの積層数7層でTE、TMのモードに対してほぼ等方的な利得特性を示すことを見出した。一般社団法人電子情報通信学会, 2006年01月26日, 電子情報通信学会技術研究報告. LQE, レーザ・量子エレクトロニクス, 105(593) (593), 35 - 38, 日本語
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2005年03月04日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 60(1) (1), 630 - 630, 日本語24aZC-4 磁場下CdTe/Cd_<0.75>Mn_<0.25>Te細線構造における価電子帯バンドミキシング(磁性半導体,領域4(半導体, メゾスコピック系・局在))
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2004年08月25日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 59(2) (2), 614 - 614, 日本語14aYC-3 CdTe/(Cd, Mn)Te 量子細線における励起子磁気ポーラロンの異方的なエネルギー緩和特性(磁性半導体, 領域 4)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2004年03月03日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 59(1) (1), 700 - 700, 日本語29pYF-12 CdTe/CdMnTeナノワイヤにおける磁気ポーラロン形成(半導体スピン物性)(領域4)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2004年03月03日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 59(1) (1), 700 - 700, 日本語29pYF-11 CdTe/(Cd,Mn)Teナノワイヤにおけるホールスピン配向の面内磁場異方性(半導体スピン物性)(領域4)
- 量子ドットの偏光制御とSOAへの応用In_xGa_<1-x>Asでキャップした自己形成InAs量子ドットの端面フォトルミネッセンス(PL)偏光特性を詳細に調べ、キャップ層のIn組成による偏光特性の変化を明らかにした。GaAsでキャップした量子ドットの端面発光はTE偏光成分が支配的であるが、キャップ層のIn組成xを増加させると、PLピーク波長が長波長側へシフトするとともに、x=0.13ではTM成分がTE成分より強くなることがわかった。また、量子ドット活性層中の光の伝播による偏光特性の変化を調べるため、励起波長を変えた端面PL測定を行うとともに、エレクトロルミネッセンス(EL)、PL偏光スペクトルの比較を行ったので結果を報告する。一般社団法人電子情報通信学会, 2003年12月11日, 電子情報通信学会技術研究報告. LQE, レーザ・量子エレクトロニクス, 103(526) (526), 5 - 8, 日本語
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2003年08月15日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 58(2) (2), 577 - 577, 日本語21aTH-3 微傾斜基板上の CdTe/CdMnTe 分数層超格子における交換相互作用の異方性と量子細線特性
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2002年08月13日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 57(2) (2), 586 - 586, 日本語8aSB-11 CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線の磁気光学特性(磁性半導体,領域4)
- 一般社団法人日本物理学会, 2002年08月13日, 日本物理学会講演概要集, 57(2) (2), 559 - 559, 日本語6pSA-15 CdTe/CdMgTe量子細線からの励起子発光(量子井戸・超格子,領域4,領域5合同,領域4)
- CdMgTe/CdTe量子細線における励起子状態微傾斜基板上に成長を行ったCdTe/Cd_<0.74>Mg_<0.26>Te量子細線からの励起子発光について調べた。時間分解分光システムを用いて量子細線に閉じ込められた1次元自由励起子発光を見い出すとともに発光寿命の温度依存性を測定し、CdTe/Cd_<0.74>Mg_<0.26>Te量子井戸に閉じ込められた2次元自由励起子発光寿命の温度依存性と比較をした。量子細線、量子井戸の自由励起子発光寿命は温度Tが増加するにともない長くなるが、お互い異なった温度依存性を示す。量子細線、量子井戸における自由励起子発光寿命の温度依存性はそれぞれ100T^<1/2>psK^<-1/2>及び11 TpsK^<-1>と表すことができるが、10K以下の温度ではT^<1/2>依存性から外れる傾向が見られた。この温度領域では自由励起子の発光の低エネルギー側に新たに発光線が確認された。この発光線は励起光強度を強くすることで顕著になることやPLスペクトルや時間分解PLスペクトルの解析から低エネルギー側の発光に起源について議論する。一般社団法人電子情報通信学会, 2001年10月04日, 電子情報通信学会技術研究報告. ED, 電子デバイス, 101(337) (337), 13 - 18, 日本語
- 2000年, COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS 1999, (166) (166), 239 - 242, 英語Initial stages of InAs-quantum dot formation studies by reflectance-difference spectroscopy and photoluminescence
- 1999年, COMPOUND SEMICONDUCTORS 1998, (162) (162), 457 - 462, 英語Self-organized process of InAs-quantum dots monitored by reflectance-difference spectroscopy
- 1997年12月, JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS, 82(11) (11), 5876 - 5876, 英語その他
- 1997年, Physical Review B, 55(7) (7), 4411 - 4416
- 1996年12月, PHYSICAL REVIEW B, 54(23) (23), 16714 - 16718, 英語
- 1996年04月, JOURNAL OF ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, 25(4) (4), 661 - 665, 英語Photocurrent anisotropy in compositional modulated superlattice of long-range ordered Ga0.5In0.5P
- 1996年, DIAMOND FILMS AND TECHNOLOGY, 6(3) (3), 139 - 145, 英語Transient cathodoluminescence spectroscopy of synthetic diamond films
- 1996年, Physical Review B, 53(23) (23), 15713 - 15718
- 1994年, SUPERLATTICES AND MICROSTRUCTURES, 15(2) (2), 137 - 140, 英語
- InGaAs/GaAs歪超格子における光学遷移の電界効果In_0.26>Ga_0.76>As(3nm), GaAs(10nm)歪超格子の光学遷移エネルギーの外部電界依存性を詳細に調べるため、エレクトロリフレクタンス・スペクトルの測定を行った。超格子に加わった電界はGaAsのFanz-Keldysh振動より精密に見積もった。観測された遷移エネルギーの電界発展特性は重い正孔、軽い正孔に対してそれぞれタイプI、タイプII型のバンド構造を反映したシュタルク階段遷移を示した。軽い正孔のシュタルク階段遷移は非線形に電界依存性し、この特性について伝達マトリックス法を用いた理論計算をもとに調べた結果、軽い正孔の第1量子準位と超格子における電子波のFabry-Perot効果により生じるポテンシャルバリア以上のエネルギーを持つ仮想準位との間の共鳴結合状態が原因であることが明らかになった。一般社団法人電子情報通信学会, 1993年11月19日, 電子情報通信学会技術研究報告. ED, 電子デバイス, 93(326) (326), 49 - 52, 日本語
- 神戸大学, 1992年03月, 神戸大学大学院自然科学研究科紀要. A, 10, 1 - 9, 英語ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF LONG-RANGE ORDERED Ga_<0.5>In_<0.5>P ALLOY SEMICONDUCTOR
- Springer, 2019年08月, 英語, ISBN: 9789811390890Energy conversion efficiency of solar cells
- コロナ社, 2012年10月, 日本語, ISBN: 9784339008425太陽電池のエネルギー変換効率
- その他, Quantum Dot Devices:Lecture Notes in Nanoscale Science and Technology, 2012年, 英語Quantum Dot Switches:Towards Nanoscale Power-Efficient All-Optical Signal Processing学術書
- 共著, コロナ社, 2011年09月, 日本語, ISBN: 9784339066210カーボンナノチューブ・グラフェンハンドブック学術書
- 単著, 株式会社エヌ・ティー・エス刊、第2編材料編・第2章ハードマテリアル・第3節「AlGaInP系半導体の自己組織化」執筆, 2009年11月, 日本語自己組織化ハンドブック学術書
- 共著, 材料編、第6章、6.3.1項「AlGaInP系赤色半導体の自己組織化」執筆, 1997年, 英語Atomic Ordering in Epitaxial Alloy Semiconductors:from the Discoveries to the Physical Understanding学術書
- 共著, サイエンスフォーラム, 1994年, 英語半導体計測評価事典学術書
- 単著, 大阪大学学位論文, 1991年02月, 英語Oriented Growth of Semiconductor Thin Films on Noncrystalline Substrates for Graphoepitaxy学術書
- 共著, INSPEC, London, 1989年, 英語Properties of Lithium Niobate学術書
- 第73回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2026年, 日本語ドリフト拡散モデルによるSiレーザーパワーコンバータの損失解析
- 第73回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 日本語中間バンド型熱放射発電素子の発電密度における再吸収過程の効果
- 36th International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference(PVSEC-36, 英語, Bangkok, タイ王国Photocurrent and Photovoltage Enhancement in Two-Step Photon Upconversion Solar Cells Based on CsPbBr3-xClx Nanocrystals with Embedded PbS Quantum Dots[招待有り]
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語InAs量子ドット成長に起因する格子不整合歪みによるGaAs層におけるAdove-Barrier状態の形成
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語In0.05Ga0.95As/GaAs多重量子井戸における非線形光学効果の発生
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語熱放射発電素子におけるバンドテイルの効果
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 英語Photophysical Properties of CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals Under Bichromatic Photoexcitation of Above-Bandgap and Sub-Bandgap Photons
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会PbS量子ドットを組み込んだCsPbBr3-xClxベースの2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会InGaAsレーザーパワーコンバータのエネルギー変換損失メカニズムの解析
- 第86回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 名城大学, 国内会議半導体光共振器中での電気光学効果を利用したテラヘルツ電界センサ:位相差信号の周波数依存性
- 53rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC 53), 2025年06月, 英語, Montreal, カナダPhotocurrent Enhancement in CsPbBr3-xClx-based Soler Cells with Embedded Pbs Quantum Dots[招待有り]
- 53rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC 53), 2025年06月, 英語, Montreal, カナダExcitation Power Dependence and Loss of Photonic Energy Conversion[招待有り]
- 53rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC 53), 2025年06月, 英語, Montreal, カナダEfficient Intraband Photoexcitation in Two-step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells Using Double-Tunnel Junction[招待有り]
- 53rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC 53), 英語, Montreal, カナダPhoton Partitioning by Band Filling in Intermediate-Band Thermoradiative Diodes”[招待有り]
- 第72回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 日本語半導体光共振器中での電気光学効果を利用したテラヘルツ電界センサ:結晶面方位の検討
- 第72回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 日本語InGaAs/GaAs多重量子井戸における励起子エネルギーに対する歪みの効果
- 第72回応用物理学会春季学術講演会半導体光共振器中での電気光学効果を利用したテラヘルツ電界センサ:位相差信号の共振器Q値依存性
- 第72回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 日本語ダブルトンネル接合を利用したアップコンバージョン太陽電池の効率的バンド内遷移
- 第72回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 日本語Siレーザーパワーコンバーターの分光評価
- 35th International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference(PVSEC-35), 英語, Shizuoka, 日本国Maximum Output Power Density by Photon Partitioning Optimization in Intermediate-Band Thermoradiative diodes
- 第43回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS43), 英語, NaraVoltage-Boost Effects Enhanced by Quantum Dots in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells
- 第85回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 新潟県, 日本国, 国内会議多重積層InAs/GaAs量子ドットを用いた光伝導アンテナの様々な励起光波長における光電流の励起光強度依存性
- 第85回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 新潟県, 国内会議InAs量子ドット成長に起因する格子不整合歪みを利用した差周波混合によるテラヘルツ電磁波発生
- 第85回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 新潟県, 日本国, 国内会議中間バンドを有する熱放射ダイオードの理論発電密度(Ⅱ)
- 第85回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 新潟県, 日本国, 国内会議Intraband Transitions Induced by Below-Bandgap Photoexcitation at CsPbBr₃/GaAs Heterointerface
- 第85回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 新潟県, 日本国, 国内会議MAPbI₃/Siヘテロ構造を利用した二段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池
- 第85回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 新潟県, 日本国, 国内会議2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池におけるバンド内赤外光学遷移の量子ドットによる増強特性
- 52th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC52), 英語Two-Step Photon Upconversion Solar Cells Based on CsPbBr3/GaAs Heterointerface
- 52th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC52), 英語Voltage Boost Effects in Solar Cells Utilizing Adiabatic Photon Up-Conversion with a Double Tunnel Junction
- 第71回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 日本語, 東京都市大学極性制御した2段階アップコンバージョン太陽電池におけるアップコンバージョン特性の変化
- 第71回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 英語, 東京都市大学Photon Up-Conversion in MAPbBr₃ Perovskite Deposited on GaAs
- 第71回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 東京都市大学中間バンドを有する熱放射ダイオードの理論発電密度
- 第34回光物性研究会, 英語Quantum-Dot-Free Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells Based on Cesium Lead(Ⅱ)Bromide/Gallinm Arsenide Inferface
- 第34回光物性研究会, 日本語局在表面プラズモン共鳴による高ドープInAs/GaAs量子ドットにおける赤外光吸収増強”
- 日本材料学会 2023年度 第3回半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会第2回研究会, 日本語, 立命館大学 朱雀キャンパスダブルトンネル接合を内包する半導体ヘテロ構造における断熱的フォトンアップコンバージョンによる太陽電池の出力電圧上昇効果
- 第42回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS42), 英語, THE KASHIHARAVoltage Boost Effects in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells with Double Tunnel Junctions
- 第42回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS42), 英語, THE KASHIHARAEnhanced Near-Infrared Absorption by Localized Surface Plasmon Resonence in Heavily-Doped InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots
- 第84回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 熊本城ホール ほか3会場, 日本国, 国内会議Influence of Substrates on Perovskite Deposited by Solution Process, a Step to Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells
- 第84回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 熊本城ホール ほか3会場, 日本国, 国内会議高ドープInAs/GaAs量子ドットにおける局在表面プラズモン共鳴による赤外光吸収増強
- 第84回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, 熊本城ホール ほか3会場, 日本国, 国内会議ダブルトンネル接合を利用したラチェット型アップコンバージョン太陽電池における電圧上昇効果
- 50th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC50), 2023年06月, 英語, プエルトリコ, 国際会議Up-Converted Carrier Dynamics in AlxGa₁-xAs/InAs-Based Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells with a Doubled-Heterointerface
- 50th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC50), 2023年06月, プエルトリコ, 国際会議Localized Surface Plasmon Pesonance of Quantum Dots in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cell Structures
- 第70回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 英語, ハイブリッド開催(上智大学&オンライン), 日本国Optimization of the Morphological Structure of Spin-Coated MAPbBr₃ on p-GaAs Substrates for Perovskite/GaAs-based Photon Up-conversion Solar Cells
- 日本材料学会 2022年度エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 日本語, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, オンライン開催, 日本国ドープされたInAs/GaAs量子ドットにおける局在表面プラズモン共鳴による電場増強効果
- 2022年度 第3回半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会 第2回研究会、2022年度第1回ナノ材料部門委員会第1回研究会, 2022年11月, 日本語, 京都大学, 日本国量子ドットを内包する半導体ヘテロナノ構造を利用した量子型赤外光検出素子の暗電流制御
- 33rd International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference(PVSEC-33), 英語, Nagoya, 国際会議Broadband Enhancement of Intraband Transition in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells with a Doubled-Heterointerface Strucure
- 第41回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS41), 2022年10月, 英語Thermal Activation Process at the Heterointerface in Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells Using hole Up-Conversion
- 第41回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS41), 2022年10月, 英語Intraband Transition in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells
- 8th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion(WCPEC-8), 英語, 国際会議High Absorptivity of Intraband Transition Occurring at Heterointerface in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells
- 第83回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語ダブルパルス-ポンプ-プローブ法によるGaAs/AlAs 多重量子井戸における超高速応答の評価
- 第83回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 英語, 東北大学&オンライン, 日本国, 国内会議Electrical Properties of AlGaAs/GaAs-Based Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells with Doubled Heterointerfaces
- 日本物理学会2022年秋季大会物性分野, 日本語“GaSb/AlGaSb多重量子井戸における障壁層励起による差周波混合過程に対する井戸幅依存性
- 9th International Symposium on Control of Semiconductor Interfaces(ISCSI-IX), 英語, 国際会議Photoluminescence Characteristics of InAs Quantum Dots in the Doubled-heterointerface of AlGaAs/GaAs-based Two-step Photon Up-conversion Solar Cells
- International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors(ICPS 2022), Sydney, 国際会議Differece on Infrared-Induced Response Between N-i-p and P-i-n Structures of Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solre Cells
- International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors(ICPS 2022), 英語, Sydney, 国際会議Intraband Absorptivity in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 第69回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2022年03月, 日本語正孔フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池の赤外光照射による光電流制御
- 第69回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2022年03月, 日本語2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池における ヘテロ界面のバンド内遷移の光吸収率
- (14th International Symposium on Advanced Plasma Science and its Applications for Nitrides and Nanomaterials / 15th International Conference on Plasma-Nano Technology & Science (ISPlasma2022 / IC-PLANTS2022),, 英語, Nagoya, 日本国, 国際会議Control of Quantum-Dot Growth for Novel Solar Cells[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 令和3年度 応用物理学会 多元系化合物・太陽電池研究会 年末講演会, 2021年12月, 日本語太陽電池のエネルギー変換効率と高効率化への道[招待有り]
- 第82回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語GaSb/AlGaSb多重量子井戸における障壁層励起での差周波混合法によるテラヘルツ電磁波発生
- 第82回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語正孔のアップコンバージョンを利用した2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池のバンド内遷移過程
- 第82回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 英語On the Simulation of Two-Step Photocurrent Generation in an InAs Quantum Dot -in-Well Intermediate Band Solar Cell
- 第82回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語エピタキシャル成長を利用した固体レーザー冷却用高品質Yb:Y-Al-O厚膜の作製
- 2021 International Conference on Solid State Devices, 2021年09月, 英語Control of Carrier Dynamics in Quantum Dots for Intermediate-Band Solar Cells[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 8th International Workshop Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures (SemiconNano2021), 英語, 国際会議Two-step up-conversion solar cells: recent progress and future direction[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 48th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 英語, Miami, 国際会議Collection of Photocarriers Varied by Effective Electron Intraband Excitation in an InAs Quantum Dot-in-Well Intermediate Band Solar Cell
- Compund Semiconductor Week(CSW)2021, 英語, Stockholm, 国際会議Lateral Photoconductivity of Multiple-Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Structure for Photoconductive Antenna Device
- 第68回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2021年03月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における差周波混合によるテラヘルツ電磁波発生の周波数依存性に対する励起子効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第68回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2021年03月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議光伝導アンテナ応用へ向けた多重積層InAs/GaAs量子ドットの光学特性評価口頭発表(一般)
- 第68回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2021年03月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議相分離したYb添加Y-Al-O透明薄膜における結晶相間エネルギー移動口頭発表(一般)
- 第68回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2021年03月, 英語Efficiency Compensation from Intraband Transitions of Opposite Carrier in a Quantum Dot-In-Well Intermediate Band Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 第68回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2021年03月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議変調ドープした二段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池における電圧上昇効果口頭発表(一般)
- SPIE Photonics West, 英語Laser Cooling Efficiency of Yb-doped Yttrium Aluminum Oxide Crystals[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- SPIE Photonics West, 英語Yb-doped Yttrium Aluminum Perovskite for Radiation Balanced Laser Application[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 応用物理学会関西支部 2020年度第1回+第2回合同講演会, 日本語, オンライン講演ウイルスと戦えるこれからの紫外光源[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第31回光物性研究会(2020), 2020年12月, 日本語, オンライン開催(Zoom), 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸間の励起子共鳴を利用した差周波混合によるテラヘルツ電磁波の増強口頭発表(一般)
- 第39回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS39), 2020年10月, 英語, オンライン開催Development of Mid-Infrared Photodetector Can Operate Under Room Temperature with High Sensitivity Using Intraband Transition
- 第39回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS39), 2020年10月, 英語, オンライン開催, 国内会議Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence Caused by Energy Transfer in Ytterbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum perovskite
- 第39回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS39), 2020年10月, 英語, オンライン開催, 国内会議Performance Analysis of an InAs/GaAs/Al0.3Ga0.7As Quantum Dot-in-Well Intermediate Band Solar Cell Under Two-Step Photoexcitations
- 第39回電子材料シンポジウム(EMS39), 2020年10月, 英語, オンライン開催, 国内会議Dramatic Enhancement of Current and Voltage in Modulation-Doped Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells
- 第81回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2020年09月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議正孔のアップコンバージョンを利用した2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池の追加赤外光による光電流減少メカニズム口頭発表(一般)
- 第81回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2020年09月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議Performance Degradation of Quantum Dot-in-Well Intermediate Band Solar Cell Under Intense Bi-Color Barrier and Intraband Photoexcitations口頭発表(一般)
- 第81回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2020年09月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議反射率変化で観測するGaAs/AlAs多重量子における重い正孔-軽い正孔励起子間相互作用に対する励起子の安定性の効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第81回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議変調ドープした二段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池における光励起効率の向上口頭発表(一般)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 2020年08月, 日本語, オンライン開催, 国内会議変調ドープによるフォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池の特性制御
- 47th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 英語, CalgaryUp-Converted Photocurrent Enhancement in Modulation-Doped Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 47th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 英語, Calgary, 国際会議Intensive-Light-Induced Backtracking Voltage Phenomenon: An Insight into Intermediate-Band Solar Cell Output Performance口頭発表(一般)
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)変調ドープした二段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池におけるアップコンバージョン電流増大
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における差周波混合によるテラヘルツ電磁波発生に対する励起子の重ね合わせ効果
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)Yb添加YAG-YAM共晶透明薄膜におけるAnti-Stokes PL過程と理想レーザー冷却効率
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)Voltage Backtracking Behavior in Intermediate-Band Solar Cell under Intensive Bi/Uni-Color Photoexcitation Examination
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)InAs量子ドットとAl0.3Ga0.7As/GaAsヘテロ界面を利用した赤外線検出器の受光感度特性
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池におけるバンド内遷移特性
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における連続波励起子共鳴励起による変調効果
- 第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 新型コロナウイルス感染拡大防止のため中止。 講演予稿集発行されたので、本講演会での発表は成立するものとする (第67回応用物理学会春季学術講演会HPより抜粋)多重積層InAs/GaAs量子ドットを用いた光伝導アンテナの作製
- SPIE Photonics West, 英語, San Francisco, 国際会議Enhancement of laser cooling efficiency in rare-earth-doped oxide at elevated high temperature[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国Control of Exciton Interference in GaAs/AlAs Multiple Quantum Wells口頭発表(一般)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国, 国際会議Excitation Energy Dependence of Hot-Carrier Extraction Process in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国, 国際会議Polarization-Insensitive Optical Gain of Highly stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Semiconductor Optical Amplifier口頭発表(一般)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国, 国際会議Effect of the accumulated Electron Density at the Hetero-Interface in Two-Step Photon-Up Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国Laser Cooling Utilizing Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence in Yb-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet口頭発表(一般)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国, 国際会議Extensively-Prolonged Electron Lifetime Within Room Temperature Upon InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot-in-Well Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 7th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 英語, Kobe, 日本国, 国際会議Infrared Photodetector Sensitized by QDs Inserted at the Hetero-Interface口頭発表(一般)
- 46th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2019年07月, 英語, Chicago, 国際会議Strong Voltage-Boost Effect in Two-Step Photon-Up Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 46th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2019年07月, 英語, Chicago, 国際会議Hot-Carrier Extraction in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 46th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2019年06月, 英語, Chicago, 国際会議Reciprocal Relationship Between Photoluminescence and Photocurrent in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- Compound Semiconductor Week2019, 2019年05月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議One-Dimensional Electronic States in Highly-Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices口頭発表(一般)
- Compound Semiconductor Week 2019, 2019年05月, 英語, Nara, Japan, 国際会議Extension of excitation energy to generate terahertz wave to smaller than GaAs bandgap energy due to growth of InAs quantum dots and nitrogen doped layer口頭発表(一般)
- Optics&Photonics International Congress 2019, 2019年04月, 英語, Yokohama, 国際会議Efficient Hot-Carrier Generation in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices口頭発表(一般)
- 第66回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2019年03月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子を用いたホットキャリア型太陽電池における開放電圧の向上口頭発表(一般)
- 2019年第66回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2019年03月, 日本語, 東京工業大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸の励起子ダイナミクスと二次の非線形光学効果との関係口頭発表(一般)
- 第66回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2019年03月, 日本語, 国内会議(Y:Yb)AGにおける高温でのanti-Stokes発光増強口頭発表(一般)
- 第37回電子材料シンポジウム, 2018年10月, 日本語, 国内会議Voltage boost effect in two-step photon up-conversion solar cell with partial absorptivityポスター発表
- 第37回電子材料シンポジウム, 2018年10月, 日本語, 国内会議Laser Cooling in Yb-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Compoundsポスター発表
- 20th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2018年09月, 英語, China, 国際会議“Effects of GaAs-Capping Temperature on The Emission Wavelength of InAs Quantum Dots Grown on Nitrogen-Doped GaAs(001)Surfaces口頭発表(一般)
- 35th European PV Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2018年09月, 英語, Belgium, 国際会議Optimal Band Gap Energies for Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells with Partial Absorptivity口頭発表(一般)
- 第79回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2018年09月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子太陽電池におけるホットキャリア電流取り出し特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第79回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2018年09月, 日本語, 名古屋国際会議場, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における第二次高調波発生口頭発表(一般)
- 第79回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2018年09月, 日本語, 国内会議2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池における理論変換効率の入射光スペクトル形状依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 平成30年度半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会第1回研究会, 2018年07月, 日本語, 奈良先端科学技術大学院大学, 国内会議多孔質炭素電極を用いた光化学電池の基礎特性口頭発表(一般)
- 平成30年度半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会第1回研究会, 2018年07月, 日本語, 奈良先端科学技術大学院大学, 国内会議Yb添加Fttrium-Aluminum化合物によるもの固体レーザー冷却口頭発表(一般)
- The 12th International Conference on Excitonic and Photonic Processes in Condensed Matter and Nano Materials, 2018年07月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議Optimization of Excitation Wavelengh in YAG:Yb for Laser cooling口頭発表(一般)
- The 12th International Conference on Excitonic and Photonic Processes in Condensed Matter and Nano Materials, 2018年07月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議Observation of electron transport in a silicon crystal using luminescence of cyanine molecule excited by energy transfer口頭発表(一般)
- 9th International Workshop on Bismuth-Containing Semiconductors, 2018年07月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Exciton Hopping Dynamics in GaAsBi口頭発表(一般)
- The 12th International Conference on Excitonic and Photonic Processes in Condensed Matter and Nano Materials, 2018年07月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議Effects of Modulation of Ultrafast Transient Carrier Dynamics by Interface on Terahertz Signal口頭発表(一般)
- 31st International Vacuum Nanoelectronics Conference, 2018年07月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Development of Mercury-Free Ultraviolet Light Emitting Devices[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 18th International Conference on Laser Optics, 2018年06月, 英語, St.Petersburg, Russia, 国際会議Generation of continuous terahertz wave with wide tunable range[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- The 7th edition of the World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, 2018年06月, 英語, Hawaii, 国際会議Carrier Collection Efficiency of Intraband-Excited Carriers in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 応用物理学会関西支部平成30年度第1回講演会, 2018年05月, 日本語, 神戸大学, 国内会議入射光スペクトル形状を考慮した2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池の理論変換効率ポスター発表
- Compound Semiconductor Week 2018, 2018年05月, 英語, Cambridge, MA, USA, 国際会議Multiple Stacking of Capping Temperature-Controlled InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots with AlGaAs Barrier Layers for Broadband Emission口頭発表(一般)
- 応用物理学会関西支部平成30年度第1回講演会, 2018年05月, 日本語, 神戸大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における重い正孔励起子励起下での差周波混合によるテラヘルツ電磁波の偏光特性ポスター発表
- International Conference on Nanophotonics and Nano-optoelectronics 2018, 2018年04月, 英語, Yokohama, 国際会議Polarization Dependent Photocurrent in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- International Conference on Nanophotonics and Nano-optoelectronics 2018, 2018年04月, 英語, Yokohama, 国際会議One-Dimensional Electronic States in Closely Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots with Different Growth Temperatures口頭発表(一般)
- International Conference on Nanophotonics and Nano-optoelectronics 2018, 2018年04月, 英語, Yokohama, 国際会議Extraction Efficiency of Up-Converted Electrons in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 第65回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2018年03月, 日本語, 国内会議吸収率を考慮した2段階フォトンアップコンバージョン太陽電池の理論変換効率口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物第65回応用物理学会春季学術講演会理学会 第72回年次大会, 2018年03月, 日本語, 早稲田大学, 国内会議エネルギー移動を利用したSi基板内部における電子拡散過程の観測口頭発表(一般)
- 第65回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2018年03月, 日本語, 国内会議YAG:Ybにおけるanti-Stokes発光の励起波長依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第65回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2018年03月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子を用いたホットキャリア型太陽電池動作実証口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物第65回応用物理学会春季学術講演会理学会 第72回年次大会, 2018年03月, 日本語, 早稲田大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸端面から放射されるテラヘルツ電磁波の偏光特性口頭発表(一般)
- 応用物理学会関西支部平成29年度第3回講演会, 2018年02月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子を用いたホットキャリア型太陽電池の動作評価ポスター発表
- SPIE Photonics West, 2018年01月, 英語, San Francisco, 国際会議Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cell: Propose and Demonstration[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第28回光物性研究会, 2017年12月, 日本語, 国内会議YAG:YbにおけるAnti-Stokes発光ポスター発表
- MTSA2017-OptoX Nano-TeraNano8, 2017年11月, 英語, Okayama, 国際会議Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- The 27th Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference, 2017年11月, 英語, Otsu, 国際会議Two-Step Photo-Excitated Electrons with Extremely-Long Lifetime in Intermedeate-band Solar Cells Using Dot-in Well Strucyure口頭発表(一般)
- The 27th Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference, 2017年11月, 英語, Otsu, 国際会議Two-Step Photn Up-Conversion Solar Cells Incorporating a Voltage Booster Hetero-Interface口頭発表(一般)
- The 27th Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference, 2017年11月, 英語, Otsu, 国際会議Infrared Absorption Characteristics in Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- The 27th Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference, 2017年11月, 英語, Otsu, 国際会議Efficient Two-Step Photocurrent in Intermediate Band Solar Cells Using Highly Homogeneous InAs/GaAs Quantum-Dot Superlattice口頭発表(一般)
- 第36回電子材料シンポジウム, 2017年11月, 日本語, 国内会議Anti-Stokes photoluminescence in Yb-doped yttrium aluminum garnetポスター発表
- International Symposium on Novel Energy Nanomaterials, Catalysts and Surfaces for Future Earth -Material Research, Characterization and Imaging by In situ/Operando XAFS and X-ray Techniques-, 2017年10月, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議One-Dimensional Miniband Formation in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Novel Energy Nanomaterials, Catalysts and Surfaces for Future Earth -Material Research, Characterization and Imaging by In situ/Operando XAFS and X-ray Techniques-, 2017年10月, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Laser-induced Hydrogen Production Using Porous Carbon口頭発表(一般)
- 第78回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2017年09月, 日本語, 国内会議低温キャップInAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子中間バンド型太陽電池における熱脱出の抑制口頭発表(一般)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成29年度第1回研究会, 2017年09月, 日本語, 国内会議低温キャップInAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子中間バンド型太陽電池における2段階光吸収の増強口頭発表(一般)
- 33rd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2017年09月, 英語, Netherlands, 国際会議Photon Up-Converted Photocurrent in a Single Junction Solar Cell with a Hetero-Interface口頭発表(一般)
- 33rd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2017年09月, 英語, Netherlands, 国際会議Increasing Photovoltage Boosted by Photon Up-Conversion in a Single-Junction Solar Cell with a Hetero-Interface口頭発表(一般)
- 第78回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2017年09月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子太陽電池におけるバンド内遷移の偏光特性口頭発表(一般)
- Nanophotonics and Micro/Nano Optics International Conference 2017, 2017年09月, 英語, Barcelona, Spain, 国際会議Generation of continuous terahertz wave by differential-frequency-mixing in a GaAs/AlAs multiple quantum well口頭発表(一般)
- 33rd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2017年09月, 英語, Netherlands, 国際会議Extended Optical Response of Two-Step Photoexcitation in InAs/GaAs Quantum-Dot Superlattice Intermediate Band Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- SemiconNano 2017: 6th International Workshop Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 2017年09月, 英語, Milano, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics in Photon Up-Conversion Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 29th International Conference on Defects in Semiconductors, 2017年07月, 英語, Matsue, 国際会議Stokes and Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence in Nitrogen ð-Doped Layer in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 2017 IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2017年06月, 英語, Washington D.C., 国際会議Increasing Current Generation by Photon Up-Conversion in a Single-Junction Solar Cell with a Hetero-Interface口頭発表(一般)
- 応用物理学会関西支部平成29年度第1回講演会, 2017年05月, 日本語, 国内会議レーザー冷却に向けたYbドープ酸化物の作製ポスター発表
- Compound Semiconductor Week 2017, 2017年05月, 英語, Berlin, 国際会議Broadband Control of Polarization Characteristics in Closely-Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- 2017 MRS Spring Meeting and Exhibit, 2017年04月, 英語, Arizona, 国際会議Control of Carrier Dynamics and Efficient Two-Step Photon Up-Conversion in Quantum-Dot Intermediate-Band Solar Cells[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第64回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2017年03月, 日本語, パシフィコ横浜, 国内会議InAs量子ドット周辺の歪み制御によるGaAs表面からのテラヘルツ電磁波発生波長の長波長化口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2017年03月, 日本語, 国内会議GaAs中のエピタキシャル窒素膜における反ストークス発光口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会 第72回年次大会, 2017年03月, 日本語, 大阪大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における波形制御パルスによる量子ビート生成III口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会 第72回年次大会, 2017年03月, 日本語, 大阪大学, 国内会議Effects of exciton oscillator strength on terahertz generation due to differential-wave-mixing in GaAs/AlAs multiple quantum wells口頭発表(一般)
- 第27回光物性研究会, 2016年12月, 日本語, 神戸大学, 国内会議Si基板からシアニン分子薄膜へのエネルギー移動による発光に対するキャリア拡散の効果ポスター発表
- 第27回光物性研究会, 2016年12月, 日本語, 国内会議GaAs中のデルタドーピング窒化層を利用した光によるフォノン制御ポスター発表
- 第27回光物性研究会, 2016年12月, 日本語, 神戸大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における励起子励起条件下での差周波混合によるテラヘルツ電磁波の高効率発生ポスター発表
- Asian Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2016, 2016年10月, 英語, Sapporo, 国際会議Variation of Terahertz Wave Characteristics Due to Covering InAs Quantum Dots by Nitrogen Atoms口頭発表(一般)
- Asian Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2016, 2016年10月, 英語, Sapporo, 国際会議Photo-Emission of Cyanine Molecule Thin Films on Si Substrate Due to Inorganic-Organic Energy Transfer口頭発表(一般)
- 第77回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2016年09月, 日本語, 朱鷺メッセ, 国内会議テラヘルツ電磁波発生による量子ドット周辺の歪みの変化の観測口頭発表(一般)
- Energy, Materials, and Nanotechnology Meeting on Epitaxy, 2016年09月, 英語, 国際会議Two-dimensional delocalized electronic states of epitaxial N d-doped layer in GaAs[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- HEMP 2016: Hot Electrons and Solar Energy, 2016年09月, 英語, 国際会議Nanosecond-scale hot-carrier cooling dynamics in one-dimensional InAs/GaAs quantum dot superlattices[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第77回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2016年09月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット中間バンド型太陽電池における電子の熱脱出過程の解明口頭発表(一般)
- 19th International Conference on Molecular-Beam Epitaxy, 2016年09月, 英語, Montpellier, 国際会議Control In-Ga Intermixing in InAs Quantum Dot on Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- HEMP 2016: Hot Electrons and Solar Energy, 2016年09月, 英語, London, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics in InAs Quantum Dot Solar Cell for Photon Ratchet[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 33rd International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2016年08月, 英語, Beijing, 国際会議Spatial Electronic Structure of an Isovalent Nitrogen Center in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 第35回電子材料シンポジウム, 2016年07月, 日本語, 国内会議Thermal carrier-escape process from the intermediate band in InAs/GaAs quantum dot solar cellsポスター発表
- UK Semiconductors 2016, 2016年07月, 英語, Sheffield, 国際会議Polarization-Insensitive Intraband Transition in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices口頭発表(一般)
- 2016 Compound Semiconductor Week, 2016年06月, 英語, Toyama, 国際会議Two-Dimensional Energy Dispersion in Thermally Annealed Epitaxial Nitrogen Atomic Sheet in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 2016 Compound Semiconductor Week, 2016年06月, 英語, Toyama, 国際会議Polarization Anisotropy of Electroluminescence and Net-Modal Gain in Highly Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum-Dot Laser Devices口頭発表(一般)
- 2016 Compound Semiconductor Week, 2016年06月, 英語, Toyama, 国際会議GaAs First-Spacer-Layer Thickness Dependence of Polarized Photoluminescence Properties of Closely-Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots with Long-Wavelength Emission口頭発表(一般)
- 32nd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2016年06月, 英語, Munich, 国際会議Extended Electron Lifetime in Intermediate-Band Solar Cells Using Dot-in-Well Structure口頭発表(一般)
- 32nd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2016年06月, 英語, Munich, 国際会議Enhancement of Two-Step Photon Absorption Due to Miniband Formation in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 第63回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2016年03月, 日本語, 国内会議急速熱アニールしたGaAs中のエピタキシャル窒素膜の輻射再結合寿命口頭発表(一般)
- 17th International Conference on Physics of Light-Matter Coupling in Nanostructures, 2016年03月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議Time-Resolved Photoluminescence of Thermally-Annealed Nitrogen Atomic Sheet in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 17th International Conference on Physics of Light-Matter Coupling in Nanostructures, 2016年03月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議Polarized Photoluminescence Properties of Closely-Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots with Long-Wavelength Emission口頭発表(一般)
- 第63回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2016年03月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子太陽電池におけるミニバンド形成が2段階光吸収に与える影響口頭発表(一般)
- 17th International Conference on Physics of Light-Matter Coupling in Nanostructures, 2016年03月, 英語, Nara, 国際会議Extremely Long Carrier Lifetime Due to Electron-Hole Separation in Quantum-Dot Intermediate-Band Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- SPIE Photonics West, 2016年02月, 英語, San Francisco, 国際会議Effective Drift Mobility Approximation in Multiple Quantum-Well Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成27年度第1回研究会, 2015年11月, 日本語, 国内会議ポリマー薄膜中のコロイドPbS量子ドットにおけるパリティ選択則の緩和口頭発表(一般)
- 2nd International Conference on Enhanced Spectroscopies, 2015年10月, 英語, Messina, 国際会議Decrease in Photoluminescence Decay Rate in InAs Quantum Dots Coupling with In Nanoparticles Due to Increase in Excitation Power口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2015年秋季大会, 2015年09月, 日本語, 国内会議ポリマー膜中のPbSコロイド量子ドットにおける磁気光学応答のヒステリシス特性ポスター発表
- EU PVSEC 2015, 2015年09月, 英語, Hamburg, 国際会議NGCPV: a New Generation of Concentrator Photovoltaic Cells, Modules and Systems (a Final Review)口頭発表(一般)
- 第76回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2015年09月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子を利用したホットキャリア型太陽電池口頭発表(一般)
- 第76回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2015年09月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子におけるホットキャリア冷却過程口頭発表(一般)
- 5th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 2015年09月, 英語, Taiwan, 国際会議Growth and Characterization of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices for Photovoltaics[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 5th International Workshop on Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 2015年09月, 英語, Taiwan, 国際会議Epitaxial Nitrogen Atomic Sheet in GaAs Grown by Nitorogen δ-Doping Technique[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- High-efficiency materials for photovoltaics, 2015年09月, 英語, London, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics in InA s /GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices for Photovoltaics[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成27年度第1回研究会, 2015年07月, 日本語, 国内会議急速熱アニールによるGaAs中のエピタキシャル窒素シートにおける2次元物性の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 21st International Conference on Electronic Properties of Two-Dimensional Systems/17th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2015年07月, 英語, Sendai, 国際会議Relaxation of Parity Selection Rules in Colloidal PbS Quantum Dots Embedded in Polymer Films口頭発表(一般)
- 34th Electronic Materials Symposium, 2015年07月, 日本語, 国内会議Hot-Carrier Distribution in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices and Its Application to Solar Cellsポスター発表
- 21st International Conference on Electronic Properties of Two-Dimensional Systems/17th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2015年07月, 英語, Sendai, 国際会議Exciation of Cyanine Dye Thin Film Via Energy Transfer from a Si Substrate口頭発表(一般)
- 21st International Conference on Electronic Properties of Two-Dimensional Systems/17th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2015年07月, 英語, Sendai, 国際会議Enhancement of Two Dimensionality in Epitaxial Nitrogen Atomic Sheet in GaAs by Rapid Thermal Annealing口頭発表(一般)
- 21st International Conference on Electronic Properties of Two-Dimensional Systems/17th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2015年07月, 英語, Sendai, 国際会議Effects of Homogeneous and Inhomogeneous Broadenings of Excitons on Amplitude of Exciton Quantum Beats口頭発表(一般)
- 21st International Conference on Electronic Properties of Two-Dimensional Systems/17th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2015年07月, 英語, Sendai, 国際会議Broadband Control of Emission Wavelength of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots by Growth Temperature GaAs Capping Layer口頭発表(一般)
- 34th Electronic Materials Symposium, 2015年07月, 日本語, 国内会議Annealing effects on the delocalized electronic states of epitaxial two-dimensional nitrogen atomic sheet in GaAsポスター発表
- 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2015年06月, 英語, New Orleans, 国際会議Ultrafast Photocarrier Transport Dynamics in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2015年06月, 英語, New Orleans, 国際会議Two-Step Photocarrier Generation in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattice Intermediate Band Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2015年06月, 英語, New Orleans, 国際会議Time-Resolved Photoluminescence of MBE-Grown leV GaAsSbN for Multi-Junction Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2015年06月, 英語, New Orleans, 国際会議Saturable Two-Step Photocurrent Generation in Intermediate-Band Solar Cells Including InAs Quantum Dots Embedded in Al0.3Ga0.7As/GaAs Quantum Wells口頭発表(一般)
- 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2015年06月, 英語, New Orleans, 国際会議Comparison of Electron and Hole Mobilities in Multiple Quantum Well Solar Cells Using a Time-of-Flight Technique口頭発表(一般)
- 11th International Conference on Excitonic and Photonic Processes in Condensed Matter and Nano Materials, Montreal, 2015年05月, 英語, Montreal, 国際会議Hot-Carrier Cooling Dynamics in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2015年03月, 日本語, 東海大学, 国内会議半導体量子井戸における励起子量子ビートのポンプ光エネルギー依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第62回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2015年03月, 日本語, 国内会議ポリマー薄膜中のコロイドPbS量子ドットにおける励起緩和過程の偏光異方性口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2015年03月, 日本語, 東海大学, 国内会議シアニン色素薄膜におけるエネルギー移動による励起子緩和時間の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第70回年次大会(2015年), 2015年03月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット超格子におけるホットキャリアダイナミクス口頭発表(一般)
- 第62回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2015年03月, 日本語, 国内会議GaAs中のエピタキシャル二次元窒素膜におけるアニール効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第24回光物性研究会, 2014年12月, 日本語, 国内会議ポリマー薄膜中のコロイドPbS量子ドットにおける励起緩和過程の偏光異方性ポスター発表
- 第25回光物性研究会, 2014年12月, 日本語, 神戸大学, 国内会議Layer-by-Layer法によるシアニン色素積層薄膜の作製と励起子緩和特性の評価口頭発表(一般)
- 第24回光物性研究会, 2014年12月, 日本語, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット太陽電池におけるキャリア脱出の影響ポスター発表
- 第24回光物性研究会, 2014年12月, 日本語, 国内会議GaAs中のエピタキシャル2次元窒素シート非局在電子状態の発光ダイナミクスポスター発表
- 第25回光物性研究会, 2014年12月, 日本語, 神戸大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸におけるダブルパルス法による励起子量子ビート制御口頭発表(一般)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成26年度第2回研究会, 2014年11月, 日本語, 国内会議低次元量子構造を利用したホットキャリア型太陽電池の提案口頭発表(一般)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会平成26年度第2回研究会, 2014年11月, 日本語, 国内会議ポリマー中に埋め込まれたPbSコロイド量子ドットにおける磁気発光強度のヒステリシス特性口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, Kobe University, 国際会議Ultrafast Optical Switch Based on Quantum Beat Oscillation in GaAs/AlAs Multiple Quantum Well[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, 国際会議Two-dimensional electronic states of epitaxial nitrogen atomic sheet in GaAs[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 6th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, 2014年11月, 英語, Kyoto International Conference Center, 国際会議Suppression of Thermal Carrier Escape and Efficient Photo-Carrier Generation by Two-Step Photon Absorption in Intermediate-Band Solar Cells Using a Dot-in-Well Structure口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, Kobe University, 国際会議Photoluminescence Decay Dynamics in Epitaxial Two-Dimensional Nitrogen Atomic Sheet in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, Kobe University, 国際会議Modulation of Photoluminescence Properties of InAs Quantum Dots on Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- WCPEC-6, 2014年11月, 英語, Kyoto International Conference Center, 国際会議Hot Carrier Intermediate Band Solar Cell Using Low-Dimensioned Quantum Structures口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, Kobe University, 国際会議Growth and Characterization of Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots for Photovoltaics[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, Kobe University, 国際会議Fabrication and Characterization of Cyanine Dye Thin Films Grown by a Layer-by -Layer Method口頭発表(一般)
- WCPEC-6, 2014年11月, 英語, Kyoto International Conference Center, 国際会議Efficient Two-Step Photon Absorption in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Recent Progress of Photonic Devices and Materials, 2014年11月, 英語, Kobe University, 国際会議Control of Electronic States Colloidal PbS Quantum Dots Embedded in Polymer Films口頭発表(一般)
- 6th Szeged International Workshop on Advances in Nanoscience 2014, 2014年10月, 英語, Hotel Forrás, Szeged, 国内会議Thermal enhancement of exciton quantum beat in a GaAs/AlAs multiple quantum well口頭発表(一般)
- Eleventh International Conference on Flow Dynamics, 2014年10月, 英語, Sendai, 国際会議Photoluminescence Properties of InAs Quantum Dots on Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2014年09月, 日本語, 国内会議低次元量子構造を利用したホットキャリア中間バンド型太陽電池口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2014年09月, 日本語, 北海道大学, 国内会議光スイッチ応用へ向けたシアニン色素薄膜の作製口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会秋季学術講演会, 2014年09月, 日本語, 北海道大学, 国内会議ダブルパルス-ポンプ-プローブ法による高温下での励起子量子ビートの観測口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2014年09月, 日本語, 国内会議GaAs中のエピタキシャル二次元窒素膜の電子状態 (II)口頭発表(一般)
- 第75回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2014年09月, 日本語, 国内会議GaAs中のエピタキシャル二次元窒素膜における発光ダイナミクス口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会 2014年秋季大会, 2014年09月, 日本語, 中部大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs 多重量子井戸におけるアップコンバージョン発光口頭発表(一般)
- 32nd International Conference on Physics of Semiconductors, 2014年08月, 英語, 国際会議Two-dimensional electronic states of epitaxial nitrogen atomic sheet in GaAs grown by nitrogen delta-doping technique口頭発表(一般)
- UK Semiconductors 2014, 2014年07月, 英語, Sheffield Hallam University, 国際会議Low-Power Pulse Modulation Based on Exciton Quantum Beat in a GaAs/AlAs Multiple Quantum Wellポスター発表
- 33rd Electronic Materials Symposium, 2014年07月, 日本語, 国内会議Enhancement of interaction among nitrogen pair centers in epitaxial two-dimensional nitrogen atomic sheet in GaAsポスター発表
- HEMP 2014, 2014年07月, 英語, Imperial College London, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics and Two-Step Photon Absorption in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Intermediate Band Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 40th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2014年06月, 英語, 国際会議Carrier Time-of-Flight Measurement Using a Probe Structure for Direct Evaluation of Carrier Transport in Quantum Structure Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 8th International Conference on Quantum Dots, 2014年05月, 英語, Pisa, 国際会議Structural Modification of InAs Quantum Dots Grown on Nitrided GaAs(001)Surfaceポスター発表
- 第61回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2014年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川, 国内会議窒素δドープGaAs(001)層上のInAs量子ドット自己形成口頭発表(一般)
- 第61回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2014年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドット太陽電池の量子準位を介した2段階光吸収口頭発表(一般)
- 第61回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2014年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川, 国内会議InAs/AlxGa1-xAs量子ドットにおけるキャリアの熱活性特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第61回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2014年03月, 日本語, 青山学院大学, 国内会議GaAs中のエピタキシャル二次元窒素膜の電子状態口頭発表(一般)
- EMN Fall Meeting, 2013年12月, 英語, Orland, Florida, USA, 国際会議Intraband Carrier Dynamics in Self-Assembled Quantum Dots for Infrared Optical Devices[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第23回光物性研究会, 2013年12月, 日本語, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドットにおけるbound-to-continuum型サブバンド間遷移の吸収係数ポスター発表
- 第23回光物性研究会, 2013年12月, 日本語, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議GaAs中におけるエピタキシャル2次元窒素膜の磁気発光特性ポスター発表
- 10th International Conference on Flow Dynamics, 2013年11月, 英語, Sendai International Center, 国際会議Fabrication of InAs Quantum Dots on Nitrided GaAs (001) Surface口頭発表(一般)
- EU PVSEC 2013, 2013年10月, 英語, Paris, 国際会議NGCPV: A New Generation of Concentrator Photovoltaic Cells, Modules and Systems口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2013年秋季大会, 2013年09月, 日本語, 徳島大学, 国内会議積層方向を制御した InAs/GaAs量子ドットの発光偏光特性ポスター発表
- 2013 JSAP-MRS Joint Symposia, 2013年09月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Large Optical Spin-Splitting in the GdN Electronic States口頭発表(一般)
- NSF Workshop on US-Japan Frontiers in Novel Photonic-Magnetic Devices, 2013年09月, 英語, Kasugano-so, Nara, 国際会議Gd Doping in AIN and Bright Ultraviolet Light Emission[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- The 12th European Conference on Molecular Electronics, 2013年09月, 英語, London, UK, 国際会議Fabrication and characterization of bilayer thin films of cyanine dyes by a layer-by-layer method towards realization of ultrafast response device with high repetition rateポスター発表
- 2013 JSAP-MRS Joint Symposia, 2013年09月, 英語, Doshisya University, 国際会議Electron Localization in GaAs:N Grown by Using δ-Doping Technique口頭発表(一般)
- 2013 JSAP-MRS Joint Symposia, 2013年09月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Effects of Built-in Electric Field on External Quantum Efficiency of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Interdimediate Band Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 2013 JSAP-MRS Joint Symposia, 2013年09月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Bright Ultraviolet Light Emitting Devices Using AlGdN[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- Collaborative Conference on Materials Research (CCMR) 2013, 2013年06月, 英語, Jeju island, South Korea, 国際会議Optical Characteristics of Quantum Dot Ensembles Grown by Using the Strain Compensation Technique[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- The 40th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2013年05月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Radiative Recombination Properties in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- The 40th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2013年05月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Polarization Controlled Emisson from Closely Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- ISCS2013, 2013年05月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Energy Relaxation of Photoexcited Electrons in Direct Si-Doped InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- ISCS2013, 2013年05月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Effect of State Filling on Intraband Carrier Dynamics in InAs/GaAs quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- ISCS2013, 2013年05月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Anisoropic Intraband Relaxation in a Multistacked Quantum Dot Ensembleポスター発表
- 第60回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2013年03月, 日本語, 神奈川工科大学, 国内会議歪み補償多層積層量子ドットにおける光学利得の面内異方性口頭発表(一般)
- 第60回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2013年03月, 日本語, 神奈川工科大学, 国内会議窒素を高濃度デルタドープしたGaAsの磁気光学特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第60回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2013年03月, 日本語, 神奈川工科大学, 国内会議斜め積層InAs/GaAs量子ドットの端面発光特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第60回応用物理学会春季学術講演会, 2013年03月, 日本語, 神奈川工科大学, 国内会議Si直接ドーピングInAs/GaAs量子ドットのキャリア緩和過程口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第68回年次大会, 2013年03月, 日本語, 広島大学, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における励起子量子ビートによる光パルス強度変調口頭発表(一般)
- SPIE Photonics West 2013, 2013年02月, 英語, California, United States, 国際会議Intraband Carrier Dynamics in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots Studied by Two-Color Excitation Spectroscopy口頭発表(一般)
- 第23回光物性研究会, 2012年12月, 日本語, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議窒素デルタドーピングによるGaAs電子状態の制御ポスター発表
- 4th International Workshop on Quantum Nanostructure Solar Cells/8th Seminar on Quantum Nanostructure Materials, 2012年12月, 英語, Kobe Ubiversity, 国際会議Intermediate-Band Solar Cells using InGaAs/InP Superlattices[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 4th International Workshop on Quantum Nanostructure Solar Cells, 8th Seminar on Quantum Nanostructure Materials, 2012年12月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices and Optical Responses[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第23回光物性研究会, 2012年12月, 日本語, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議In0.53Ga0.47As/InP超格子における2段階光吸収を利用した中間バンド型太陽電池ポスター発表
- Sixth International Meeting on Molecular Electronics, 2012年12月, 英語, Grenoble, France, 国際会議Control of energy transfer rate towards ultrafast response due to changing number ratio of energy donor-acceptor cyanine dye molecules口頭発表(一般)
- 平成24年度第1回半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会研究会, 2012年09月, 日本語, 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 和歌山, 国内会議量子ドット光アンプの利得スペクトル測定口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2012年秋季大会, 2012年09月, 日本語, 横浜国立大学, 国内会議光共振器構造中のInAs/GaAs量子ドットにおけるサブバンド間遷移ダイナミクス口頭発表(一般)
- 第73回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2012年09月, 日本語, 愛媛大学・松山大学, 国内会議光共振器構造中のInAs/GaAs量子ドットにおける2段階光吸収の増強口頭発表(一般)
- 第73回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2012年09月, 日本語, 愛媛大学・松山大学, 国内会議SiダイレクトドーピングによるInAs量子ドットのフェルミ準位の変化口頭発表(一般)
- The17th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2012年09月, 英語, MBE, Nara, 国際会議Miniband Formation in Closely-Stacked InAs GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- 第73回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2012年09月, 日本語, 愛媛大学・松山大学, 国内会議InフラックスによるInAs/GaAs量子ドットの積層方向の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第73回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2012年09月, 日本語, 愛媛大学・松山大学, 国内会議InAs供給量を制御した近接積層InAs/GaAs量子ドットの発光特性口頭発表(一般)
- The17th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2012年09月, 英語, MBE, Nara, 国際会議Effects of Excess Electrons on Recombination Lifetime in Directly Si-doped InAs GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- European Optical Society Annual Meeting 2012, 2012年09月, 英語, Aberdeen, UK, 国際会議Effect of fifth nonlinear polarization on exciton Rabi oscillation in GaAs/AlxGa1-xAs double heterostructure thin films口頭発表(一般)
- The17th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2012年09月, 英語, MBE, Nara, 国際会議Control of Stacking Direction of InAs GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- Photon12 IOP's premier conference in optics and photonics, 2012年09月, 英語, Durham, UK, 国際会議Control of response of exciton polariton confined in GaAs thin films by controlling pump and probe pulsesポスター発表
- The17th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2012年09月, 英語, MBE, Nara, 国際会議Control of Electronic Structure of GaAs Using Nitrogen δ-doping Technique口頭発表(一般)
- High-efficiency materials for photovoltaics, 2012年09月, 英語, London, UK, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics of Electrons in Intermediate States of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第2回光科学異分野横断萌芽研究会, 2012年08月, 日本語, 岡崎コンファレンスセンター, 国内会議GaAs中の配列制御された窒素ペアに束縛された励起子の光物性口頭発表(一般)
- UK Semiconductors, 2012年07月, 英語, Sheffield, UK, 国際会議Ultrafast photonic Mach-Zehnder switch using quantum dot vertical cavity structures口頭発表(一般)
- The 10th International Conference on Excitonic Processes in Condensed Mattsr, Nanostructured and Molecular Materials, 2012年07月, 英語, EXCON, Groningen, Netherlands, 国際会議Tuning Optical and Ferromagnetic Properties of GdN Thin Films by Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers口頭発表(一般)
- The 10th International Conference on Excitonic Processes in Condensed Mattsr, Nanostructured and Molecular Materials, 2012年07月, 英語, EXCON, Groningen, Netherlands, 国際会議Strong Electron-Hole Correlation in Bound Exciton in Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- The Nineteenth International Workshop on Active-Matrix Flatpanel Displays and Devices, 2012年07月, 英語, JSAP, Kyoto, 国際会議Physical Properties of Amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O Films Deposited Under Various Sputtering Pressure口頭発表(一般)
- The 10th International Conference on Excitonic Processes in Condensed Mattsr, Nanostructured and Molecular Materials, 2012年07月, 英語, Groningen, Netherlands, 国際会議Intraband Optical Response in InAsGaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- The 10th International Conference on Excitonic Processes in Condensed Mattsr, Nanostructured and Molecular Materials, 2012年07月, 英語, EXCON, Groningen, Netherlands, 国際会議Excitation Effects of Confined Exciton Polariton on Pulse Shape Propagating in GaAs Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 31st International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2012年07月, 英語, ICPS, Zurich, Switzerland, 国際会議Evaluation of Minority and Majority Spin Band Energies of Ferromagnetic GdN Thin Films Using Optical Absorption Spectroscopy口頭発表(一般)
- 31nd International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2012年07月, 英語, ETH, Zurich, Switzerland, 国際会議Determination of Magnetic Anisotropies in GdN Thin Film by Ferromagnetic Resonance口頭発表(一般)
- 31nd International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2012年07月, 英語, ETH, Zurich, Swiss, 国際会議Delocalization of Exciton States in InAs GaAs Quantum Dot Superlattices口頭発表(一般)
- 31st Electronic Materials Symposium, 2012年07月, 日本語, ラフォーレ修善寺, 国内会議Delocalization of electronic states formed by nitrogen pairs in GaAsポスター発表
- International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, 2012年06月, 英語, ICOOPMA, Nara, 国際会議High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography Using Broadband Light Sources with Strain-Controlled InAs GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, 2012年06月, 英語, ICOOPMA, Nara, 国際会議Extremely Uniform Excitonic States in Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAs[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, 2012年06月, 英語, ICOOPMA, Nara, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics in Multiple Stacked Quantum Dots Under Spacer Layer Excitation Conditions口頭発表(一般)
- 38th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, 2012年06月, 英語, IEEE, Austin, United States of America, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics in Intermediate States of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots Embedded in Photonic Cavity Structure[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 2012 MRS Spring Meeting and Exhibit,, 2012年04月, 英語, Materials Research Society, SanFrancisco, United States of America, 国際会議Analysis of Spin Splitting in Ferromagnetic GdN Epitaxial Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第67回年次大会, 2012年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 西宮市, 国内会議歪み補償多層積層量子ドットにおける非共鳴励起キャリアダイナミクスポスター発表
- 第59回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2012年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 東京都, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける束縛励起子発光線幅の温度依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第59回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2012年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 新宿区, 国内会議近接積層InAs/GaAs量子ドットの光物性口頭発表(一般)
- 第59回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2012年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 新宿区, 国内会議GaAsエピタキシャル界面への窒素のデルタドーピングと高均一発光特性口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第22回光物性研究会, 2011年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 熊本市, 国内会議半導体中の励起子非線形光学応答のコヒーレント制御ポスター発表
- 第22回光物性研究会, 2011年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 熊本市, 国内会議積層InAs量子ドットにおける光学利得の異方性ポスター発表
- Workshop on Innovation and Pioneering Technology 2011, 2011年12月, 英語, WINPTech組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Switching characteristics of exciton response in GaAs thin filmsポスター発表
- 21st International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference PVSECPVSEC-21, 2011年12月, 英語, Fukuoka, 国際会議Suppression of Nonradiative Recombination Process in Directly Si-Doped InAs Quantum Dotsポスター発表
- 第22回光物性研究会, 2011年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 熊本市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における励起子応答の光スイッチング特性ポスター発表
- 第22回光物性研究会, 2011年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 熊本市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子における励起子-格子相互作用ポスター発表
- 第22回光物性研究会, 2011年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 熊本市, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs超格子における励起子超高速応答ポスター発表
- Workshop on Innovation and Pioneering Technology 2011, 2011年12月, 英語, WINPTech組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Effects of fifth-order nonlinear polarization on optical control of excitonic states confined in GaAs thin films by using Rabi oscillationポスター発表
- The 18th International Display Workshops, 2011年12月, 英語, Nagoya, 国際会議Effects of Argon Plasma Irradiation on Amorphous In-Ga-Zu-Ofilm Evaluated by Microwave Photoconductivity Decay Method[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 21st International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference PVSECPVSEC-21, 2011年12月, 英語, Fukuoka, 国際会議Effect of Spacer Layer Thickness on Optical Properties of Multi-Stacked InGaAs Quantum Dot Grown on GaAs(311)B Substrate口頭発表(一般)
- Workshop on Innovation and Pioneering Technology 2011, 2011年12月, 英語, WINPTech組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Effect of control of number ratio of energy donor-acceptor cyanine dye molecules in thin films on Förster energy transferポスター発表
- 8th International Conference on Flow Dynamics, 2011年11月, 英語, ICFD organizing committee, 仙台市, 国際会議Optical Properties of Quantum Dot Superlatticesポスター発表
- 15th International Conference on Thin Films,2011, 2011年11月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Magneto-Optical Effect in GaN Epitaxial Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 21st International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference PVSECPVSEC-21, 2011年11月, 英語, Fukuoka, 国際会議Effects of Absorption Balance in Intermediate Band Quantum Dots Solar Cellsポスター発表
- 15th International Conference on Thin Films,2011, 2011年11月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Correlation Between Local Atomic Structure and Ultra Violet Luminescence of AlGdN Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 平成23年度第1回半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会研究会, 2011年10月, 日本語, 材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 神戸市, 国内会議光共振器を有する中間バンド型太陽電池の光吸収増強効果口頭発表(一般)
- 平成23年度第1回半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会研究会, 2011年10月, 日本語, 材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会, 神戸市, 国内会議近接積層量子ドット成長を利用した偏波無依存光応答の実現口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2011年秋季大会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議歪み補償多層積層量子ドットにおける非共鳴励起緩和過程ポスター発表
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議不純物制御したInAs量子ドットにおける発光再結合ダイナミックス口頭発表(一般)
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける束縛励起子発光線の起源口頭発表(一般)
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議多層積層高密度量子ドットにおける光学利得口頭発表(一般)
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議近接積層に伴う量子ドットのフォトルミネッセンス偏光特性口頭発表(一般)
- Epitaxial Growth and Fundamental Properties of Semiconductor Nanostructures, 2011年09月, 英語, Austria, 国際会議Photoluminescence Polarization Anisotropy in Closely Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- 12th International Conference on Optics of Excitons in Confined Systems, 2011年09月, 英語, OECS組織委員会, Paris, 国際会議Photoluminescence Dynamics of Spacer Layer Carriers in Multi Stacked Quantum Dotsポスター発表
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議Layer-by-Layer法による交互吸着シアニン色素薄膜の作製口頭発表(一般)
- 12th International Conference on Optics of Excitons in Confined Systems, 2011年09月, 英語, OECS組織委員会, Paris, France, 国際会議Interaction of quantized exciton polaritons with nonresonant pump pulse in GaAs thin flimsポスター発表
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜中の光電場に対する局所場の効果ポスター発表
- 日本物理学会2011年秋季大会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における励起子状態の光制御に対する入射光エネルギー依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2011年秋季大会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子分子の磁気光学特性ポスター発表
- 第72回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 山形市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子のフォノンサイドバンド発光口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2011年秋季大会, 2011年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議GaAs nipi超格子におけるコヒーレントプラズモン振動のドーピング濃度依存性ポスター発表
- 2011 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials, 2011年09月, 英語, SSDN組織委員会, Aichi, 国際会議Effect of Capping Layer Growth on Bound Exciton Luminescence in Nitrogen δ-Doped GaAsポスター発表
- High-Efficiency Materials for Photovoltaics, Imperial College London, 2011年08月, 英語, London, 国際会議Carrier Dynamics in Quantum Dot Superlattices[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 37th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, 2011年07月, 英語, Seattle, 国際会議Two-Photons Transition in Intermediate Band Solar Cells口頭発表(一般)
- 第30回電子材料シンポジウム, 2011年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員, 大津市, 国内会議In-plane optical anisotropy in stacked InAs quantum dots with interconnected electron statesポスター発表
- 第30回電子材料シンポジウム, 2011年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員, 大津市, 国内会議Electronic states in multiply stacked InAs/GaAs quantum dots studied by polarized photoluminescence spectroscopyポスター発表
- 第30回電子材料シンポジウム, 2011年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員, 大津市, 国内会議Capping layer dependence of bound exciton luminescence in nitrogen delta-doped GaAsポスター発表
- 23rd International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2011年05月, 英語, Germany, 国際会議Optical Phase Shifter Using Quantum Dots in a Vertical Cavity口頭発表(一般)
- 38th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2011年05月, 英語, ISCS組織委員会, Germany, 国際会議Near-Field Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of CdTe/Cd0.75Mn0.25Te Tilted Superlatticesポスター発表
- 38th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2011年05月, 英語, ISCS組織委員会, Berling, Germany, 国際会議Diamagnetic shift of exciton bound to the nitrogen pairs in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 2011 MRS Spring Meeting and Exhibit, 2011年04月, 英語, SanFrancisco, 国際会議Ultraviolet Light Emitting Devices Using AlGdN[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議非共鳴励起下における励起子ポラリトンと光電場の結合口頭発表(一般)
- 第60回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける束縛励起子発光線のキャップ層成長条件依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第58回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける束縛励起子発光線のキャップ層成長条件依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第66回年次大会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 新潟市, 国内会議多層積層量子ドット励起子とスペーサー層キャリアとの相関口頭発表(一般)
- 第58回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議多層積層量子ドットにおける偏光特性の励起光強度依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第58回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議重心運動閉じ込め励起子の量子ビートの生成と検出口頭発表(一般)
- 第58回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議近接多層積層量子ドットのフォトルミネッセンス偏光特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第58回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議シアニン色素薄膜におけるエネルギー移動の飽和のメカニズム口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第66回年次大会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 新潟市, 国内会議GaAs 薄膜における励起子状態制御に対する空間電場コヒーレンスポスター発表
- 「ナノ構造・物性」第3回研究会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 神戸大学自然科学系融合研究環ナノエンジニアリング研究チーム, ナノ学会ナノ構造・物性部会, 神戸市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子の輻射再結合寿命口頭発表(一般)
- 第59回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議GaAs 中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子の磁気光学特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第58回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 厚木市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素ペアに束縛された励起子の磁気光学特性口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第66回年次大会, 2011年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 新潟市, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs超格子における励起子非線形光学特性に対するミニバンド形成の効果ポスター発表
- 日本表面科学会第67回表面科学研究会<In-situモニタリングの視点からみた表面制御・評価技術~現状と課題~, 2011年02月, 日本語, 東京都, 国内会議自己形成量子ドット成長過程のその場観察と新規光デバイスの作製[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議歪み補償積層量子ドットの光学異方性ポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議変調ドープGaAsにおけるコヒーレントプラズモンのドーピング濃度依存性ポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける励起子微細構造の反磁性シフトポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議積層超高密度量子ドットにおけるキャリアダイナミクスポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議検出パルス制御によるGaAs薄膜中の閉じ込め励起子の超高速応答ポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 大阪市, 国内会議希土類化合物半導体GdNにおけるバンド端光吸収の磁気光学特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議シアニン色素薄膜におけるエネルギー移動に対するドナー‐アクセプタ分子数比の効果ポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議GaSb/AlGaSb多重量子井戸構造における発光特性ポスター発表
- 第21回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員, 大阪市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における閉じ込め励起子状態の光制御ポスター発表
- 第22回光物性研究会, 2010年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素等電子トラップ束縛励起子の発光ダイナミクスポスター発表
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics Technology 2010, 2010年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Effect of spectral width of probe pulses on response of excitons confined in GaAs thin filmsポスター発表
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics Technology 2010, 2010年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Biexcitonic contribution to nonlinear optical response of excitons in GaAs/AlAs superlatticesポスター発表
- 日本材料学会平成22年度第2回半導体エレクトロニクス部門研究会, 2010年11月, 日本語, 日本材料学会, 堺市, 国内会議量子ドットの多層積層化に伴う偏光異方性の発現と制御口頭発表(一般)
- 平成22年度東北大学電気通信研究所共同プロジェクト研究会, 2010年11月, 日本語, 宮城県, 国内会議自己形成量子ドットの精密な成長制御と3次元構造化[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 日本材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス研究部門平成22年度第2回研究会, 2010年11月, 日本語, 大阪府, 国内会議AIGdN結晶薄膜を利用したナローバンド深紫外発光デバイスの開発と基礎特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第6回量子ナノ材料セミナー, 2010年10月, 日本語, 茨城県, 国内会議量子ドット超格子によるキャリアダイナミックス制御[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- The 6th International Workshop on Nano-scale Spectroscopy and Nanotechnology, 2010年10月, 英語, NSS organizing committee, 神戸市, 国際会議In-Plane Polarization Anisotropy in Vertically Stacked InAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議量子ドット太陽電池における吸収係数の理論的解析口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2010年秋季大会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 堺市, 国内会議変調ドープGaAsにおける長寿命コヒーレントプラズモン口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議多層積層量子ドットにおける高次励起子準位励起効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議積層量子ドットにおける偏光特性に対する電子的結合効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 長崎市, 国内会議深紫外光源用Gd添加AIN薄膜の構造と発光強度の関係”口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2010年秋季大会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 堺市, 国内会議高密度多層積層量子ドットにおけるキャリア移動口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 長崎市, 国内会議希土類窒化物半導体GdNの強磁性相転移に伴うバンド端構造変化口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 長崎市, 国内会議プラズマチューブアレイを用いたフィルム型水銀フリー深紫外光源口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議シアニン色素薄膜におけるエネルギー移動の高効率化口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 長崎市, 国内会議Siを直接ドープしたInAs量子ドットにおける発光増強機構口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 長崎市, 国内会議Siダイレクトドーピングをした積層量子ドットの中間バンド型太陽電池への応用口頭発表(一般)
- 2010年秋季第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議III-V半導体中不純物制御と励起子物性口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 日本物理学会2010年秋季大会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 堺市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における閉じ込め励起子状態の制御性ポスター発表
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 長崎市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜におけるレーザースペクトル幅制御による励起子応答制御口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2010年秋季大会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 堺市, 国内会議GaAsAlAs超格子における励起子非線形光学応答特性に対する励起子分子の寄与口頭発表(一般)
- 第71回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2010年09月, 日本語, 長崎市, 国内会議AINバッファー層導入による深紫外蛍光体AIGdNの発光強度向上口頭発表(一般)
- The 30th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2010年07月, 英語, ICPS organizing committee, Seoul, Korea, 国際会議Magneto-Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of Exciton Fine Structure in Nitrogen d-Doped GaAsポスター発表
- 第29回電子材料シンポジウム, 2010年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員, 伊豆, 国内会議Long-lived oscillation due to coherent plasmons in a modulation doped GaAsポスター発表
- 9th International Conference on, 2010年07月, 英語, EXCON組織委員会, Brisbane, Australia, 国際会議Intraband relaxation process in highly stacked quantum dotsポスター発表
- 9th International Conference on, 2010年07月, 英語, EXCON組織委員会, Brisbane, Australia, 国際会議Excitation power dependence of nonlinear optical response of excitons in GaAs/AlAs superlatticesポスター発表
- The 9th International Conference on Excitonic and Photonic Processes in Condensed and Nano Materials, 2010年07月, 英語, EXCON organizing committee, Brisbane, Australia, 国際会議Bound Biexciton Luminescence in Nitrogen d-Doped GaAsポスター発表
- 35th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, 2010年06月, 英語, Waikiki, Hawaii, 国際会議Multi-Stacked InAs/GaNAs Quantum dots with Direct Si Doping for use in Intermediate Band Solar Cell口頭発表(一般)
- 35th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, 2010年06月, 英語, PVSC組織委員会, Honolulu, USA, 国際会議Intraband relaxation of photoexcited carriers in multiple stacked quantum dots and quantum dot chainsポスター発表
- The 37th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2010年06月, 英語, 応用物理学会, 高松市, 国際会議Interaction between Conduction-Band Edge and Nitrogen-Related Localized Levels in Nitrogen d-Doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 37th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2010年06月, 英語, ISCS組織委員会, 高松市, 国際会議Interaction between conduction-band edge and Nitrogen-related localized levels in Nitrogen d-doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 35th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, 2010年06月, 英語, PVSC組織委員会, Honolulu, USA, 国際会議Energy band structure design for quantum-dot, intermediate-band solar cellsポスター発表
- 22nd International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2010年06月, 英語, IPRM組織委員会, 高松市, 国際会議All-optical switch using InAs quantum dots in a vertical cavity口頭発表(一般)
- 22rd International Conference on Indium Phoshide and Related Materials, 2010年05月, 英語, ISCS組織委員会, Kagawa, 国際会議Propagation Velocity of Excitonic Polaritons Confined in GaAs Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 22rd International Conference on Indium Phoshide and Related Materials, 2010年05月, 英語, Kagawa, 国際会議Optical and Ferromagnetic Properties of GdN Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 37th International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2010年05月, 英語, ISCS組織委員会, 高松市, 国際会議Energy band structure and half-filled condition in the quantum-dots intermediate band solar cells口頭発表(一般)
- The International Conference on Nanophotonics 2010, 2010年05月, 英語, ICNP organizing committee, つくば市, 国際会議Emission properties of excitons strongly localized to nitrogen pairs in GaAs[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 22rd International Conference on Indium Phoshide and Related Materials, 2010年05月, 英語, Kagawa, 国際会議Control of Polarization Properties of Electroluminescence from Vertically-Stacked InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots for 1.3 μm-band Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers口頭発表(一般)
- 22rd International Conference on Indium Phoshide and Related Materials, 2010年05月, 英語, Kagawa, 国際会議Broadband Light Source Using InAs Quantum Dots With InGaAs Strain-Reducing Layers口頭発表(一般)
- Quantum Dot 2010, 2010年04月, 英語, Nottingham, 国際会議Direct Impurity Doping into InAs Quantum dots by Utilizing self-assembling Growth Steps口頭発表(一般)
- 第57回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 平塚市, 国内会議中間バンド型量子ドット太陽電池のエネルギー変換効率に及ぼすバンド構造の影響口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第65回年次大会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 岡山市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける発光スペクトルの反磁性シフトポスター発表
- 第57回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 平塚市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAs における電子状態の磁場依存性ポスター発表
- 第57回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 平塚市, 国内会議積層量子ドットにおける光励起キャリアの緩和ダイナミクスポスター発表
- 第57回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 平塚市, 国内会議垂直共振器型量子ドット全光スイッチにおける2 段階飽和口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第65回年次大会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 岡山市, 国内会議高密度多層積層量子ドットにおける励起子緩和ダイナミクス口頭発表(一般)
- 第57回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 平塚市, 国内会議シアニン色素添加ポリマー薄膜におけるエネルギー移動特性の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第57回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 平塚市, 国内会議GaAsN 量子井戸からInAs 量子ドットへのキャリアトンネリング特性ポスター発表
- 日本物理学会第65回年次大会, 2010年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 岡山市, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs超格子における励起子非線形応答の励起光強度依存性ポスター発表
- SPIE Photonics West, 2010年01月, 英語, San Francisco, 国際会議Vertically-Stacked InAs Quantum Dots for Polarization-Independent Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers口頭発表(一般)
- Photonic West 2010, 2010年01月, 英語, SPIE, San Francisco, 国際会議Vertically-stacked InAs quantum dots for polarization-independent semiconductor optical amplifiersポスター発表
- SPIE Photonics West, 2010年01月, 英語, San Francisco, 国際会議Vertical-Geometry All-Optical Switches Based on InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots in a Cavity口頭発表(一般)
- Photonic West 2010, 2010年01月, 英語, SPIE, San Francisco, 国際会議Vertical-geometry all-optical switches based on InAs/GaAs quantum dots in a cavityポスター発表
- Abst. Symposium on Surface and Nano Science 2010, 2010年01月, 英語, Shizukuishi, 国際会議Exciton Fine Structures of Ordered Nitrogen Pairs in GaAs Fabricated by Using Reconstructed Surface[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第20回光物性研究会, 2009年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議歪み補償積層InAs量子ドットにおける面内励起子移動のバンド内緩和過程への効果ポスター発表
- 第20回光物性研究会, 2009年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議シアニン色素添加ポリマー薄膜におけるエネルギー移動特性に対するスペクトル重なりの効果ポスター発表
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Temperature dependent carrier tunneling in self-assembled InGaAs quantum dots with a dilute nitride quantum-well injectorポスター発表
- Abstr. Workshop on Information, Nano, and Photonics Technology 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Optical Nonlinearity of InAs Quantum Dots within a Vertical Cavity Structure for All-Optical Switching Devices口頭発表(一般)
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Optical nonlinearity of InAs quantum dots within a vertical cavity structure for all-optical switching devicesポスター発表
- 第20回光物性研究会, 2009年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における閉じ込め励起子の双極子モーメントポスター発表
- 第20回光物性研究会, 2009年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素等電子束縛励起子における励起子ダイナミクスポスター発表
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Energy band structure for intermediate band solar cellsポスター発表
- Abstr. Workshop on Information, Nano, and Photonics Technology 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Energy band structure for intermediate band solar cells口頭発表(一般)
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Effects of in-plain exciton transfer on intraband relaxation process in stacked InAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- Abstr. Workshop on Information, Nano, and Photonics Technology 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Effects of In-Plain Exciton Transfer on Intraband Relaxation Process in Stacked InAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Effective dipole moments of excitons in GaAs thin filmsポスター発表
- Workshop on Information, Nano and Photonics 2009, 2009年12月, 英語, WINPTECH組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Direct impurity doping into self-assembled InAs/GaAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- International Symposium on Quantum Nanophotonics and Nanoelectronics, 2009年11月, 英語, ISQNN組織委員会, 東京都, 国内会議Thermal effects on exciton dynamics in quantum dot chains口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium for Phosphor Materials 2009 (Phosphor Safari ), 2009年11月, 英語, Niigata, 国際会議Narrowband Ultraviolet Light Emitting Devices Using Rare-Earth Ions[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議量子ドット埋め込み面型非対称共振器を用いた超高速全光スイッチ口頭発表(一般)
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議量子ドット埋め込み面型共振器光スイッチにおけるサブバンド間緩和の効果ポスター発表
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAsにおける束縛励起子分子発光口頭発表(一般)
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議シアニン色素薄膜におけるフェルスター型エネルギー移動による励起子緩和特性の制御ポスター発表
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議SiダイレクトドーピングしたInAs量子ドットにおけるキャリア補償効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議InAs/GaAs量子ドットの積層構造による端面発光の偏波制御口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2009年秋季大会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 熊本市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜の励起子非線形光学応答制御における第一パルス光強度依存性ポスター発表
- 日本物理学会2009年秋季大会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 熊本市, 国内会議GaAs中の窒素等電子束縛励起子微細構造におけるポピュレーションポスター発表
- 第70回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 富山市, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における励起子非線形光学特性の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2009年秋季大会, 2009年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 熊本市, 国内会議GaAs/AlAs多重量子井戸における励起子非線形光学応答の増強口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. SemiconNano2009, 2009年08月, 英語, Anan, 国際会議Exciton Polarization Splitting of Nitrogen Pairs in GaAs[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 16th International Conference on Electron Dynamics in Semiconductors, Optoelectronics and Nanostructures, 2009年08月, 英語, EDISON組織委員会, Montpellier, 国際会議Enhancement of optical nonlinearity by spatially expanded excitons in GaAs/AlAs multiple quantum wells口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2009年07月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Spatial Coherence Effect on Transient Response of Confined Excitons in GaAs Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor structures, 2009年07月, 英語, MSS組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Spatial coherence effect on transient response of confined excitons in GaAs thin filmsポスター発表
- Abstr. 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2009年07月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Resonant Enhancement of Excitonic Photoluminescence via Biexciton Process in Stacked InAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor structures, 2009年07月, 英語, MSS組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Resonant enhancement of excitonic photoluminescence via biexciton process in stacked InAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor structures, 2009年07月, 英語, MSS組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Polarization controlled emission from stacked InAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- Abstr. 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2009年07月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Polarization controlled emission from electronically coupled stacked InAs quantum dots口頭発表(一般)
- 第28回電子材料シンポジウム, 2009年07月, 日本語, 電子材料シンポジウム運営委員会, 大津市, 国内会議Multiband optical absorption in stacked InAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- 第28回電子材料シンポジウム, 2009年07月, 日本語, 電子材料シンポジウム運営委員会, 大津市, 国内会議Magnetic-field control of the exciton fine polarization splitting of nitrogen pair centers in GaAsポスター発表
- 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor structures, 2009年07月, 英語, MSS組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議Magnetic-field control of exciton fine structure splitting in nitrogen -doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2009年07月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Magnetic-Field Control of Exciton Fine Structure Splitting in Nitrogen Delta-Doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. Internationa Symposium on Carbon Nanotube Nanoelectronics, 2009年07月, 英語, Matsushima, 国際会議Field Emission Characteristics of Carbon Nanofiber Nanocomposites口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2009年07月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議All-Optical Switching Using InAs GaAs Quantum Dots within a Vertical Cavity Structure口頭発表(一般)
- 14th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor structures, 2009年07月, 英語, MSS組織委員会, 神戸市, 国際会議All-optical switching using InAs/GaAs quantum dots within a vertical cavity structureポスター発表
- 第56回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2009年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, つくば市, 国内会議量子ドット埋め込み面型共振器構造を用いた超高速全光スイッチ口頭発表(一般)
- 第56回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2009年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, つくば市, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAs における等電子束縛励起子微細構造の磁場制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第56回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2009年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, つくば市, 国内会議高密度積層量子ドットにおける発光増強機構口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 20th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2009年03月, 英語, Newport Beach, 国際会議Quantum Dots in a Vertical Cavity for All-Optical Switching Devices口頭発表(一般)
- 第56回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2009年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, つくば市, 国内会議InAs 量子ドットの積層構造制御と発光特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第56回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2009年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, つくば市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における励起子過渡応答に対する空間コヒーレンス効果口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 15th International Symposium on Intercalation Compounds, 2009年03月, 英語, Beijing, 国際会議Control of Exciton Fine Structure of Nitrogen Nanospace in GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 2009International conference on solid State Devices and Materials, 2009年, 英語, miyagi, 国際会議Quantum Dots in a Vertical Cavity for All‐Optical Switching Devices口頭発表(一般)
- ナノ学会ナノ構造・物性部会 第1回研究会, 2009年01月, 日本語, ナノ学会, 神戸市, 国内会議超高速全光スイッチに向けた励起子光学非線形応答制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第19回光物性研究会, 2008年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議積層超高密度量子ドットの発光特性に対する3次元的結合効果ポスター発表
- 第19回光物性研究会, 2008年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議シアニン色素添加ポリマー薄膜における励起子緩和時間の制御ポスター発表
- Abstr. 8th International Conference on Nano-Molecular Electronics 2008, 2008年12月, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Side Electron Emission Device Using A Composite of Carbon Nanofibers and Aluminumポスター発表
- Abstr. The IUMRS International Conference in Asia, 2008年12月, 英語, Nagoya, 国際会議Narrowband ultraviolet field-emission device using Gd-doped AlN[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- 第19回光物性研究会, 2008年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議GaAs 薄膜における励起子ポラリトン伝播効果ポスター発表
- 第69回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2008年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 春日井市, 国内会議積層量子ドットにおける励起子発光強度に対する電子間結合効果口頭発表(一般)
- 第69回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2008年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 春日井市, 国内会議原子層窒素ドーピングによるInAs 量子ドットからのIn 偏析制御ポスター発表
- 第69回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2008年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 春日井市, 国内会議原子層窒化InAs 量子ドットにおける励起子緩和時間の制御ポスター発表
- 日本物理学会2008年秋季大会, 2008年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 盛岡市, 国内会議GaAs 薄膜における励起子ポラリトン伝播効果の膜厚依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第69回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2008年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 春日井市, 国内会議GaAs 薄膜における閉じ込め励起子の密度制御口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2008年秋季大会, 2008年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 盛岡市, 国内会議GaAs 薄膜における超高速励起子密度制御ポスター発表
- Abstr. 15th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2008年08月, 英語, Vancouver, 国際会議Selective Impurity Doping into InAs Quantum Dots by Controlling the Self-Assembled Process口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 15th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2008年08月, 英語, Vancouver, 国際会議Influence of Indium Segregation on Optical Properties in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- 15th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2008年08月, 英語, MBE国際会議組織委員会, Vancouver, 国際会議Influence of indium segregation on optical properties in InAs/GaAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- Abstr. Third International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic Materials and Applications, 2008年07月, 英語, Edmonton, 国際会議Transient Response in Negative Time Delay due to Pulse Propagation in GaAs Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- Third International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, 2008年07月, 英語, ICOOPMA組織委員会, Edmonton, 国際会議Transient reflectivity response with negative time delay caused by femtosecond pulse propagation in GaAs thin filmsポスター発表
- 第27回電子材料シンポジウム, 2008年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員会, 伊豆長岡, 国際会議Propagation effect on transient response of excitons confined in GaAs thin filmsポスター発表
- Third International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, 2008年07月, 英語, ICOOPMA組織委員会, Edmonton, 国際会議Lengthening of photoluminescence decay time owing to expansion of electron envelope functions in stacked quantum dotsポスター発表
- Abstr. Third International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic Materials and Applications,, 2008年07月, 英語, Edmonton, 国際会議Lengthening of Exciton Lifetime owing to Expansion of Electron Envelope Functions in Stacked Quantum Dotsポスター発表
- 第27回電子材料シンポジウム, 2008年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員会, 伊豆長岡, 国際会議Growth and characterization of double-stacked InAs self-assembled quantum dots for polarization control of edge emissionポスター発表
- Abstr. The 15th International Conference on Luminescence and Optical Spectroscopy of Condenced Matter, 2008年07月, 英語, Lyon, 国際会議Fine structure of bound excitons in nitrogen-doped GaAs口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. Third International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic Materials and Applications, 2008年07月, 英語, Edmonton, 国際会議Exciton Response Controlled by Introducing a Spacer Layer in Nitrided InAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- Third International Conference on Optical, Optoelectronic and Photonic Materials and Applications, 2008年07月, 英語, ICOOPMA組織委員会, Edmonton, 国際会議Exciton response controlled by introducing a spacer layer in nitrided InAs quantum dotsポスター発表
- Abstr. Carbon, 2008年07月, 英語, Nagano, 国際会議Bright flexible field emission display device using Carbon nanofiber nanosomposites口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. The 15th International Conference on Luminescence and Optical Spectroscopy of Condenced Matter, 2008年07月, 英語, Lyon, 国際会議Anisotropic Linear Polarization Luminescence in CdTe/CdMnTe Quantum Wires口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 8th International Conference on Excitonic Process in Condensed Matter, 2008年06月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Optical Control of Residual Excitons for Ultrafast Nonlinear Response in GaAs Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- 8th International Conference on Excitonic Processes in Condensed Matter, 2008年06月, 英語, EXCON組織委員会, 京都市, 国際会議Optical control of residual excitons for ultrafast nonlinear response in GaAs thin films口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 8th International Conference on Excitonic Process in Condensed Matter, 2008年06月, 英語, Kyoto,, 国際会議Near-Field Photoluminescence of Exciton Magnetic Polarons in CdTe/Cd0.75Mn0.25Te Quantum Wires口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 20th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2008年05月, 英語, Paris, 国際会議Exciton Fine Structure of Nitrogen Isoelectronic Center口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. International Conference on Physics of Light-Matter Coupling in Nanostructures, 2008年04月, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Tailor-Made Optical Properties of InAs Quantum Dots by Controlling Indium Segregation口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 3rd International Laser, Light-Wave and Microwave Conference, 2008年04月, 英語, Yokohama, 国際会議Optical Cancellation of Exciton Population in GaAs Thin Films口頭発表(一般)
- Third International Laser, Light-Wave and Microwave Conference, 2008年04月, 英語, ILLMC組織委員会, 横浜市, 国際会議Optical cancellation of exciton population in GaAs thin films口頭発表(一般)
- 第55回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2008年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 船橋市, 国内会議端面発光偏波制御を目指したInAs 量子ドット積層構造の作製口頭発表(一般)
- 第55回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2008年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 船橋市, 国内会議積層量子ドットにおける励起子振動子強度の温度依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第55回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2008年03月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 船橋市, 国内会議GaAs薄膜における閉じ込め励起子の超高速非線形応答の励起光強度依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第63回年次大会, 2008年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 東大阪市, 国内会議GaAs 薄膜における複数準位励起下での閉じ込め励起子の過渡反射スペクトルポスター発表
- 第18回光物性研究会, 2007年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会組織委員会, 大阪市, 国内会議スペクトル分解反射型ポンプ・プローブ法によるGaAs薄膜中閉じ込め励起子の過渡応答測定ポスター発表
- MRS Fall Meeting, 2007年11月, 英語, Boston, 国際会議A Specimen Preparation Technique for 3D Charactreization of Nano Materials at Specific-Site Using FIB-STEM/TEM System口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2007年10月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Three-Dimensional Structure of A Single InAs/GaAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dot Observed by Electron Tomography口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2007年10月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Exciton Fine Sructure of Isoelectronic Centers in Nitrogen Doped GaAsポスター発表
- International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors, 2007年10月, 英語, Kyoto, 国際会議Anisotropic Zeeman Effect in CdTe/CdMnTe Quantum Wiresポスター発表
- 6th Internaltiona Symposium on Atomic Level Characterizations for New Materials and Devices, 2007年10月, 英語, Kanazawa, 国際会議3D Characterization of A Single InAs Quantm Dotポスター発表
- 第68回応用物理学会学術講演会, 2007年09月, 日本語, 日本応用物理学会, 札幌市, 国内会議液滴エピタキシー法による自己形成InGaAs口頭発表(一般)
- 2007 Japan-Germany Nanophotonics Seminar, 2007年09月, 英語, Yonago, 国際会議Control of Optical Polarization in Quantum Dots[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- International Conference on II-VI Compounds, 2007年09月, 英語, Jeju, 国際会議Anisotropic Magnetic-Field Evolution of Radiative Recombination Lifetime in CdTe/CdMnTe Quantum Wires口頭発表(一般)
- 第26回電子材料シンポジウム 論文集、pp. 157-158 G4, 2007年07月, 日本語, EMS組織委員会, 大津市, 国内会議Optical Emission and Dynamics from Coupled States in Stacked Quantum Dotsポスター発表
- 16th International Conference on Dynamical Processes in Excited States of Solids, 2007年06月, 英語, DPC組織委員会, Segovia, Spain, 国際会議Photoluminescence dynamics of coupled quantum dotsポスター発表
- Proc. 19th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2007年05月, 英語, Matsue, 国際会議Real Time Probing of Self-Assembling Process Steps in InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Growthポスター発表
- 19th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2007年05月, 英語, Matsue, 国際会議Multidirectional Transmission Electron Microscope Observation of a Single InAs/GaAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dot口頭発表(一般)
- 19th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2007年05月, 英語, IPRM組織委員会, Matsue, Japan, 国際会議Control of Optical Emission from Coupled Excitonic States in Quantum Dot Superlattice Structuresポスター発表
- 第54回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2007年03月, 日本語, 青山学院大学, 国内会議結合量子ドットの発光ダイナミクス口頭発表(一般)
- International Workshop on Nitride Semiconductors 2006, 2006年10月, 英語, Kyoto, Japan, 国際会議Bright Electron Emission from Si-doped AlN Thin Filmsポスター発表
- The 16th International Microscopy Congress, 2006年09月, 英語, Sapporo, 国際会議High-Resolutioon Transimission Electron Microscope Study on Nitrided InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- The 14th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2006年09月, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Atomically Controlled Doping of Nitrogen on GaAs(001) Surfaces口頭発表(一般)
- 28th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2006年07月, 英語, Vienna, 国際会議Magnetic-Field Evolution of Valence-Band States in One-Dimensional Diluted Magnetic Semiconductorsポスター発表
- 28th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, 2006年07月, 英語, Vienna, 国際会議Confined Electronic Structures of Nitrogen Isoelectronic Centers in GaAs Grown by Atomically Controlled Doping Techniqueポスター発表
- 7th International Conference on Excitonic Process in Condensed Matter, 2006年06月, 英語, Winston-Salem, 国際会議Excitonic State and Magnetic Effects in CdTe/Cd(Mg,Mn)Te Quantum Wires[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- The 14th International Conference on Molecular Beam Epitaxy, 2006年06月, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Emission-Wavelength Extension of Nitrided InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots with Different Sizes口頭発表(一般)
- 4th International Conference on Semiconductor Quantum Dots 2006, 2006年05月, 英語, Chamonix, 国際会議Polarization Insensitive Optical Gain of Columnar Quantum Dotsポスター発表
- CLEO/QELS, 2006年05月, 英語, Long Beach, 国際会議Magneti-Field Sensitive Polarization Anisotropy in One-Dimensional Diluted Magnetic Semiconductors口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 18th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2006年05月, 英語, Princeton, 国際会議Emission-Wavelength Extension of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots by Controlling Lattice-Mismatched Strain口頭発表(一般)
- 第52回応用物理学関係連合講演会,30a-YL-12, 2005年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 埼玉大学, 国内会議低温成長AIMを用いた有機電界放出発光素子口頭発表(一般)
- 第52回応用物理学関係連合講演会,30a-ZM-1, 2005年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 埼玉大学, 国内会議原子層窒化によるInAs/GaAs量子ドット発光の長波長化-量子ドット発光の窒化条件依存性-口頭発表(一般)
- 第52回応用物理学関係連合講演会,30a-ZM-3, 2005年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 埼玉大学, 国内会議原子層窒化InAs/GaAs量子ドットの長波長化発光メカニズム口頭発表(一般)
- 第52回応用物理学関係連合講演会,30a-ZM-8, 2005年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 埼玉大学, 国内会議InAs/GaAsコラム量子ドットの発光強度の積層数依存性口頭発表(一般)
- 第52回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2005年, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 埼玉大学, 国内会議低温成長AIN薄膜を用いた有機電界放出型発光素子口頭発表(一般)
- International Symposium on Compound Semiconductors 2005, 2005年, 英語, Rust, 国際会議Valence-Band Mixing Induced by sp-d Exchange Interaction in CdMnTeQuantum Wirs口頭発表(一般)
- International Conference on Quantum Electronics 2005 and the Pacific Rim Conference on Laser and Electro-Optics 2005, 2005年, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Valence-Band Mixing in CdTe/CdMnTeNano-Wire Structures in Magnetic Field口頭発表(一般)
- 2005 International Conference on Solid State Device and Materials, 2005年, 英語, Kobe, 国際会議Long-Wavelength Emission from Strain Controlled InAs/GaAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dots口頭発表(一般)
- International Conference on Materials for Advanced Technologies 2005, 2005年, 英語, Singapore, 国際会議InGaAs Capping Layer Caused Modification to the Optical Properties of InAs Quantum Dotポスター発表
- International Symposium on Quantum Dots and Photonic Crystal 2005, 2005年, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Emission-Wavelength Extension in Nitrided InAs/GaAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dotsポスター発表
- International Conference on Quantum Electronics 2005 and the Pacific Rim Conference on Laser and Electro-Optics 2005, 2005年, 英語, Tokyo, 国際会議Bound-Exciton Luminescence from Nitrogen Doped GaAs Grown by Site-Controlled Doping Technique[招待有り]口頭発表(招待・特別)
- Extended Abstr. International Symposium on Quantum Dots and Photonic Crystal 2005,Tokyo, 2004年09月, 英語Thermal Carrier Activation Process in InGaAs Capped InAs Quantum Dots
- 第65回応用物理学会学術講演会,1a-P2-4, 2004年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 東北学院大学, 国内会議原子層窒化によるInAs量子ドット発光の長波長化を波長制御口頭発表(一般)
- Extended Abstr. 2004 International Conference on Solid State Device and Materials (p.7-3), 2004年09月, 英語, Tokyo, 国内会議Optical Polarization Properties of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot Semiconductor Optical Amplifier.口頭発表(一般)
- 第65回応用物理学会学術講演会,シンポジウム「量子ドットの将来像と実現のためのマイルストーン」, 2004年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 東北学院大学, 国内会議InAs量子ドット表面の窒化による成長界面の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第65回応用物理学会学術講演会、シンポジウム「量子ドットの将来像と実現のためのマイルストーン」, 2004年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 仙台, 国内会議InAs量子ドット成長のその場RDS評価と界面制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第65回応用物理学会学術講演会,1a-P1-3, 2004年09月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 東北学院大学, 国内会議GsAs(001)に挿入した窒素原子層の創るisoelectronic trapからの狭線幅発光口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2004年秋季大会,14aYC-3, 2004年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 青森大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線における励起子磁気ポーラロンの異方的なエネルギー緩和特性口頭発表(一般)
- 14th International Conference on Crystal Growth.(T02-1-4), 2004年08月, 英語, Grenoble, 国際会議Anisotropic Exchange Interaction caused by Hole-Spin Reorientation in (CdTe)0.5(CdMnTe)0.5 Tilted Superlattices Grown in CdMgTe(001) Visinal Surface.口頭発表(一般)
- The 2004 International Conference on Ultrafast Phenomena., 2004年07月, 英語, Niigata, 国内会議Ultrafast Anisotropic Processes of Exciton Magnetic Polarons in CdTe/CdMnTe Quantum Wires.口頭発表(一般)
- 27th International Conference on the Physics and Semicinductors.(H5-95), 2004年07月, 英語, Flagstaff Arizona, 国際会議Order-Parameter Dependence of Sponteneous Electron Accumulation at GaInP/GaAs Studied by Raman-Scattering and Photoluminescence.口頭発表(一般)
- 27th International Conference on the Physics and Semicinductors.(J5-67), 2004年07月, 英語, Flagstaff Arizona, 国際会議Hole-Spin Reorentation in (CdTe)0.5 Tiltid Superlattices Grown on CdMgTe(001) Visinal Surface.口頭発表(一般)
- 23th Electronic Materials Symposium, 2004年07月, 英語, 未記入, Izu, 国内会議Anisotropic Magneto-Optical Effects in CdTe/CdMnTe Tilted Superlattices Grown on CdTe0.74Mg0.26Te(001)Vicinal Surface口頭発表(一般)
- 23th Electronic Materials Symposium, 2004年07月, 英語, 未記入, Izu, 国内会議1.3 micro-m Emission from Nitridized InAs Quantum Dot口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr.3rd International Conference on Semiconductor Quantum Dots,THP8,Banff, 2004年05月, 英語Temperature-Optimized Nitridation of Self-Assembled InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots for Long-Wavelength Emission
- Proc. 16th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials.(pp. 640-642), 2004年05月, 英語, Kagoshima, 国内会議Nitridized InAs/GaAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dots for Optical Communication Wavelength.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. European Material Research Society (1337), 2004年05月, 英語, Strasburg, 国際会議Narrow Bandwidth Photoluminescence Lines from Nitrogen Doped GaAs Grown by Atomically Controlled Doping.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. 3rd International Conference on Semiconductor Quantum Dots, TP15, 2004年05月, 英語, Banff, 国際会議Capping Layer Induced Optical Polarization Control of InAs/GaAs Quantum Dots.口頭発表(一般)
- 第51回応用物理学関係連合講演会 (30p-YN-13), 2004年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 東京工科大学, 国内会議低温成長AIN薄膜の電子エミッション特性に及ぼすSiドープの影響口頭発表(一般)
- 第51回応用物理学関係連合講演会 (30p-YG-17), 2004年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 東京工科大学, 国内会議原子層窒化によるInAs量子ドット発光の長波長化口頭発表(一般)
- 第51回応用物理学関係連合講演会 (28p-ZK-10), 2004年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 東京工科大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMnTeナノワイヤ構造におけるZeemanシフトの異方性と正孔スピンの再配列口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第59回年次大会 29aYF-12, 2004年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 九州大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMnTeナノワイヤにおける磁気ポーラロン形成口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会第59回年次大会 29aYF-11, 2004年03月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 九州大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMnTeナノワイヤにおけるホールスピン配向の面内磁場異方性口頭発表(一般)
- 平成15年度材料学会半導体エレクトロニクス部門委員会研究会, 2004年01月, 日本語, 神戸大学ベンチャービジネスラボラトリー, 国内会議磁性イオンを希薄ドープした半導体量子ナノワイヤ中のスピン制御口頭発表(一般)
- Pre-Conference of IEEE International Semiconductor Laser Conference 2004, IEICE LQE/OPE Technical Meeting., 2003年12月, 日本語, Kobe, 国内会議量子ドットの偏光制御とSOAへの応用口頭発表(一般)
- 第14回光物性研究会研究会 pp.339-342, 2003年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議窒素を希薄ドープしたGaAsからの狭線幅発光口頭発表(一般)
- 第14回光物性研究会研究会 pp.263-266, 2003年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線における磁気ポーラロン形成口頭発表(一般)
- 第14回光物性研究会研究会 pp.259-262, 2003年12月, 日本語, 光物性研究会, 大阪市立大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMnTe量子細線における交換相互作用の面内異方性口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. International Symposium on Quantum Dots and Photonic Crystals 2003, P-15, 2003年11月, 英語, Tokyo, 国内会議Optical Properties of Nitridized InAs Quantum Dots.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. International Symposium on Quantum Dots and Photonic Crystals 2003, P-19, 2003年11月, 英語, Tokyo, 国内会議Optical Polarization Control in Edge-Emitting InAs/GaAs Quantum Dot.口頭発表(一般)
- 日本物理学会2003年秋期大会, 21aTH-3, 2003年09月, 日本語, 日本物理学会, 宮崎ワールドコンベンションセンター, 国内会議微傾斜基盤上のCdTe/CdMnTe分数層超格子における交換相互作用の異方性と量子細線特性口頭発表(一般)
- Extended Abstr. 2003 International Conference on Solid State Device and Materials., 2003年09月, 英語, Tokyo, 国内会議Control of InGaAs Capping Layer Induced Optical Polarization in Edge-Emitting Photoluminescence of InAs Quantum Dots.口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会学術講演会 30p-G-16, 2003年08月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 福岡, 国内会議低温成長AlSiN薄膜からの高効率電子放出口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会学術講演会 1p-K-6, 2003年08月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 福岡, 国内会議窒素をデルタドープしたGaAs(001)からの狭線幅発光口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会学術講演会 31p-K-15, 2003年08月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 福岡, 国内会議原子層窒化によるInAs量子ドット発光の長波長化口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会学術講演会 31p-K-14, 2003年08月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 福岡, 国内会議InAs量子ドットの端面発光における偏光特性の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会学術講演会 31p-ZF-3, 2003年08月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 福岡, 国内会議CdTe/CdMgTe量子細線におけるスピン緩和特性口頭発表(一般)
- 第64回応用物理学会学術講演会 2a-ZL-8, 2003年08月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 福岡, 国内会議CdTe/(Cd,Mn)Te量子細線中の磁気ポーラロン形成口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. The 10th International Workshop on Femtosecond Technology, WP-26, p.120, 2003年07月, 英語, Tsukuba, 国内会議Spin Relaxiation Process in CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum Wires口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 22th Electronic Materials Symposium, H14, p.277-278, 2003年07月, 英語, Moriyama, 国内会議Polarization Controle of Cleaved-Edge Photoluminescence from InAs Quantum Dots Capped by InGaAs.口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 22th Electronic Materials Symposium, H13, pp.275-276, 2003年07月, 英語, Moriyama, 国内会議Photoluminescence from Postnitridized InAs Quantum Dots.口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 22th Electronic Materials Symposium, I6, p.291-292, 2003年07月, 英語, Moriyama, 国内会議Observation of Anisotropic Giant Magneto-Optical Effects in CdTe/CdMnTe Quantum Wires.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. The 10th International Workshop on Femtosecond Technology, WP-25, p.119, 2003年07月, 英語, Tsukuba, 国内会議Narrow Bandwidth Photoluminescence from Nitrogen-Delta Doped GaAs.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. The 11th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2003年07月, 英語, Nara, 国内会議InAsN Quantum Dots Fabricated by Posnitridation of InAs.口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 22th Electronic Materials Symposium, G12, pp.241-242, 2003年07月, 英語, Moriyama, 国内会議Highly Efficient Field Emission from Low Temperature Grown AlSiN Thin Film.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. The 10th International Workshop on Femtosecond Technology, TB-6, p.67, 2003年07月, 英語, Tsukuba, 国内会議Excitation Intensity Dependence of Edge-Emitting Photoluminescence Properties in InAs Quantum Dots.口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 23th Electronic Materials Symposium., 2003年07月, 英語, Izu, 国内会議Anisotropic Magneto-Optical Effects in CdTe/CeMnTe Tilted Superlattices Grown on CdTe0,74Mg0.26Te(001) Vicinal Surface.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr. The 11th International Conference on Modulated Semiconductor Structures, 2003年07月, 英語, 未記入, Nara., 国内会議Anisotropic Exchange Interaction in CdTe/CdMnTe Quantum Wires.口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 23th Electronic Materials Symposium., 2003年07月, 英語, Izu, 国内会議1.3 Micro-m Emission from Mitridized InAs Quantum Dot.口頭発表(一般)
- Abstr.2003 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, p.116, 2003年06月, 英語, Baltimore, 国際会議Wideband Polarization Insensitivity in Quantum Dot Optical Amplifier.口頭発表(一般)
- Proc. 15th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials., 2003年05月, 英語, Santa Barbara, 国際会議Selective Characterization of Interface Electric Field in GaAs/GaInP Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor by Fourier Transformed Photoreflectance.口頭発表(一般)
- ナノ学会 PpⅡー7, 2003年05月, 英語, ナノ学会, 神戸大学, 国内会議Photoluminescence Polarization Properties and Electronic States in InAs/GaAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dots.口頭発表(一般)
- 第50回応用物理学関係連合講演会 (29a-YAー11), 2003年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川大学, 国内会議歪キャップ層導入によるInAs量子ドットの端面発光偏光特性の制御口頭発表(一般)
- 第50回応用物理学関係連合講演会 (29p-V-7), 2003年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川大学, 国内会議高濃度SiドープAINの基礎吸収端構造口頭発表(一般)
- 第50回応用物理学関係連合講演会 (29a-ZH-8), 2003年03月, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMgTe量子細線における磁気工学特性の異方性口頭発表(一般)
- 第50回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2003年, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川大学, 国内会議歪キャップ層導入によるInAs量子ドットの端面発光偏光特性の制御その他
- 第50回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2003年, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川大学, 国内会議高濃度SiドープAINの基礎吸収端構造その他
- 第50回応用物理学関係連合講演会, 2003年, 日本語, 応用物理学会, 神奈川大学, 国内会議CdTe/CdMgTe量子細線における磁気光学特性の異方性その他
- 応用物理学会1985年05月 - 現在
- 日本物理学会1986年10月 - 2021年12月
- Spring-8利用者懇談会正会員1993年05月 - 1999年03月
- 日本真空協会1993年07月 - 1997年12月
- 日本金属学会1992年07月 - 1997年12月
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業, 挑戦的研究(萌芽), 神戸大学, 2025年06月 - 2027年03月中間バンド構造による高出力放射冷却型発電デバイスの実現
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業, 基盤研究(B), 神戸大学, 2024年02月 - 2026年03月ヘテロ界面に挿入した量子ドットによる赤外増感型光電変換の実現
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(A), 基盤研究(A), 神戸大学, 2019年04月 - 2023年03月p型とn型に挟まれたダイオード構造の真性層に、AlGaAs/GaAsヘテロ界面にInAs量子ドットを挿入した量子ナノ構造を作製し、電子のみを蓄積したヘテロ界面において価電子バンド-伝導バンド間光学遷移とバンド内光学遷移の連続した2段階の遷移による電子のエネルギーをアップコンバージョンによって増強されたバンド内光吸収に基づく赤外波長域に応答する光電変換特性を実現する。本年度は以下のように実施した。 (1)量子ナノ構造の作製と基礎光学特性評価:分子線エピタキシー技術を利用してGaAs(001)基板上にAlGaAs/GaAsヘテロ界面にInAs量子ドットを挿入した量子ナノ構造を内包するダイオード構造を作製し、ヘテロ界面にSi変調ドーピングによって電子密度を制御した量子構造を作製した。変調ドーピングによる界面電界の制御を明らかにして、光電流取り出し特性を詳細に明らかにした。 (2)バンド内光学遷移分極の制御:バンド内光学遷移強度は、光電場で誘起される電子分極の大きさと遷移始状態の電子占有率に比例する。量子ドットのサイズ、密度による光学応答への影響を明らかにするため電子で満たされた量子ドットにおけるプラズモン共鳴特性を明らかにして中赤外領域における光アンテナ効果を理論的に予測した。具体的には、量子ドットの形状・サイズに依存したプラズモン共鳴特性を計算し、8~16マイクロメートルの広範囲にわたる制御性を明らかにするとともに、量子ドット間のプラズモン共鳴状態の結合によるモード分散を明らかにした。 (3)光吸収係数の定量評価とアップコンバージョン光電流の最大化:デバイスを試作して光近赤外から中赤外に広がる広い波長範囲で光応答特性を明らかにし、ヘテロ界面電子濃度に依存すると予想されるバンド内光学遷移を確認した。
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業 挑戦的研究(萌芽), 挑戦的研究(萌芽), 神戸大学, 2020年07月 - 2022年03月本研究では量子ドットとヘテロ界面を融合した量子ナノ構造を有する新しい赤外光センシングデバイスを開発した。このデバイスはヘテロ界面における高効率なバンド内光学遷移エンジニアリングを原理として駆動しており、量子ドット形状による光増感が特徴である。開発したデバイスはAl0.3Ga0.7As/GaAsヘテロ界面にInAs量子ドットを挿入した構造で、ヘテロ界面に蓄積される電子が赤外光で励起されて光電流を生じる量子型デバイスである。赤外光センシングは量子ドットによって顕著に増強した。理論計算により、量子ドット界面に局在する強いプラズモンモードによって赤外光の電場が増強していることが明らかになった。
- 学術研究助成基金助成金/国際共同研究加速基金(国際共同研究強化(B)), 2018年10月 - 2021年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 学術研究助成基金助成金/挑戦的研究(萌芽), 2018年06月 - 2020年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2016年04月 - 2019年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 学術研究助成基金助成金/挑戦的萌芽研究, 2015年04月 - 2017年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 特別研究員奨励費, 2014年04月 - 2017年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 研究成果展開事業(マッチングプランナー プログラム), 2016年, 研究代表者水銀を使わないシート型殺菌用紫外光源の開発競争的資金
- 学術研究助成基金助成金/挑戦的萌芽研究, 2013年04月 - 2015年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2012年04月 - 2015年03月, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学技術振興機構, 研究成果展開事業 マッチングプランナープログラム 探索試験, 2015年, 研究代表者マッチングプランナー「水銀を使わないシート型殺菌用紫外光源の開発」競争的資金
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(A), 基盤研究(A), 東京大学, 2010年 - 2012年InAs/GaAsSb系タイプII量子ドットを応用した中間バンド型太陽電池の作製と特性評価の研究を行った。励起キャリアの長寿命化の効果により、中間バンドを介した2段階の光吸収過程を室温で明瞭に観察することに成功した。次に、量子構造における光励起キャリアの励起・緩和過程を超高速で追跡し、光応答特性を明らかにするため、ポンプ・プローブ方式の超高速発光寿命特性を解析した。Siを直接ドープしたInAs/GaAs量子ドットでは無輻射遷移の抑制効果の励起エネルギー依存の詳細を明らかにするとともに、直接ドープによってチャージした量子ドットでは光励起したキャリアが再び基底状態にまで緩和する過程を抑制できることを見出した。さらに、量子ドット超格子により形成された中間バンドは、量子ドット端面からの発光がTEモード、TMモードが等価に近づくことで形成が確認できる。InAs量子ドットのスペーサー層の膜厚コントロールによるEL発光の偏光依存性について測定を行った結果、中間層10nmの試料においてはTM偏光の発光が大きくなっており、量子ドット間の結合が強くなっていることを確認した。
- 学術研究助成基金助成金/挑戦的萌芽研究, 2011年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 特別研究員奨励費, 2010年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(A), 2009年競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2009年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/特定領域研究, 2008年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/特定領域研究, 2008年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2007年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(A), 2006年競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/萌芽研究, 2006年競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2005年競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/萌芽研究, 2005年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 科学研究費補助金/基盤研究(B), 2005年, 研究代表者競争的資金
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(B), 基盤研究(B), 神戸大学, 2003年 - 2004年光増幅デバイスは光通信における光源レーザ、光ファイバ、受光デバイスを機能的に融合させるキーデバイスである。特に半導体光増幅(Semiconductor Optical Amplifier : SOA)デバイスは半導体の自在なバンド構造設計技術を生かして多波長光通信に適している。しかし、SOAには増幅特性に偏光異方性がありデバイス構成上大きな制約を受け、利用の用途が限定されている。これを克服するためには偏光に無依存な吸収端の実現が不可欠であるが未だ実現されていない。本研究では偏光無依存基礎吸収端の実現を目指して量子ドットの形状と光学遷移の偏光異方性の関係に着目した研究を行った結果、量子ドットの基礎吸収端偏光特性を決めている重要な制御因子が明らかになり、偏光特性を自在に制御して偏光無依存SOAに必要な理想的な基礎吸収端を実現するに至った。詳細は以下の通りである。 (1)量子ドット形状の精密な制御を実現 形状制御量子ドット作製のためにコラムナ量子ドット成長技術と研究代表者らが行ってきた2次元ぬれ層の原子レベルの制御による新しい量子ドット成長技術を融合させ、スタックによってドット形状のアスペクト比を自在に制御することに成功した。 (2)量子ドットの内部歪み制御 量子ドットを窒化する技術を初めて開発し、ドット内に加わるの歪み制御を行った。 これら一連の研究よって下記の成果を達成した: ●新しいコラムナ量子ドットによるドット形状と内部ひずみ制御による電子状態の制御 ●光通信帯域のバンドギャップと偏光制御の同時実現 ●量子ドットの不均一広がりを利用したワイドバンドな偏光無依存特性の実現
- 日本学術振興会, 科学研究費助成事業 基盤研究(B), 基盤研究(B), 神戸大学, 2002年 - 2003年量子ドット材料で通常のバルク半導体にくらべて、量子閉じ込めによる光非線形応答の増強や、キャリア緩和・供給機構の高速化による高速化が期待され、将来の光通信には不可欠となる超高速光アンプや光スイッチとして期待されている。しかし、現状の量子ドットは理想的な形状ではなく基板上で扁平な形状を有しており、これが強い偏光依存性(通常TE)など光学特性を阻害しており、また、超高速性と高非線形性に与える影響等は全く理解されていない。 本研究において、独自の多層積層量子ドット<コラムナドット>によるドット形状制御を検討し、積層数の最適化によって等方的形状を実現することによって偏光無依存量子ドットが実現できることを明らかにした。さらにドット・キャップ層組成の変化により偏光を制御する可能性を検討し、InAs/GaAs量子ドットにおいてはキャップ層のIn組成を増加させるとアスペクト比が大きい、従来より等方的なドット形状を実現できる(TEM観察によっても示された)こと、それに対応して端面PL発光特性をTM偏光化できることを発見し、実用的光素子で重要な偏光無位存特性の実現可能性を明らかにした。 一方我々が従来から行なってきている研究によって、量子ドットにおける吸収飽和回復特性の高速化の効果が確認され光アンプでは1-3psの超高速がえられることが示された。さらに、ドット形状による位相緩和特性を測定することにより、ドット大径化による位相緩和の長寿命化(非線形性の増大が可能)が明らかになった。 これらを総合的に検討した結果、ドット形状の等方化、大径化によって、超高速性を保ったまま、高い非線形応答を持つ量子ドットが実現できることを初めて明かにすることができた。
- 量子型赤外線センサ特願2019-138335, 2019年07月26日, 国立大学法人神戸大学, 特開2021-022662, 2021年02月18日, 特許第7291942号, 2023年06月08日特許権
- UVB領域の紫外発光蛍光体および紫外発光デバイス特願2018-82670, 2018年04月23日, 特開2019-189722, 2019年10月31日, 特許7030333, 2022年02月25日特許権
- 紫外発光蛍光体と紫外発光デバイス及び紫外発光蛍光体の作製方法特願2017-25385, 2017年02月14日, 特許6955656, 2021年10月06日特許権
- 電池、水素光合成装置および炭素化合物光合成装置特願2017-26222, 2017年02月15日, 特許6900024, 2021年06月18日特許権
- 高変換効率太陽電池およびその調製方法特願2014-113313, 2014年05月30日, 大学長, 特許6385720, 2018年08月17日特許権
- 紫外発光デバイス及び紫外蛍光体の作製方法特願2016-026434, 2016年02月15日特許権
- 深紫外半導体光デバイス(韓)10-2010-7007275, 2008年09月03日, 大学長, 10-1478391, 2014年12月24日特許権
- 蛍光体結晶薄膜とその作製方法特願2011-521822, 2010年07月07日, 大学長, 特許5476531, 2014年02月21日特許権
- 量子ドットの形成方法及び半導体装置の製造方法特願2008-200251, 2008年08月01日, 大学長, 特許5102141, 2012年10月05日特許権
- 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法特願2012-198903, 2012年09月10日特許権
- 有機フィールドエミッションデバイス特願2006-088557, 2006年03月28日, 大学長, 特許5011523, 2012年06月15日特許権
- 電子放出装置2007-157877, 2007年06月14日, 大学長, 特許4822549, 2011年09月16日特許権
- 深紫外蛍光薄膜および深紫外蛍光薄膜を用いたランプ特願2008-79820, 2008年03月26日, 特開2009-238415, 2009年10月15日特許権
- 応力測定装置特願平10-97530, 1998年04月09日, 特許第3979611号, 2007年07月06日, 2007年09月19日特許権
- 量子光半導体装置2002-273178, 2002年09月19日, 2004-111710, 2004年04月08日, 特許第3854560号, 2006年09月15日特許権
- 半導体の接合容量評価方法及び接合容量測定装置特願2001-310782, 2001年10月05日, 2003年04月18日, 2006年03月10日, 特許第3777394号特許権
- 量子ドット半導体素子及び該製造方法並びに量子ドット半導体素子を用いた量子ドット半導体レーザ、光増幅素子、光電変換素子、光送信機、光中継機及び光受信機特願2003-181776, 2003年06月25日, 特開2005-19654, 2005年01月20日特許権
- β-FeSi2とその製造方法及びβ-FeSi2を含む半導体集積回路特願2001-189001, 2001年06月22日特許権
研究シーズ
■ 研究シーズ- 新しい紫外光源の開発と応用シーズカテゴリ:ライフサイエンス, ものづくり技術(機械・電気電子・化学工業), 環境・農学研究キーワード:ウイルス不活化, 殺菌, 樹脂硬化, 農薬フリー, 皮膚治療研究の背景と目的:紫外光はUVA(315-400nm)、UVB (280-315nm)、UVC (100-280nm)の3つの波長領域からなる。それぞれの波長に最適な光源開発、特に水銀を使わない次世代光源の開発は不可欠である。また、紫外光の応用分野は工業、医療、農業、食品など多岐にわたり広い応用が期待できる。われわれは特に工業・医療・農業応用に適したUVBとウイルス不活化・殺菌に適したUVCに注目している。研究内容:紫外光源はこれまで水銀ランプが使用されてきたが、2017年に発効した水銀条約以降水銀の使用が大きく制限されている。われわれは水銀を使用しない水銀フリーの光源、あるいは水銀条約の規制をクリアした水銀レス光源の開発を行っている。特に水銀レス光源では、低コストの冷陰極蛍光ランプ(CCFL)に注目している。CCFLは,冷陰極と細管の採用によって、水銀条約の規制を十分クリアする超低濃度の水銀でも従来の水銀ランプ以上の発光強度を実現する。現在、UVB用光源とUVC用光源御開発に成功し、その応用を進めている。 【UVB応用】 高速樹脂硬化、皮膚治療(ナローバンドUVB治療)、農薬フリー植物病害抑制。 【UVC応用】 殺菌(2秒照射で黄色ブドウ球菌99.9%以上不活化)、ウイルス不活化(1秒照射でSARS-CoV-2を99.9%不活化)、オゾンの高効率生成(オゾンを利用したクリーンな空間を実現)。

図1 CCFL光源
期待される効果や応用分野:紫外光は応用は応用範囲が広く、実用化が期待される。また今後、水銀を使用しない光源の開発へとどんどん研究が進んでいる分野であり、広く企業と連携を図りたい。 - 高性能太陽電池の開発シーズカテゴリ:エネルギー, ナノテク・材料研究キーワード:太陽電池, 量子構造研究の背景と目的:再生可能エネルギーはカーボン・ニュートラルを実現する切り札として注目されています。再生可能エネルギーでは太陽光の利用が特に注目されています。地上に到達する太陽エネルギーは1平方mあたり約1kWもあり、これをいかに効率よく電気エネルギーに変換できるかが重要です。われわれは、精密な理論に基づき透過損失と熱損失を極限まで抑えた新しい太陽電池構造の設計を行っています。研究内容:われわれは半導体ヘテロ構造と量子構造を融合した量子ナノ構造を利用して、太陽光スペクトルの光吸収特性と生成されたキャリアのダイナミックスを精密に制御する研究を行っています。特に、これまでの太陽電池では赤外光は太陽電池をそのまま透過して利用できませんでしたが、私たちは、ヘテロ界面を利用して赤外域に高感度に応答する高効率な「バンド内光遷移」を実現しました。この技術を利用すると、近赤外から中赤外の波長範囲を広く吸収してこれまでにない高効率な太陽電池が実現できます。具体的にはAlGaAsとGaAsのヘテロ界面にInAsの量子ドットを挿入した量子ナノ構造で、理論的には60%を超えるエネルギー変換効率が実現可能です。
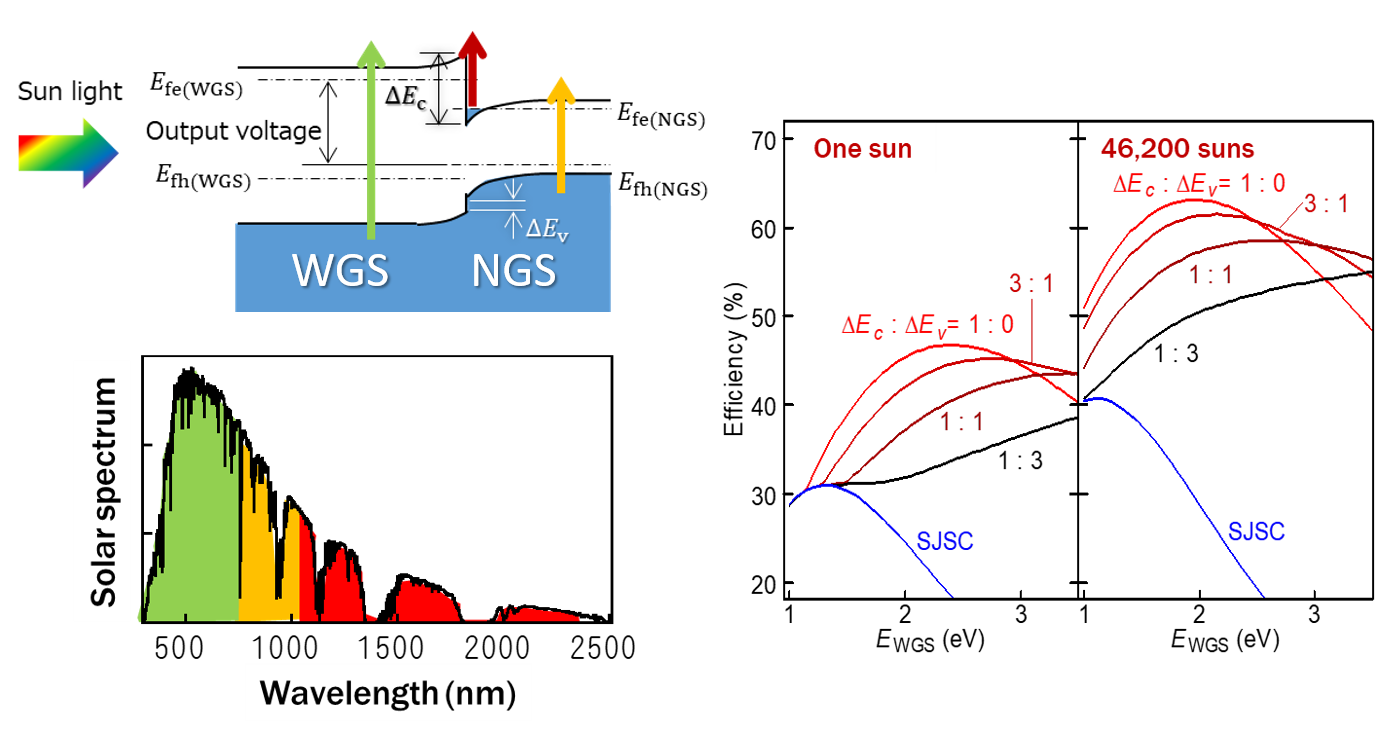
ヘテロ構造を利用したアップコンバージョン型太陽電池の概念とエネルギー変換効率予測
期待される効果や応用分野:太陽電池構造の最適化は、室内照明を利用したエネルギーの再利用やレーザーなどを利用したリモートエネルギー伝送などにも応用でき、これからのグリーン社会を支えていきます。関係する業績:“Energy Conversion Efficiency of Solar Cells” T. Kita, Y. Harada, and S. Asahi (Springer, 2019). S. Asahi, H. Teranishi, K. Kusaki, T. Kaizu, and T. Kita, Nature Communications 8, 14962 (2017).

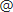 eedept.kobe-u.ac.jp
eedept.kobe-u.ac.jp